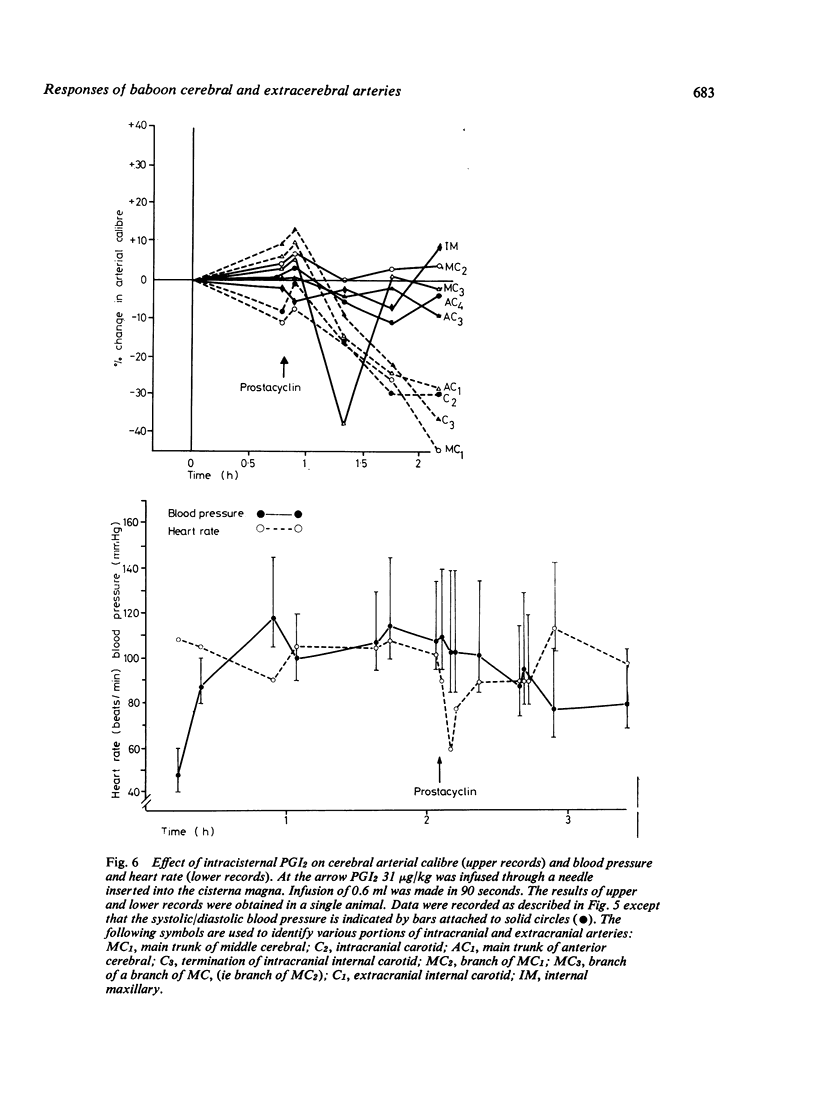
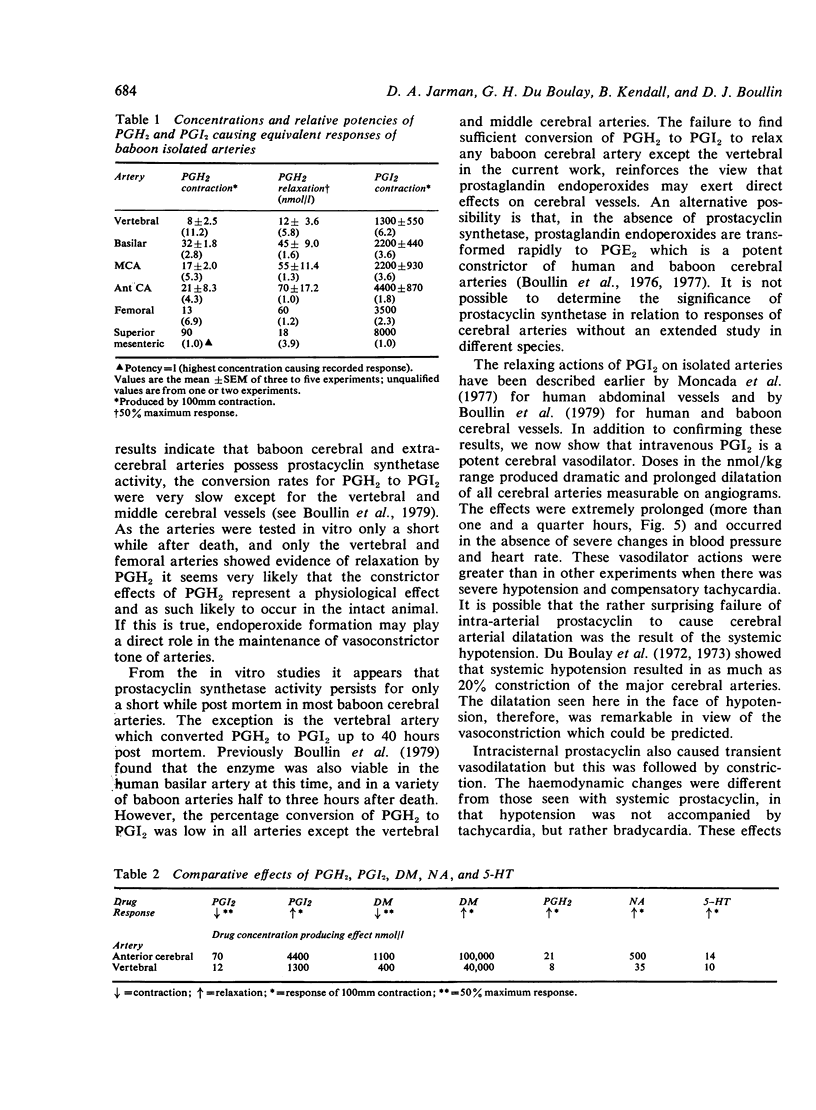
Abstract
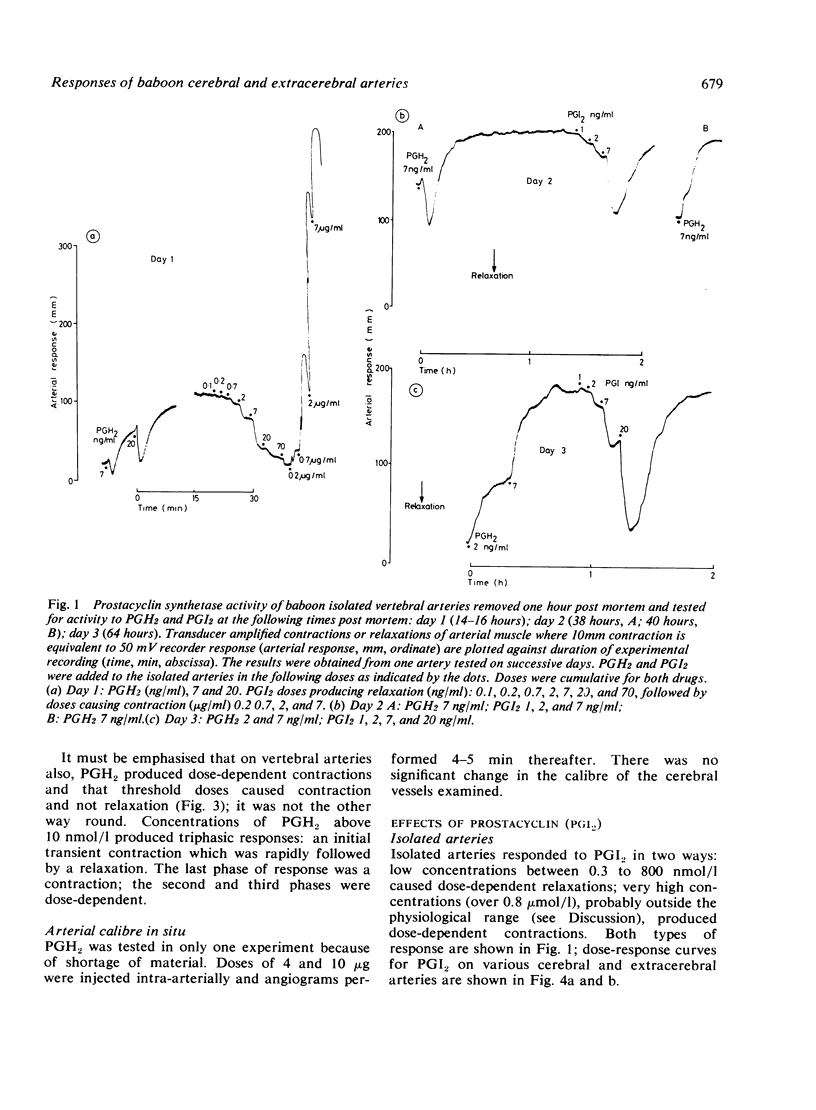
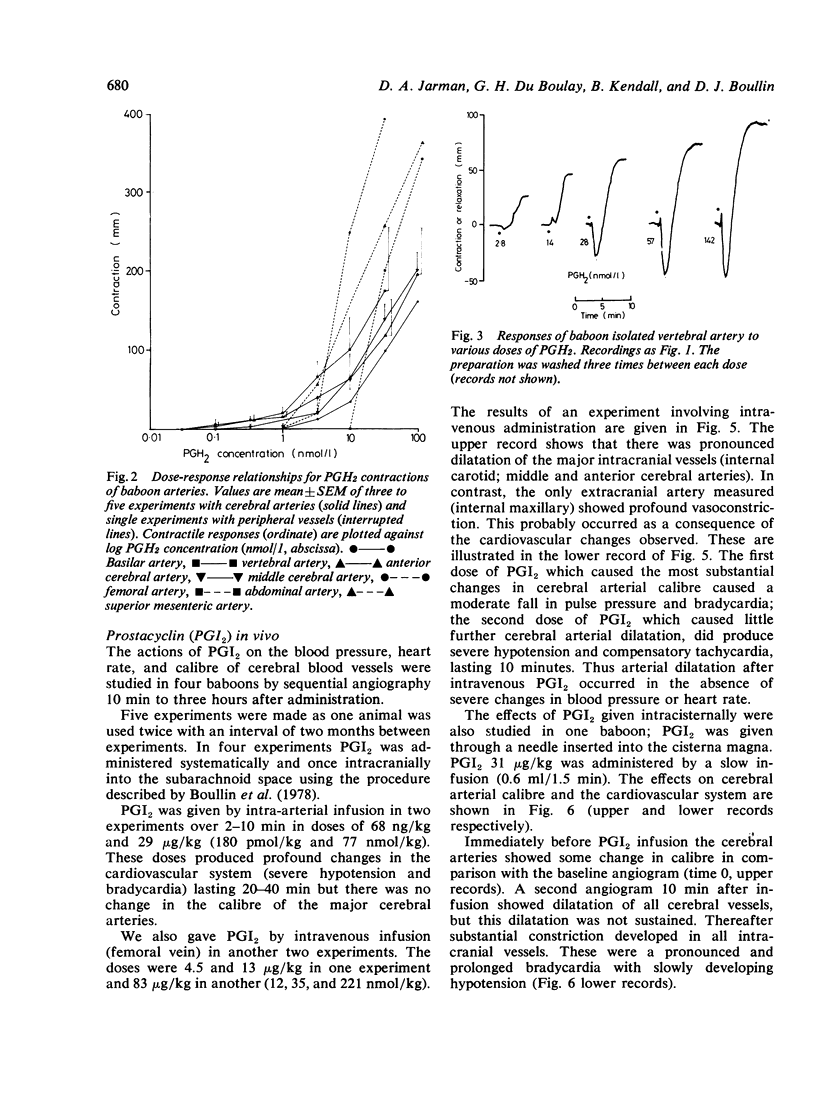
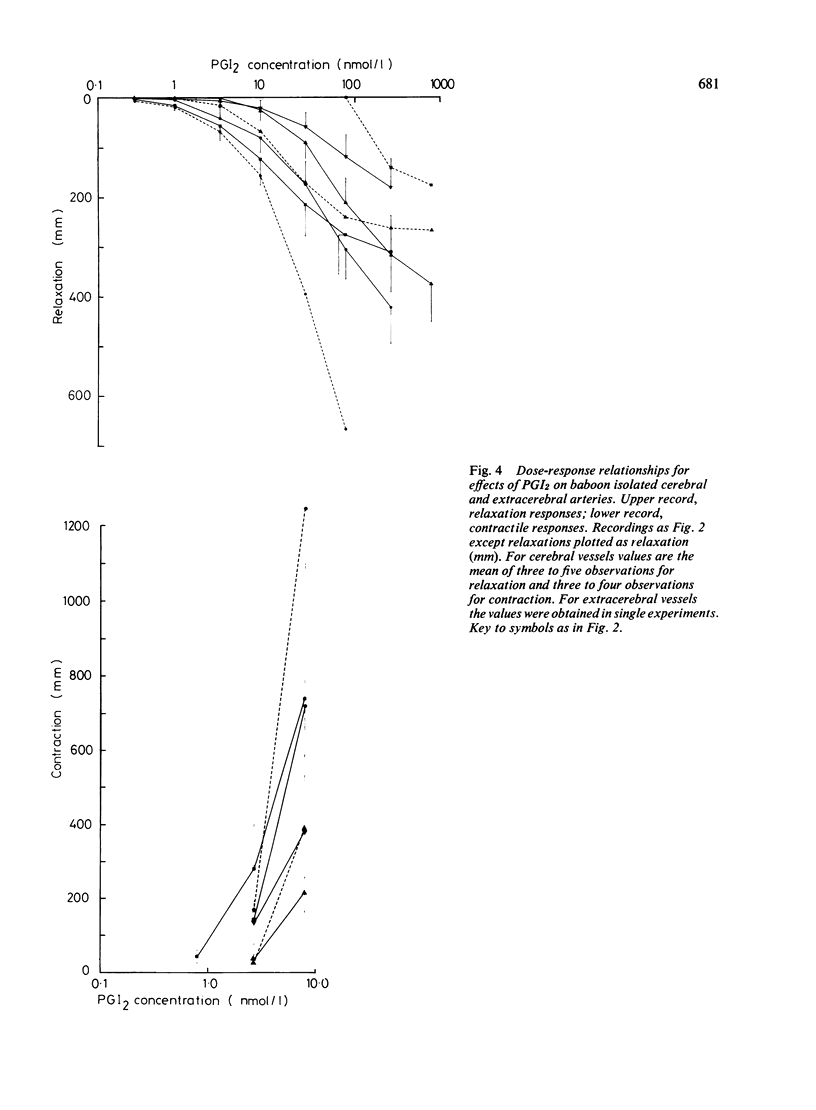
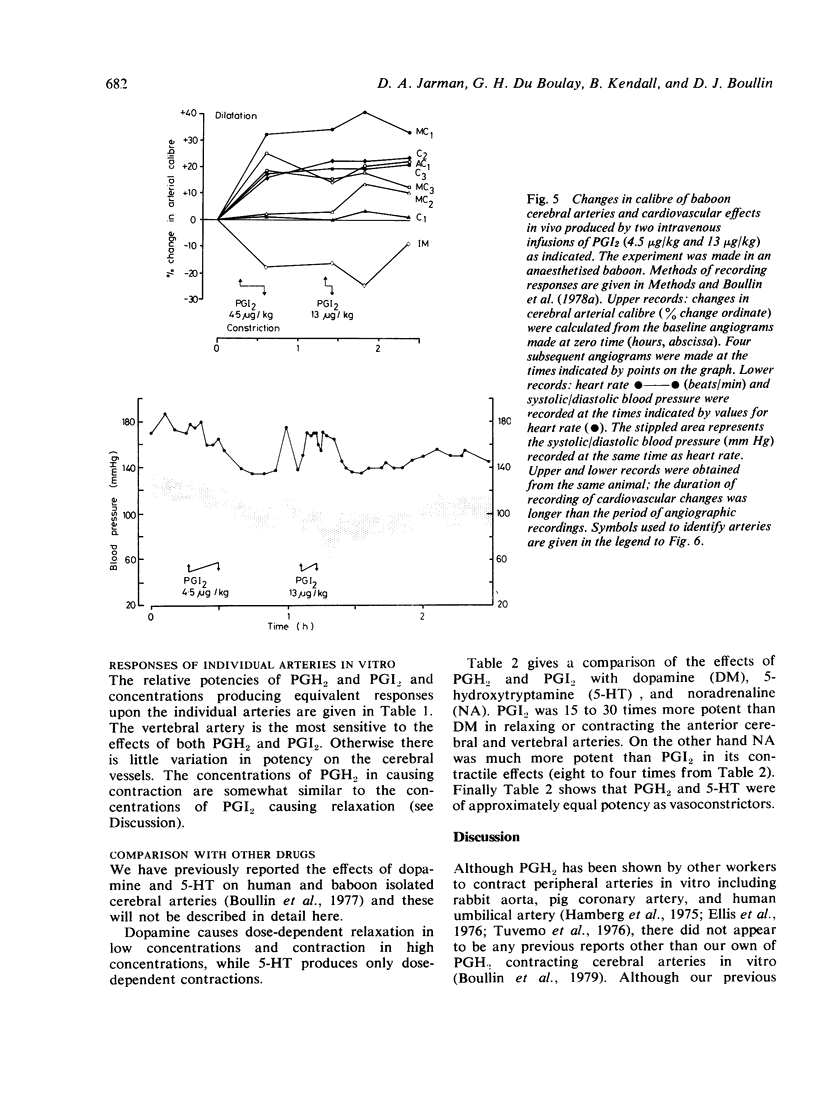
The responses of baboon cerebral and extracerebral arteries to prostaglandin endoperoxide (PGH2) and prostacyclin (PGI2) were investigated on isolated arteries and in vivo by serial angiography. Both PGH2 and PGI2 could produce dose-dependent contraction or relaxation of isolated arteries. PGH2 induced relaxation was indicative of prostacyclin synthetase activity, the enzyme which converts PGH2 to PGI2. In isolated arteries tested one to four hours post mortem only the vertebral artery showed prostacyclin synthetase activity. Thus PGH2 induced contraction of cerebral arteries may be indicative of a physiological function. Vasomotor tone may in part be the result of a balance between PGH2 constriction and PGI2 dilatation. In vivo PGI2 infusion caused pronounced and prolonged dilatation of cerebral arteries, which lasted longer than the cardiovascular changes. As PGI2 is the most potent cerebral vasodilator drug tested, it may be of clinical use in the treatment of cerebral vasospasm.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blaso W. P., Boullin D. J. Vasoconstrictor activity of cerebrospinal fluid from patients with cerebral arterial spasm [proceedings]. J Physiol. 1978 Sep;282:39P–40P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boullin D. J., Adams C. B., Mohan J., Green A. R., Hunt T. M., du Boulay G. H., Rogers A. T. Effects of intracranial dopamine perfusion: behavioural arousal and reversal of cerebral arterial spasm following surgery for clipping of ruptured cerebral aneurysms. Proc R Soc Med. 1977;70 (Suppl 2):55–70. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boullin D. J., Bunting S., Blaso W. P., Hunt T. M., Moncada S. Responses of human and baboon arteries to prostaglandin endoperoxides and biologically generated and synthetic prostacyclin: their relevance to cerebral arterial spasm in man. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1979 Feb;7(2):139–147. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1979.tb00914.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boullin D. J., Du Boulay G. H., Rogers A. T. Aetiology of cerebral arterial spasm following subarachnoid haemorrhage: evidence against a major involvement of 5-hydroxy-tryptamine in the production of acute spasm. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1978 Sep;6(3):203–215. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1978.tb04586.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boullin D. J., Mohan J., Grahame-Smith D. G. Evidence for the presence of a vasoactive substance (possibly involved in the aetiology of cerebral arterial spasm) in cerebrospinal fluid from patients with subarachnoid haemorrhage. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1976 Aug;39(8):756–766. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.39.8.756. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Du Boulay G., Symon L., Ackerman R. H., Dorsch D., Kendall B. E., Shah S. H. The reactivity of the spastic arteries. Neuroradiology. 1973 Feb;5(1):37–39. doi: 10.1007/BF02464628. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Du Boulay G., Symon L., Shah S., Dorsch N., Ackerman R. Cerebral arterial reactivity and spasm after subarachnoid haemorrhage. Proc R Soc Med. 1972 Jan;65(1):80–82. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis E. F., Oelz O., Roberts L. J., 2nd, Payne N. A., Sweetman B. J., Nies A. S., Oates J. A. Coronary arterial smooth muscle contraction by a substance released from platelets: evidence that it is thromboxane A2. Science. 1976 Sep 17;193(4258):1135–1137. doi: 10.1126/science.959827. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamberg M., Hedqvist P., Strandberg K., Svensson J., Samuelsson B. Prostaglandin endoperoxides IV. Effects on smooth muscle. Life Sci. 1975 Feb 1;16(3):451–462. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(75)90266-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moncada S., Gryglewski R., Bunting S., Vane J. R. An enzyme isolated from arteries transforms prostaglandin endoperoxides to an unstable substance that inhibits platelet aggregation. Nature. 1976 Oct 21;263(5579):663–665. doi: 10.1038/263663a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moncada S., Higgs E. A., Vane J. R. Human arterial and venous tissues generate prostacyclin (prostaglandin x), a potent inhibitor of platelet aggregation. Lancet. 1977 Jan 1;1(8001):18–20. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)91655-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schianchi P. M., Hughes J. T. Cerebral artery spasm: histological changes in necropsies of cases of subarachnoid hemorrhage. Adv Neurol. 1978;20:521–534. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starling L. M., Boullin D. J., Grahame-Smith D. G., Adams C. B., Gye R. S. Responses of isolated human basilar arteries to 5-hydroxytryptamine, noradrenaline, serum, platelets, and erythrocytes. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1975 Jul;38(7):650–656. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.38.7.650. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanabe Y., Sakata K., Yamada H., Ito T., Takada M. Cerebral vasospasm and ultrastructural changes in cerebral arterial wall. An experimental study. J Neurosurg. 1978 Aug;49(2):229–238. doi: 10.3171/jns.1978.49.2.0229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuvemo T., Strandberg K., Hamberg M., Samuelsson B. Formation and action of prostaglandin endoperoxides in the isolated human umbilical artery. Acta Physiol Scand. 1976 Feb;96(2):145–149. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1976.tb10183.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Deckere E. A., Nugteren D. H., Ten Hoor F. Prostacyclin is the major prostaglandin released from the isolated perfused rabbit and rat heart. Nature. 1977 Jul 14;268(5616):160–163. doi: 10.1038/268160a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


