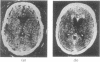
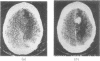
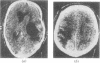
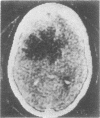
Abstract
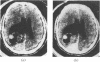
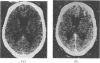
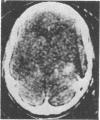
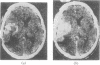
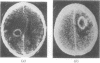
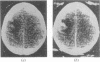
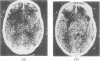
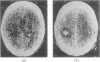
The false positive and false negative computed tomography diagnoses of glioma made using an EMI 1010 machine on a consecutive series of patients seen over a period of two years are recorded. About 1.5% of gliomas were not detected on initial CAT scan, 6.5% were misdiagnosed as benign lesions, and in 6.5% of the cases identified as glioma a non-malignant condition was subsequently diagnosed.
Full text
PDF
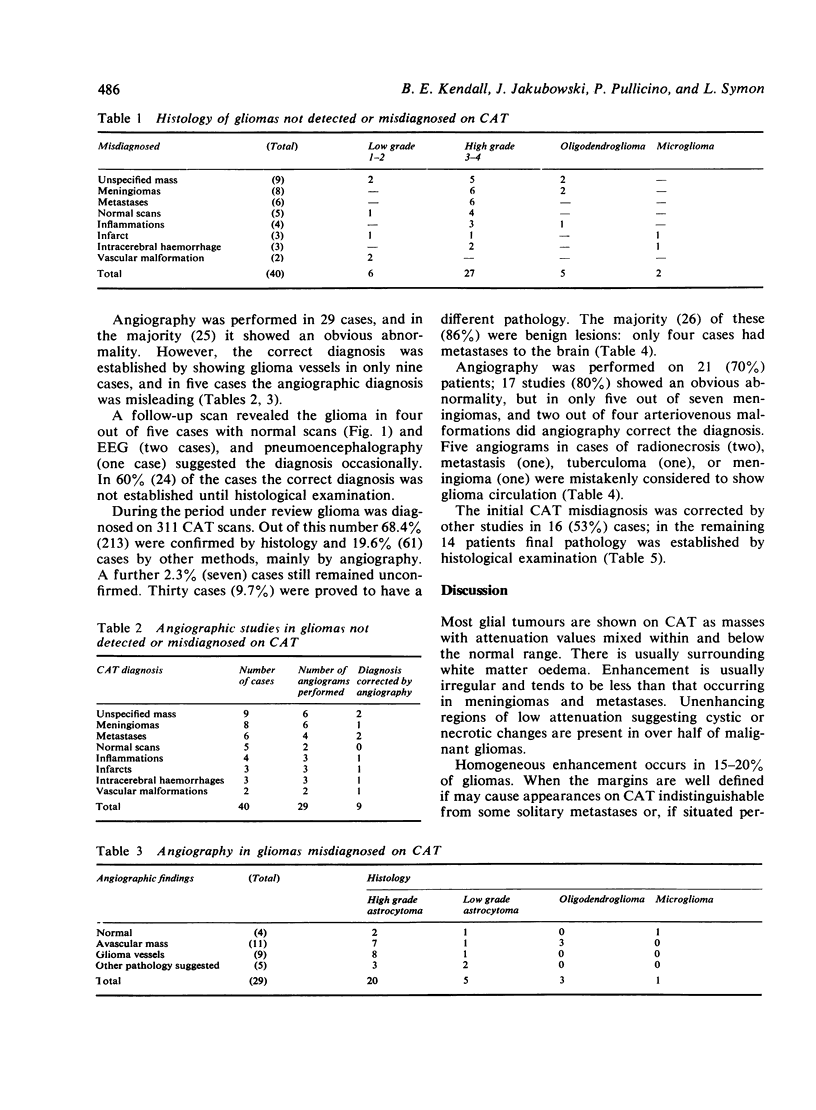
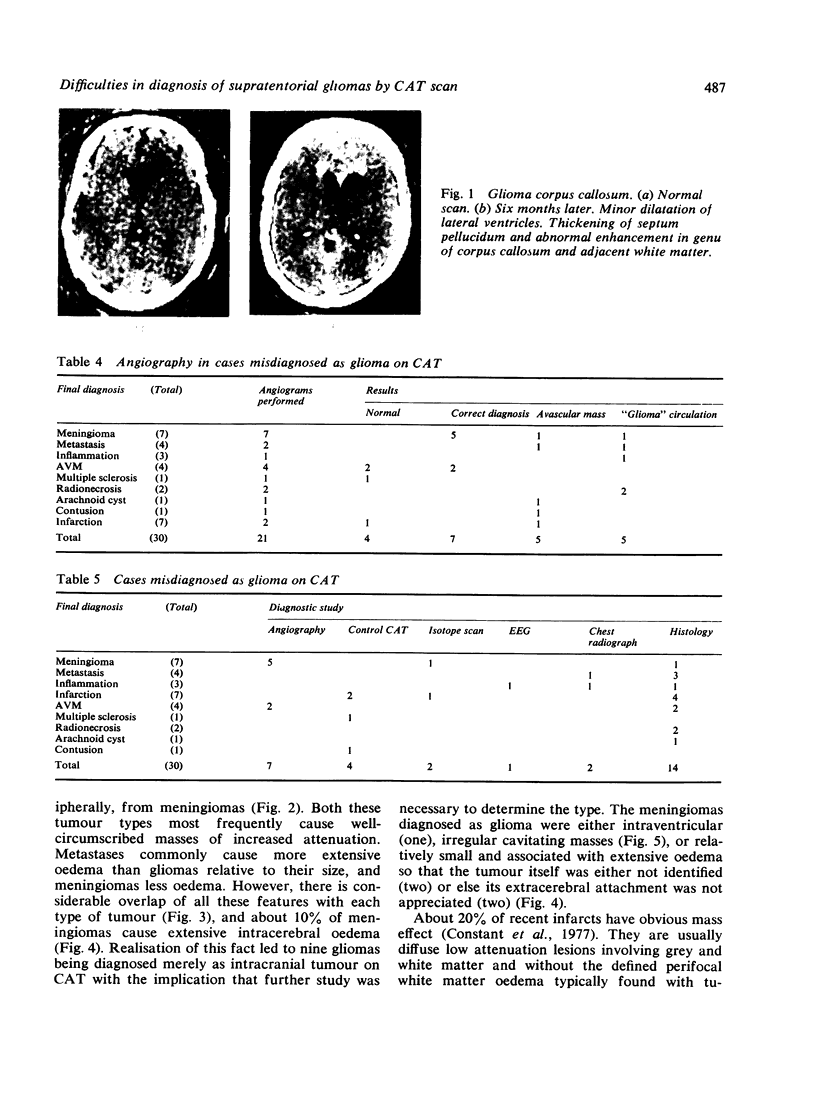
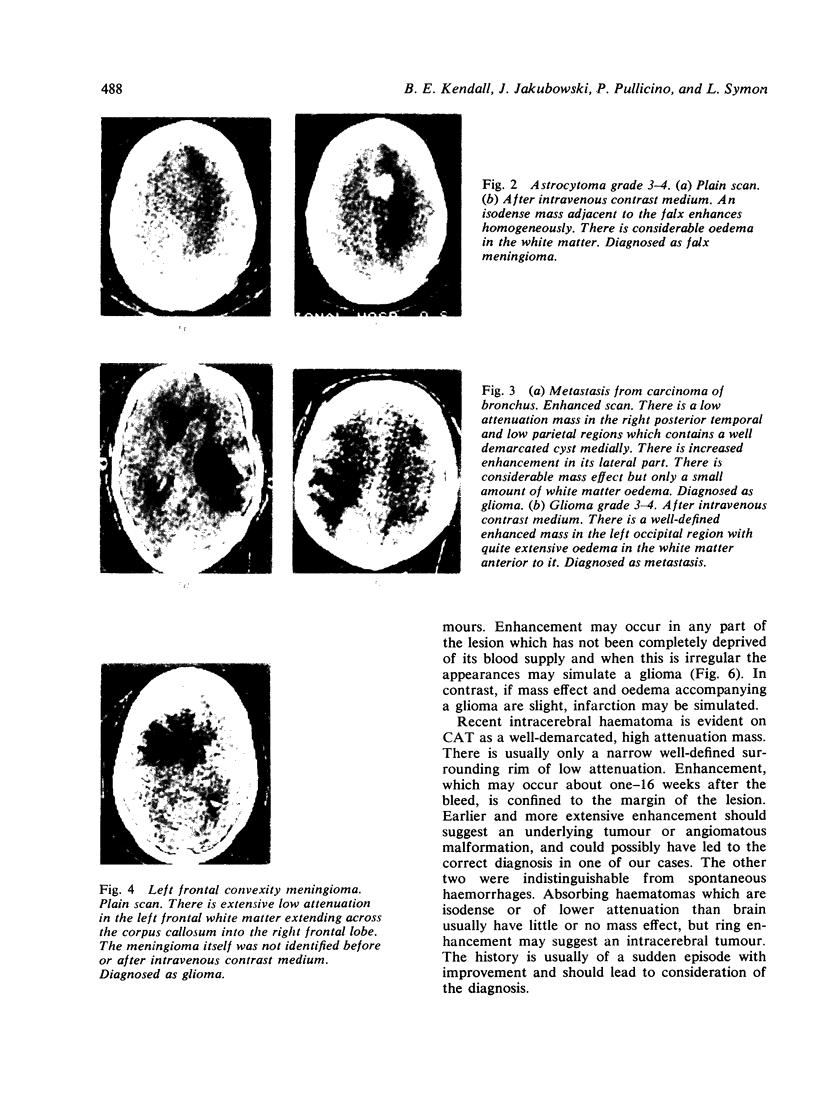
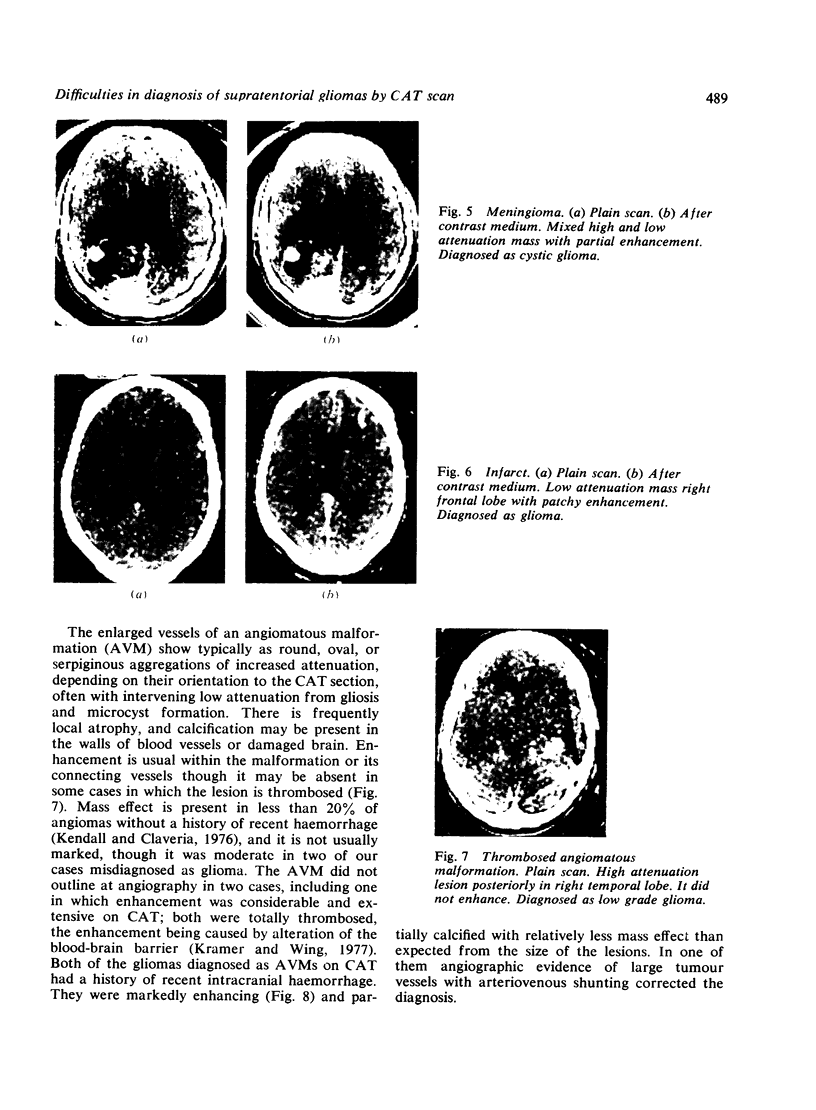

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Kendall B. E., Claveria L. E. The use of computed axial tomography (CAT) for the diagnosis and management of intracranial angiomas. Neuroradiology. 1976;12(3):141–160. doi: 10.1007/BF00341859. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer R. A., Wing S. D. Computed tomography of angiographically occult cerebral vascular malformations. Radiology. 1977 Jun;123(3):649–652. doi: 10.1148/123.3.649. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radue E. W., Kendall B. E. Iodide and xenon enhancement of computed tomography (CT) in multiple sclerosis (MS). Neuroradiology. 1978 May 31;15(3):153–158. doi: 10.1007/BF00329059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]