Abstract
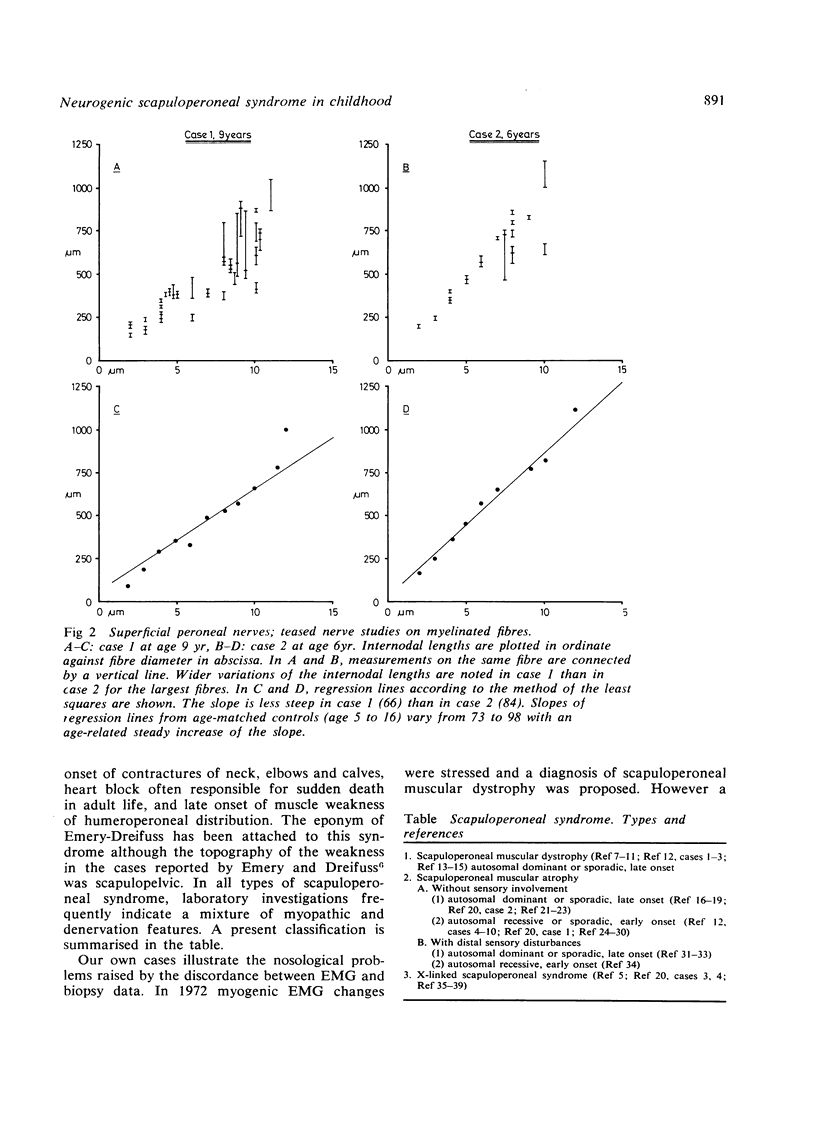
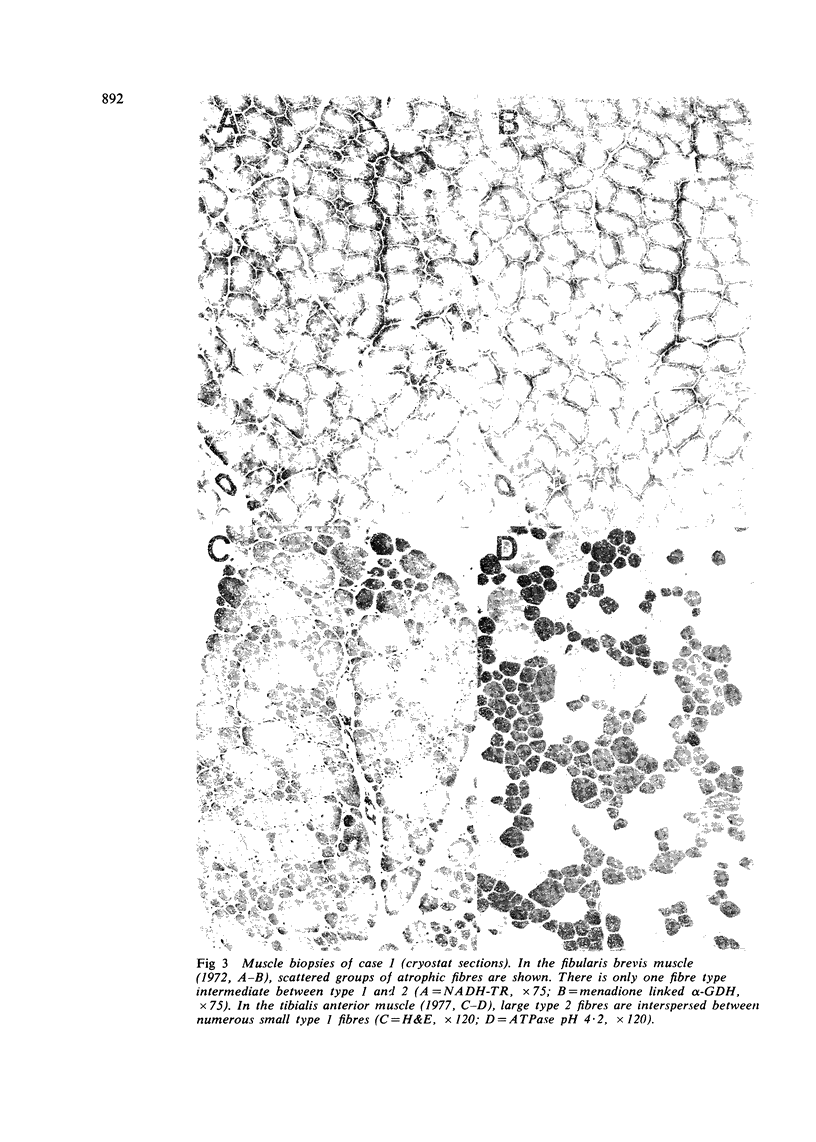
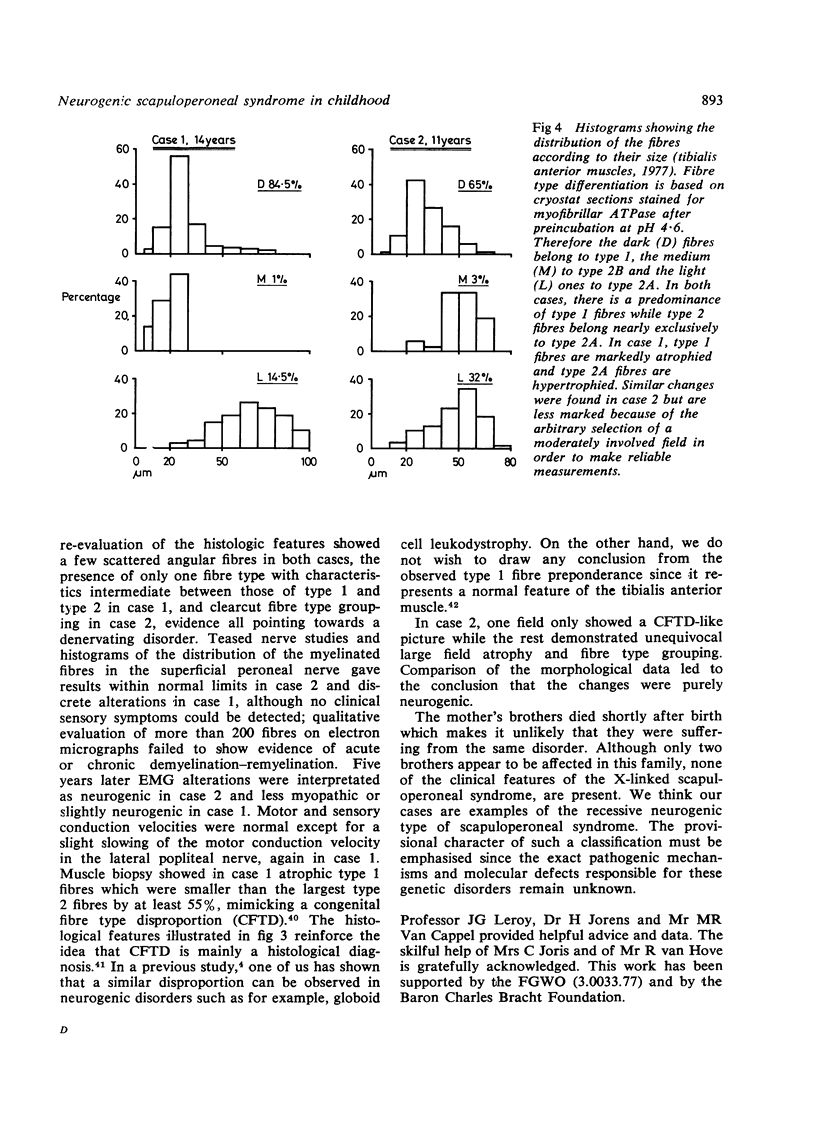
Two brothers presented with a slowly progressive scapuloperoneal syndrome starting in early childhood. Initially there were myopathic EMG changes, but these changed to those of denervation. Neuromuscular biopsies at an interval of five years confirmed the neurogenic character of the muscle atrophy.
Full text
PDF


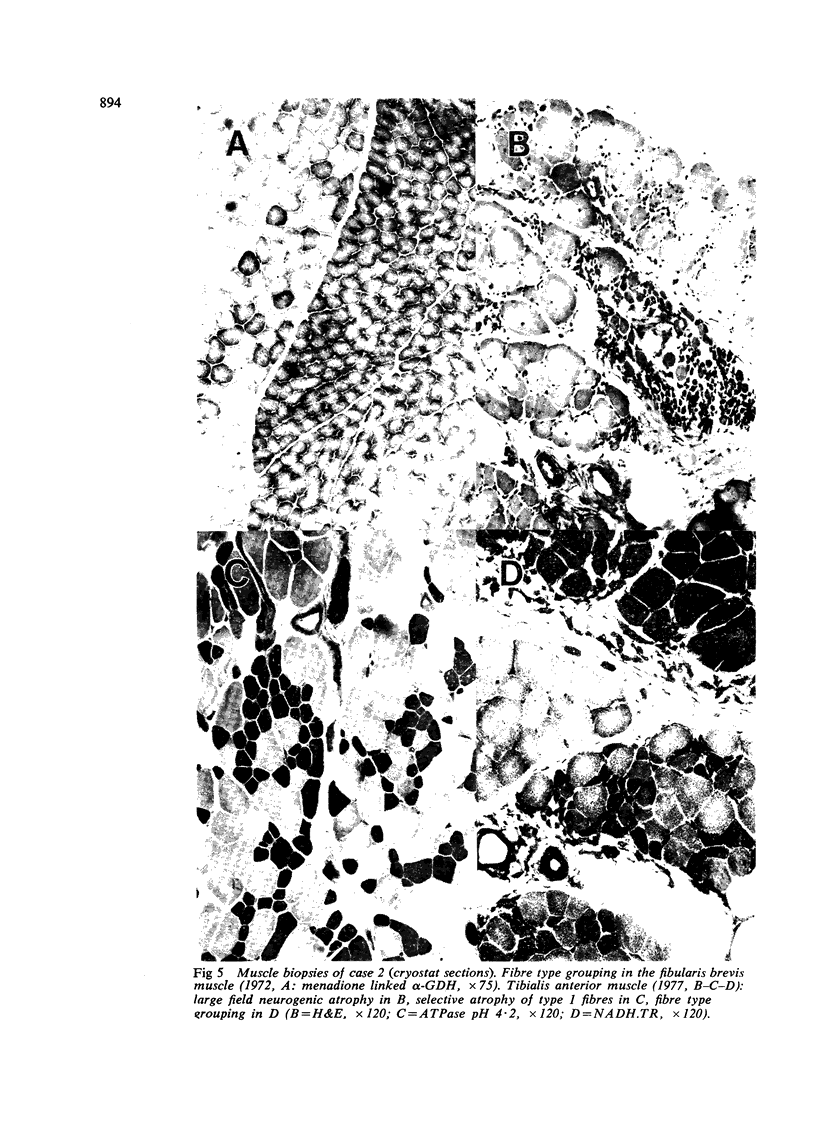


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cammann R., Vehreschild T., Ernst K. Eine neue Sippe von x-chromosomaler benigner Muskeldystrophie mit Frühkontrakturen (Emery Dreifuss) Psychiatr Neurol Med Psychol (Leipz) 1974 Jul;26(7):431–438. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavanagh N. P., Lake B. D., McMeniman P. Congenital fibre type disproportion myopathy. A histological diagnosis with an uncertain clinical outlook. Arch Dis Child. 1979 Oct;54(10):735–743. doi: 10.1136/adc.54.10.735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delwaide P. J., Schoenen J. Atrophie scapulo-péronière sporadique d'origine myogène. Rev Neurol (Paris) 1976 Jun;132(6):424–429. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emery A. E., Dreifuss F. E. Unusual type of benign x-linked muscular dystrophy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1966 Aug;29(4):338–342. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.29.4.338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emery E. S., Fenichel G. M., Eng G. A spinal muscular atrophy with scapuloperoneal distribution. Arch Neurol. 1968 Feb;18(2):129–133. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1968.00470320031003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feigenbaum J. A., Munsat T. L. A neuromuscular syndrome of scapuloperoneal distribution. Bull Los Angeles Neurol Soc. 1970 Apr;35(2):47–57. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAUSMANOWA-PETRUSEWICZ I., ZIELINSKA S. [On the nosological role of the scapulo-peroneal syndrome]. Dtsch Z Nervenheilkd. 1962;183:377–382. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson M. A., Polgar J., Weightman D., Appleton D. Data on the distribution of fibre types in thirty-six human muscles. An autopsy study. J Neurol Sci. 1973 Jan;18(1):111–129. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(73)90023-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaeser H. E. Scapuloperoneal muscular atrophy. Brain. 1965 Jun;88(2):407–418. doi: 10.1093/brain/88.2.407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazakov V. M., Bogorodinsky D. K., Skorometz A. A. Myogenic scapuloperoneal syndrome - muscular dystrophy in the K. kindred. Reexamination of the K. family described for the first time by Oransky in 1927. Eur Neurol. 1975;13(4):350–359. doi: 10.1159/000114689. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin J. J., Clara R., Ceuterick C., Joris C. Is congenital fibre type disproportion a true myopathy? Acta Neurol Belg. 1976;76(5-6):335–344. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin J. J., Joris C. The sciatic nerve in juvenile metachromatic leucodystrophy: a quantitative evaluation. Acta Neurol Belg. 1973 May-Jun;73(3):175–191. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mawatari S., Katayama K. Scapuloperoneal muscular atrophy with cardiopathy. An X-linked recessive trait. Arch Neurol. 1973 Jan;28(1):55–59. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1973.00490190073010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meadows J. C., Marsden C. D. Scapuloperoneal amytrophy. Arch Neurol. 1969 Jan;20(1):9–12. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1969.00480070019002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munsat T. L. Infantile scapuloperoneal muscular atrophy. Neurology. 1968 Mar;18(3):285–285. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Negri S., Caraceni T., Cornelio F. A case of scapulo-tibio-peroneal syndrome. Electromyographic and histoenzymologic considerations. Eur Neurol. 1973;10(1):31–40. doi: 10.1159/000114259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Probst A., Ulrich J., Kaeser H. E., Heitz P. Scapulo-peroneal muscular atrophy. Full autopsy report. Unusual findings in the anterior horn of the spinal cord. Lipid storage in muscle. Eur Neurol. 1977;16(1-6):181–196. doi: 10.1159/000114899. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reniers J., Martin L., Joris C. Histochemical and quantitative analysis of muscle biopsies. J Neurol Sci. 1970 Apr;10(4):349–367. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(70)90053-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ricker K., Mertens H. G., Schimrigk K. The neurogenic scapulo-peroneal syndrome. Eur Neurol. 1968;1(5):257–274. doi: 10.1159/000113668. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ricker K., Mertens H. G. The differential diagnosis of the myogenic (facio)-scapulo-peroneal syndrome. Eur Neurol. 1968;1(5):275–307. doi: 10.1159/000113669. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotthauwe H. W., Mortier W., Beyer H. Neuer Typ einer recessiv X-chromosomal vererbten Muskeldystrophie: Scapulo-humero-distale Muskeldystrophie mit frühzeitigen Kontrakturen und Herzrhythmusstörungen. Humangenetik. 1972;16(3):181–200. doi: 10.1007/BF00273464. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowland L. P., Fetell M., Olarte M., Hays A., Singh N., Wanat F. E. Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy. Ann Neurol. 1979 Feb;5(2):111–117. doi: 10.1002/ana.410050203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEITZ D. Zur nosologischen Stellung des sogenannten scapulo-peronealen Syndroms. Dtsch Z Nervenheilkd. 1957;175(6):547–552. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STARK P. Etude clinique et génétique d'une famille atteinte d'atrophie musculaire progressive neurale (amyotrophie de Charcot-Marie). J Genet Hum. 1958 Jul;7(1-2):1–32. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scarlato G., Valli G., Bracchi M. Quantitative histological and neurophysiological studies in scapulo-peroneal syndrome. Acta Neurol (Napoli) 1978 Aug;33(4):327–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuchmann L. Spinal muscular atrophy of the scapulo-peroneal-type. Z Kinderheilkd. 1970;109(2):118–123. doi: 10.1007/BF00438809. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz M. S., Swash M. Scapuloperoneal atrophy with sensory involvement: Davidenkow's syndrome. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1975 Nov;38(11):1063–1067. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.38.11.1063. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serratrice G., Gastaut J. L., Pellissier J. F., Pouget J. Amyotrotrophies scapulo-péronières chroniques de type Stark-Kaeser. (A propos de 10 observations) Rev Neurol (Paris) 1976 Dec;132(12):823–832. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serratrice G., Roux H., Aquaron R., Gambarelli D., Baret J. Myopathies scapulo-péronières. A propos de 14 observations dont 8 avec atteinte faciale. Sem Hop. 1969 Oct 26;45(43):2678–2683. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spalke G., Hökendorf H., von Roques P. The differential diagnosis of scapuloperoneal amyotrophy. J Neurol. 1976 Jun 14;212(3):253–269. doi: 10.1007/BF00314527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi K., Nakamura H., Nakashima R. Scapuloperoneal dystrophy associated with neurogenic changes. J Neurol Sci. 1974 Dec;23(4):575–583. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(74)90029-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. K., Calne D. B., Elliott C. F. X-linked scapuloperoneal syndrome. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1972 Apr;35(2):208–215. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.35.2.208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. K., Schott G. D., Morgan-Hughes J. A. Adult onset scapuloperoneal myopathy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1975 Oct;38(10):1008–1015. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.38.10.1008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waters D. D., Nutter D. O., Hopkins L. C., Dorney E. R. Cardiac features of an unusual X-linked humeroperoneal neuromuscular disease. N Engl J Med. 1975 Nov 13;293(20):1017–1022. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197511132932004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zellweger H., McCormick W. F. Scapuloperoneal dystrophy and scapuloperoneal atrophy. Helv Paediatr Acta. 1968 Dec;23(6):643–649. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]