Abstract
The CiaR/H two-component system is involved in regulating virulence and competence in Streptococcus pneumoniae. The system is known to regulate many genes, including that for high-temperature requirement A (HtrA). This gene has been implicated in the ability of the pneumococcus to colonize the nasopharynx of infant rats. We reported previously that deletion of the gene for HtrA made the pneumococcal strains much less virulent in mouse models, less able to grow at higher temperatures, and more sensitive to oxidative stress. In this report, we show that the growth phenotype as well as sensitivity to oxidative stress of ΔciaR mutant was very similar to that of a ΔhtrA mutant and that the expression of the HtrA protein was reduced in a ciaR-null mutant. Both the in vitro phenotype and the reduced virulence of ΔciaR mutant could be restored by increasing the expression of HtrA.
Streptococcus pneumoniae (the pneumococcus) is an important human pathogen. This gram-positive organism is a major cause of a variety of diseases such as pneumonia, bacteremia, meningitis, otitis media, and sinusitis in both adults and children all over the world (40, 43). The nasopharynx is the major reservoir of pneumococci, from which they can spread to other sites such as bloodstream or lung tissues (44).
Pathogenic bacteria encounter a number of environmental stresses during their life cycle such as temperature shifts, variations in osmolarity, changes in pH, and nutrient deprivation (45). The pneumococcus responds to these stresses, particularly heat stress, by mediating a cascade of events leading to the synthesis of a unique group of proteins called heat shock proteins (HSPs) (7). The production of these proteins represents a protective cellular response to cope with the stress-induced damage of proteins (26). HSPs are molecular chaperones or proteases that take part in protein quality control during normal growth and under stress-inducing conditions (6, 12).
Recent studies have demonstrated the role of bacterial two-component signal-transducing systems in mediating adaptive responses to environmental signals (30, 38). The pneumococcal CiaR/H two-component system consists of a sensor histidine kinase, CiaH, anchored in the cell membrane and a cytoplasmic response regulator, CiaR, which is a DNA-binding protein involved in the regulation of genes in response to environmental signals sensed by CiaH (15). This system was identified as 1 of 13 two-component signal-transducing systems in two genomic screens (24, 42). Pleotropic effects caused by cia mutations in the pneumococcus include sensitivity to cefotaxime, an ability to form protoplast, susceptibility to lysis by deoxycholate (11), and a tendency to early lysis (24). CiaH mutants also have transformation deficiency (8, 11, 16). In vivo, CiaR/H has been shown to contribute to colonization of the mouse lung (42) and the nasopharynx of infant rats (35) and to be involved in systemic infection in mice (27). Previous studies have shown that the CiaR/H regulon contains many genes, including the high-temperature requirement A gene (29, 35).
High-temperature requirement A (HtrA), also known as DegP or DO protease (36), is a stress-induced serine protease that manifests both general molecular chaperone and proteolytic activities and switches from chaperone to protease in a temperature-dependent manner (37), the protease activity being most apparent at elevated temperature. It is involved in the degradation of periplasmic misfolded proteins in Escherichia coli (39). The evidence points to a major role for this protease in helping organisms to survive environmental stresses such as elevated temperature and oxidative and osmotic stresses (13, 31, 46). HtrA is known to be involved in the virulence of many gram-negative bacteria such as Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium (2), Brucella abortus (9), and Yersinia enterocolitica (25). This protease is also required for full virulence of the gram-positive bacterium Streptococcus pyogenes (20). An HtrA homologue has also been identified in S. pneumoniae (10) and is regulated by the CiaR/H two-component system (29, 35). These studies demonstrated that CiaR positively regulates HtrA and that this regulation is probably direct, as the CiaR was shown to bind to DNA upstream of the htrA gene. An S. pneumoniae strain lacking the htrA gene showed decreased fitness in a competitive model of colonization (35). HtrA was identified as a virulence factor of the pneumococcus in a signature-tagged mutagenesis screen (17).
We previously reported that HtrA plays a crucial role in virulence of the pneumococcus (18), as HtrA-deficient strains are attenuated in both pneumonia and bacteremia models of infection. HtrA is involved in resistance to temperature and oxidative stress and also in genetic competence. Here we present evidence that the contribution of the CiaR/H system to thermotolerance, oxidative stress tolerance, and virulence of S. pneumoniae is mediated through HtrA.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Bacterial strains, primers, and growth conditions.
Bacterial strains and oligonucleotide primers used in this study are listed in Table 1. S. pneumoniae strains were grown routinely on blood agar base 2 (Oxoid, Basingstoke, United Kingdom) supplemented with 5% (vol/vol) defibrinated horse blood (BAB; E&O Laboratories, Bonnybridge, United Kingdom) and in brain heart infusion (BHI) broth at 37°C. E. coli ultracompetent cells (Stratagene) used for cloning were grown on Luria-Bertani broth or Luria-Bertani agar plates. Where appropriate, antibiotics were added to the growth medium at the following concentrations: ampicillin at 50 μg/ml, erythromycin at 1 mg/ml for E. coli or 1 μg/ml for S. pneumoniae, and spectinomycin at 100 μg/ml.
TABLE 1.
List of bacterial strains and primers used in this study
| S. pneumoniae strain or primer | Details or primer sequence | Source, reference, or primer use |
|---|---|---|
| Strain | ||
| D39 | Serotype 2, NCTC 7466 | 1a |
| 0100993 | Serotype 3, clinical isolate | 42 |
| cia spc 136b | R6 mariner mutant of CiaR | 28 |
| D39ΔciaR | D39 with mariner insertion in ciaR | This work |
| 0100993 ΔciaR | 0100993 with replacement of ciaR with ermAM | 42 |
| D39ΔhtrA | D39 with replacement of htrA with spec cassette | 18 |
| D39/pAL2YI | D39 with the empty pAL2YI vector | This work |
| D39/phtrA+ | D39 with pAL2-HtrA plasmid | This work |
| D39ΔhtrA/phtrA+ | D39ΔhtrA complemented with pAL2-HtrA | This work |
| D39ΔciaR/phtrA+ | D39ΔciaR complemented with pAL2-HtrA | This work |
| Primer | ||
| MP144 | CGAACCAAGCTGGAATATCT | PCR of CiaR/H; upstream of ciaR (28) |
| MP145 | AACCATGTCAGGATCGTAGT | PCR of CiaR/H; downstream of ciaH (28) |
DNA techniques and transformation.
Chromosomal DNA was prepared from S. pneumoniae as described elsewhere (4). PCR, restriction endonuclease digestions, DNA ligation, and DNA electrophoresis were performed according to standard protocols (34). Kits from QIAGEN were used for DNA purification and plasmid preparations according to the manufacturer's instructions. Transformation of E. coli with plasmid DNA was carried out according to the manufacturer's instructions (Stratagene). Transformation of S. pneumoniae D39 (serotype 2) was done by using a modification of the method of Lacks and Hotchkiss (23). Competent cells of D39 were prepared as follows: 200 μl of a glycerol stock of cells (previously frozen down at an optical density at 600 nm [OD600] of ∼0.6) was used to inoculate 10 ml of CAT medium (32) supplemented with 20% glucose and 0.5 M K2HPO4 (CAT/GP medium) and incubated at 37°C until they reached an OD600 of 0.3 to 0.4. Cells were then harvested by centrifugation at 5,000 × g for 10 min at 4°C, and cell pellets were resuspended in CAT/GP medium containing 20% glycerol and frozen down at −80°C as 100-μl aliquots. An aliquot of competent cells was thawed and diluted 1/10 in CAT/GP medium supplemented with 4% bovine serum albumin and 0.1 M CaCl2 (CTM medium), and 100 ng of CSP1/ml was added (33). Different concentrations of transforming DNA (0.5 to 2 μg) were then added, and the cells were incubated at 37°C for 10 min and then at 30°C for 20 min. Transformed cells were selected on BAB plates with appropriate antibiotic selection.
Construction of the plasmid expressing the htrA gene in S. pneumoniae.
htrA was expressed in pAL2 plasmid (3) from the constitutive promoter of an S. pneumoniae aminopterin resistance operon (ami) (1). The construction of the pAL2-HtrA plasmid was described elsewhere (18), and a schematic representation of it is shown in Fig. 1. To test whether the effect of the presence of the pAL2-HtrA plasmid was solely due to htrA insertion, the EcoRI-digested pAL2 fragment containing the ami promoter was self-ligated to create the empty plasmid pAL2YI. This plasmid was used to transform the D39 wild type to generate the D39/pAL2YI strain.
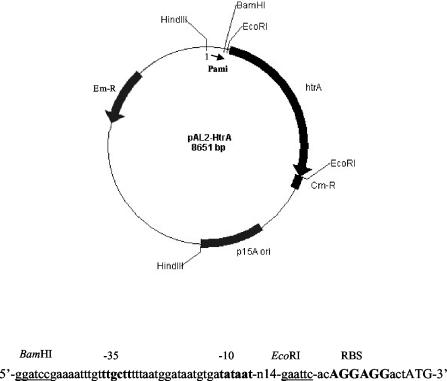
FIG. 1.
A schematic representation of pAL2-HtrA plasmid used for expression of the htrA gene in S. pneumoniae. The pAL2-HtrA plasmid was modified from pAL2 plasmid (3) as explained in Materials and Methods. Arrows indicate the locations and orientations of open reading frames. The nucleotide sequence shows the region between the ami promoter and the start codon of htrA. The gram-positive ribosome-binding site is shown in bold and uppercase characters, the htrA start codon is shown in uppercase characters, and restriction sites are underlined. Em-R, erythromycin resistance gene; Cm-R, chloramphenicol resistance gene.
Construction of ΔhtrA and ΔciaR mutants and complementation with HtrA in serotype 2 background.
The ΔhtrA mutant was constructed as described elsewhere (18). The ΔciaR mutant strain cia spc 136b (28) was used to move the ΔciaR mutation into D39 by PCR amplification of a 6-kb fragment corresponding to the ΔciaR mutation by the use of primer pair MP144 and MP145 (28); the amplified fragment was used directly to transform the D39 wild type to create D39ΔciaR. Transformant cells were selected on spectinomycin. The pAL2-HtrA plasmid, which carries an erythromycin-resistant cassette, was used to transform D39ΔhtrA and D39ΔciaR mutants to generate the complemented strains D39ΔhtrA/phtrA+ and D39ΔciaR/phtrA+, in which HtrA is expressed from the plasmid.
Western immunoblotting.
Total cellular proteins were extracted from cultures grown to mid-log phase as static cultures in BHI broth. Cell pellets were collected by centrifugation at 5,000 × g for 15 min and were resuspended in 1 ml of phosphate-buffered saline (PBS). Cell suspensions were sonicated four times at 30 s each time with a 13-mm probe (Sonicator, Vibra cell; Sonics & Materials Inc.) with a power output of 36 W. The tubes containing the samples were kept in crushed ice during sonication. The cell debris was removed by centrifugation at 13,000 × g for 10 min. Concentrations of total proteins were determined by the Bradford assay, with the use of bovine serum albumin as a standard (5). For Western blot analysis, 15 μg of total proteins from each strain was separated on sodium dodecyl sulfate-10% polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, electroblotted onto nitrocellulose membranes (Amersham), and reacted with specific antiserum against HtrA by a standard protocol (34). To ensure that nitrocellulose was not saturated with bound HtrA, a dilution series was performed; the results confirmed that using this amount of total cell protein, band intensity was related to the amount of HtrA.
In vitro experiments.
To compare the abilities of ΔciaR of both type 2 and type 3 pneumococci and the complemented strain D39ΔciaR/phtrA+ mutants to grow at normal and elevated temperatures to those of their wild types, the same number of viable cells (106 CFU/ml) was used to inoculate BHI broth prewarmed at 37 and 40°C. At 1-h intervals, samples were withdrawn to measure the OD600 and viable counts. The sensitivity of D39ΔciaR and D39ΔciaR/phtrA+ strains to H2O2 was tested by exposing aliquots of cultures grown to an OD of ∼0.3 to 40 mM of H2O2 for 5, 10, and 15 min at room temperature. The viable cells were counted by plating onto blood agar plates before and after the exposure to H2O2, and the result was expressed as percent survival (19).
Mice and infections.
Female outbred MF1 mice (25 to 30 g of body weight) were purchased from Harlan Olac, Bicester, United Kingdom. They were used at the age of 9 weeks. For intranasal infection, mice were lightly anesthetized with 1.5% (vol/vol) halothane and a 50-μl infectious dose (106 CFU/mouse for type 2 strains or 107 CFU/mouse for type 3 strains) was administered to the nostrils of mice held vertically (21). For intraperitoneal infection, the infectious dose (2 × 105 CFU/mouse) was resuspended in 200 μl of sterile PBS and administered into the peritoneal cavity of mice. After the infectious dose was administered, mice were observed and the development of symptoms was recorded.
Bacteriological investigation.
At prechosen intervals after infection, groups of mice were sacrificed by cervical dislocation and a blood sample was removed via cardiac puncture. Lungs were removed and homogenized in 5 ml of PBS with a glass handheld tissue homogenizer (Jencons, Leighton Buzzard, United Kingdom). Viable bacteria in lung and blood samples were counted by plating out serial 10-fold dilutions on BAB (22).
Competition experiments.
Competitive analysis of virulence was examined using a slight modification of the method of Hava and Camilli (17). Essentially, challenge doses of wild-type and mutant strains were mixed in a 1:1 ratio and inoculated intranasally at 2 × 106 and 2 × 105 bacteria for intraperitoneal infections. After 24 and 48 h, bacteria were recovered from the lungs and blood. The number of wild-type versus mutant bacteria recovered was determined by plating on nonselective and selective media, and competitive indices were calculated as the ratio of mutant to wild-type bacteria recovered from each animal.
Statistical analysis.
Statistical analyses were carried out using StatView 4.1 (Abacus Concept). Survival times were analyzed by using nonparametric Mann-Whitney U analysis. Bacteriology results are expressed as geometric means ± standard errors of the means (SEM). Comparisons of bacterial loads in the time course bacteriology experiment were performed using unpaired t tests. In all analyses, a P value of <0.05 was considered statistically significant.
RESULTS
Introduction of a ΔciaR mutation into S. pneumoniae.
A ΔciaR mutation in strain 0100993 was made by allelic replacement with an erythromycin resistance marker and was kindly provided by Martin Burnham (42). To perform the complementation experiments with the pAL2-HtrA plasmid (erythromycin selection) we needed to use another antibiotic marker to disrupt the ciaR gene. We therefore constructed a ΔciaR strain of D39 with resistance to spectinomycin by transformation with a 6-kb fragment amplified by PCR from strain ciaspec136b (28). This mutation was confirmed by PCR and sequencing (data not shown).
HtrA Western immunoblot analysis.
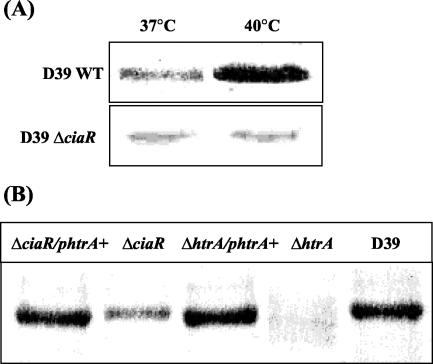
As CiaR is involved in virulence and regulates htrA, which we have shown previously to be a crucial virulence factor (18), we asked whether the CiaR phenotype was associated with the down-regulation of htrA. To test this we constructed a plasmid to allow the constitutive expression of HtrA in the pneumococcus. Plasmid pAL2-HtrA (Fig. 1) allows the expression of HtrA from the pneumococcal ami promoter (1). Western blotting was used to examine the levels of HtrA expressed by pneumococcal strains. The level of expression of HtrA was shown to be higher at 40°C than at 37°C in the wild-type D39 but not in the D39ΔciaR mutant (Fig. 2A), confirming HtrA to be an HSP of the pneumococcus and to be up-regulated by CiaR in response to heat shock. As expected, HtrA expression was abolished in D39ΔhtrA. We could restore levels of expression of HtrA in the D39ΔhtrA mutant to levels similar to wild-type levels with the plasmid pAL2-HtrA. The level of HtrA was reduced but not abolished in ΔciaR, and introduction of pAL2-HtrA into the ΔciaR strain resulted in expression of levels of HtrA similar to wild-type levels (Fig. 2B). Western blotting is semiquantitative, but a dilution series of samples allowed us to confirm that we were loading amounts of HtrA that were not saturating for the nitrocellulose membrane. Visual examination of these blots suggests that deletion of CiaR results in an approximately fourfold reduction in HtrA. Expression of HtrA in the ΔciaR strain from the plasmid restored the level of HtrA to that of the wild type. Expression of HtrA from the plasmid in the wild-type strain did not increase total levels of HtrA (data not shown).
FIG. 2.
Western immunoblot analysis. (A) Expression of HtrA at 37 and 40°C in wild-type (WT) strain D39 and strain D39ΔciaR. (B) Levels of HtrA in strain D39ΔhtrA and strain D39ΔciaR and their complemented strains grown at 37°C.
In vitro growth phenotype of ΔciaR mutants.
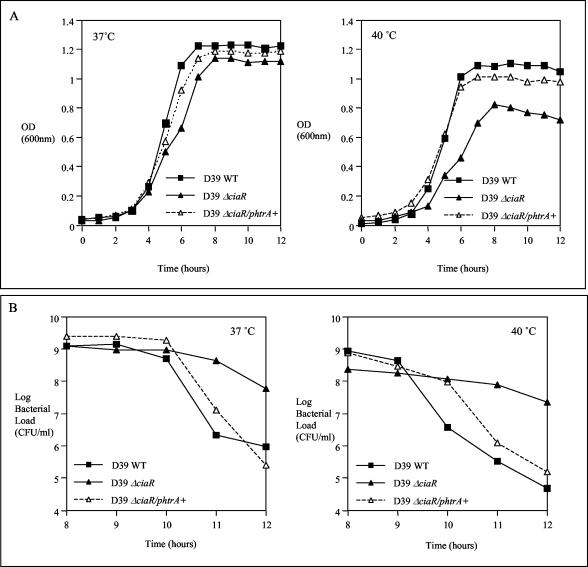
We have shown before that HtrA is involved in the ability of the type 2 pneumococci to grow at elevated temperature and that the effect of htrA deletion was to slow growth rather than prevent it (18). We also found that the D39ΔhtrA mutant has a decreased rate of autolysis compared to its parent strain at 40°C, as indicated by viable counts at the stationary and decline phases of growth (data not shown). We also studied the growth phenotype of D39ΔciaR mutant at normal and elevated temperatures. In similarity to the results seen with D39ΔhtrA, the growth of the D39ΔciaR mutant was less than that of the wild type at 40°C, as judged by OD (Fig. 3A). The D39ΔciaR strain showed a decreased rate of autolysis after reaching the stationary phase of growth at both 37 and 40°C compared to the D39 wild type (Fig. 3B). This growth phenotype of strain D39ΔciaR could be restored by increasing HtrA levels in the complemented strain D39ΔciaR/phtrA+ (Fig. 3). Introduction of the pAL2YI vector had no effect on the growth of strain D39 at either 37 or 40°C (data not shown). Also, introduction of the pAL2-HtrA plasmid into the D39 wild-type strain did not result in altered growth at these temperatures.
FIG. 3.
Growth curves of D39 wild-type (WT), D39ΔciaR, and D39ΔciaR/phtrA+ strains at 37 and 40°C; results are represented as OD600 values in panel A and as viable counts after reaching the stationary phase of growth in panel B. A total of 106 CFU/ml of each strain was used to inoculate BHI broth prewarmed at the indicated temperatures, and samples were withdrawn at 1-h intervals to measure the OD600 values and viable counts.
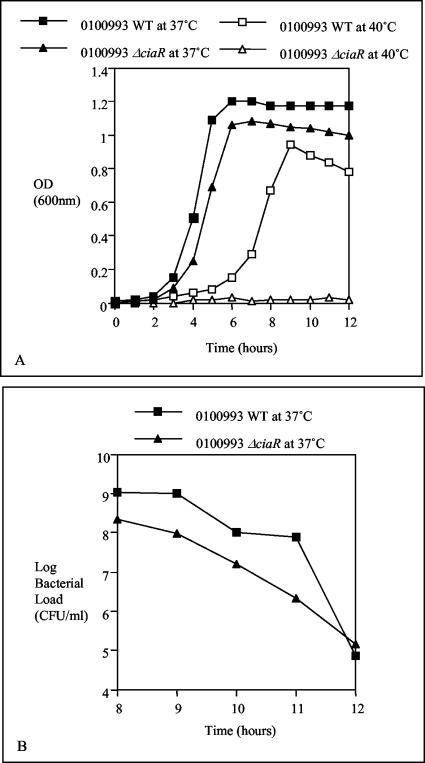
The effect of ciaR mutation in type 3 strain 0100993 was more dramatic at elevated temperature when compared to type 2 results. Growth of the 0100993 ΔciaR mutant was similar to that of the wild type and a similar rate of autolysis was seen at 37°C, whereas growth at 40°C was prevented by the mutation (Fig. 4).
FIG. 4.
Growth curves of the type 3 0100993 wild-type (WT) strain and its ΔciaR mutant at 37 and 40°C; results are represented by OD600 values in panel A and by viable counts in panel B. The growth of the 0100993 ΔciaR mutant was impaired at 40°C and showed a rate of autolysis similar to that of the wild type at 37°C.
Sensitivity of the D39ΔciaR strain to oxidative stress is similar to that of the D39ΔhtrA mutant and can be restored by complementation with HtrA.
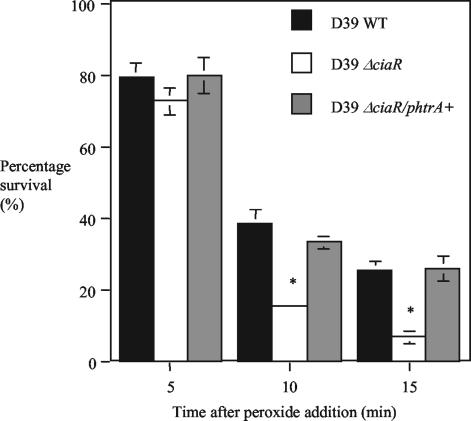
We have shown previously that HtrA is involved in the ability of D39 to resist oxidative stress (18). To determine whether reduced expression of HtrA in strain D39ΔciaR resulted in sensitivity to oxidative stress we compared D39ΔciaR to the wild type and the complemented strain D39ΔciaR/phtrA+ for sensitivity to hydrogen peroxide. The D39ΔciaR strain was significantly more sensitive to peroxide than the parent strain D39 after 10 and 15 min of exposure to hydrogen peroxide. There was no statistically significant difference 5 min after peroxide treatment, probably because strain D39ΔciaR still expresses some HtrA. By restoring HtrA to a level similar to that of the wild type in D39ΔciaR/phtrA+, the strain was again identical to the wild type in response to oxidative stress (Fig. 5). The sensitivity of strain D39ΔciaR to oxidative stress is therefore similar to what we reported previously for strain D39ΔhtrA (18) and could be explained by the down-regulation of HtrA in the CiaR-null mutant.
FIG. 5.
H2O2 sensitivity assay for D39 wild-type (WT), D39ΔciaR, and D39ΔciaR/phtrA+ strains. H2O2 (40 mM) was added to 1-ml aliquots of culture grown to an OD600 of ∼0.3. Viable counts were performed on BAB plates before and after the addition of peroxide, and the percentages of survival were calculated. Values expressed are the means (± SEM) of three independent experiments. *, P < 0.05 for lower survival for the D39ΔciaR mutant than the wild type.
The ΔciaR mutant displays attenuated virulence in vivo.
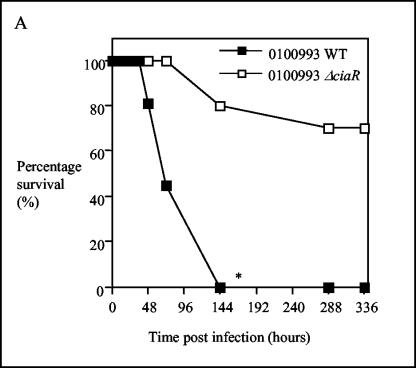
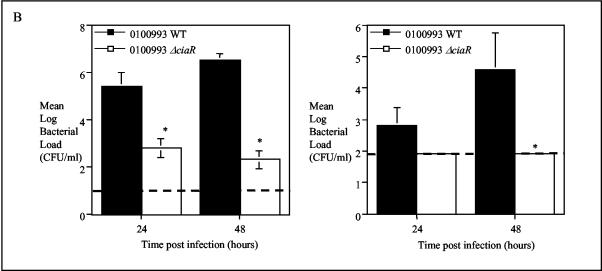
The CiaR/H system has previously been reported to play a role in mouse lung colonization (42) and colonization of the nasopharynx of infant rats (35) and has also been identified as playing a role in a mouse model of systemic disease (27). We confirmed and further investigated the role of CiaR in our model of infection. Initially we compared a ΔciaR mutant on a serotype 3 background with its wild-type parent (strain 0100993). This is the same mutant as that used by Throup and coworkers (42) and Sebert and coworkers (35) in the studies described above. All animals challenged intranasally with 107 CFU of the parent strain were moribund by 144 h postinfection. In contrast, the 0100993 ΔciaR mutant only caused the moribund state in 25% of the animals (Fig. 6A). Analysis of bacteriology showed that the 0100993 ΔciaR strain grew to a viable count of approximately 103 CFU in lung compared to 106 CFU for the wild-type organism. The level of bacteremia caused by the 0100993 ΔciaR strain was below the limit of detection of the assay (approximately 100 organisms per ml) (Fig. 6B). Competition experiments showed that CiaR plays a role in both the lung and systemic infection models (Table 2). We have also confirmed that CiaR plays a role in the virulence of strain D39 (see below).
FIG. 6.
Effect of CiaR on virulence of strain 0100993. (A). Survival of animals given 107 CFU of wild-type or ΔciaR bacteria by the intranasal route; n = 10. (B). Mean (SEM) bacteriology in lung (left) and blood (right) during infection, n = 5. The broken line represents the limit of detection of the assay. (A) *, P < 0.05 for shorter survival times for the wild-type (WT) strain than for the ΔciaR mutant; (B) *, P < 0.05 for lower bacterial loads for the ΔciaR strain than for the wild-type strain.
TABLE 2.
Competitive index for 0100993 wild type versus 0100993 ΔciaR in intranasal and intraperitoneal infectionsa
| Mouse | Competitive index
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Intranasal infectionb | Intraperitoneal infectionc | |
| 1 | 0.14 | 0.07 |
| 2 | 0.12 | 0.013 |
| 3 | 0.014 | 0.032 |
| 4 | 0.007 | 0.03 |
| 5 | 0.012 | NDd |
The in vivo competitive index was calculated for each animal as the ratio of mutant to wild-type strains divided by the input ratio of mutant to wild type. Intranasal and intraperitoneal infections were done in two separate groups of five mice.
Mean, 0.059; SEM, 0.02.
Mean, 0.036; SEM, 0.012.
ND, none detected.
HtrA can complement the CiaR mutation and restore virulence.
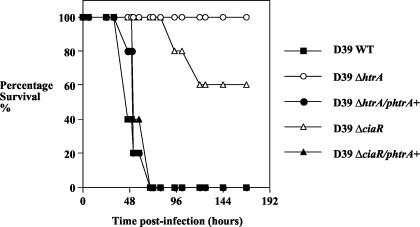
As the growth phenotype and sensitivity to peroxide of the D39ΔciaR mutant could be restored by complementation with HtrA, we investigated the virulence phenotype of the knockout and complemented strains in our mouse pneumonia model. For these studies, all mutants used were on a D39 background and a dose of 106 CFU was given intranasally. For the D39 wild-type strain, all animals succumbed to the infection by 72 h whereas no animals became sick when challenged with strain D39ΔhtrA (Fig. 7). A ΔciaR mutant of D39 showed attenuation in the model, with 40% of the animals becoming moribund during the experiment. When the pAL2-HtrA plasmid was introduced into the D39ΔhtrA strain it was restored to full virulence. Moreover, when the level of HtrA expression was corrected in the ΔciaR mutant this was also restored to full virulence.
FIG. 7.
Effect of complementation with HtrA on virulence. Strains D39ΔhtrA and D39ΔciaR show reduced virulence, as judged by survival time. Complementation with HtrA (from plasmid pAL2-HtrA) causes these strains to revert to full virulence. WT, wild type.
DISCUSSION
The CiaR/H two-component system is known to be important in a number of aspects of pneumococcal biology. Mutations in the histidine protein kinase ciaH conferred resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics, suggesting that the system may control genes important in cell wall metabolism (14). The system is also involved in the control of bacterial lysis (11, 16, 24) and the regulation of genetic competence (8, 14, 28). Previous studies have shown that this system plays a role in colonization of the lungs of mice (42) and the nasopharynx of infant rats (35). We have used the same mutant of S. pneumoniae (kindly provided by Martin Burnham of SmithKlineBeecham [now GlaxoSmithKline]) used in these two studies to show that CiaR/H also plays a major role in the causation of disease in the mouse. The ΔciaR/H mutant of strain 0100993 was much reduced in its overall virulence (as judged by survival times) when given intranasally. The mutant organism grew to about 103 CFU in lungs compared to 106 for the wild-type organism (a reduction of 3 logs). A large reduction in growth in the lung was also observed by Throup et al. (42), who observed a reduction of approximately 5 logs in growth in the lung due to disruption of the CiaR/H operon. In studies of colonization of the rat nasopharynx (35), inoculation of wild-type organisms resulted in maximum colonization levels of about 10 6 CFU/ml of nasal wash whereas the ΔciaR/H mutant did not colonize the nasopharynx. In the experiments reported here, the mutant organism only invaded the bloodstream to very low levels (at the limit of detection of 100 organisms per ml). This two-component system therefore seems to be very important for colonization and growth in the lungs and also for invasion of the bloodstream.
Low-level bacteremia following intranasal challenge could be caused either by poor invasion from the lungs or by poor growth in the blood. Competition experiments using wild-type and mutant strains showed that the mutant was much less able to colonize the lungs and also less able to grow systemically. We have confirmed that CiaR also plays a role in the virulence of type 2 strain D39. It is important to investigate the role of these systems in more than one strain, as we have recently shown that the contribution of two-component systems to virulence can be strain dependent (4). A role of CiaR/H in the systemic virulence of D39 was also shown by Marra and coworkers (27).
As CiaR/H plays a role in virulence, the next question is how does this system mediate pathogenesis of infection? The cia regulon has already been defined and includes genes important for the synthesis and modification of cell wall polymers, peptide pheromone and bacteriocin production, and the htrA-spoJ region (29). Because it is already known that CiaR/H regulates the gene for HtrA (29, 35) and that deletion of the htrA gene reduces the ability of the pneumococcus to colonize the nasopharynx (35) and attenuates a type 2 pneumococcal strain in both pneumonia and bacteremia models of infection (18), we attempted to define the contribution of HtrA to the overall CiaR/H phenotype.
Both CiaR-null and HtrA-null mutants have reduced virulence, and the CiaR/H system is known to regulate HtrA expression. We therefore investigated whether the reduced virulence of a ΔciaR mutant could be explained by a down-regulation of HtrA expression. To do this we made a ΔciaR version of strain D39 and confirmed that this was less virulent. The reduction in lung colonization was of the order of several orders of magnitude, a finding similar to that of previous studies (42). Western blotting indicated that strain D39ΔciaR expressed approximately fourfold less HtrA protein than wild-type D39. When HtrA was expressed from a plasmid in the D39ΔciaR strain, Western blotting showed the level of HtrA was restored to that of the wild type. We also found that when HtrA was expressed from the plasmid in the wild-type strain, there was no increase in the level of HtrA protein. This finding is surprising and suggests that there is a regulatory mechanism for controlling maximal levels of HtrA and that this mechanism may not be dependent on the presence of CiaR/H. Restoring the level of HtrA to wild-type levels in strain D39ΔciaR produced a strain that was again fully virulent in mice. This shows that the virulence phenotype of D39ΔciaR can be completely explained by the reduced expression of HtrA. Interestingly, D39 ΔciaR still expresses low levels of HtrA; this may explain why it is more virulent than D39ΔhtrA.
We have shown in this study that HtrA behaves as a typical HSP, with levels of the protein increasing after exposure of bacteria to a temperature of 40°C. Interestingly, we also demonstrated that the increased expression of HtrA at high temperature is dependent on the presence of CiaR/H. Based on these findings we predicted that strain D39ΔciaR would be defective in growth at 40°C (due to decreased expression of HtrA). Analysis in vitro indicates that the growth of the D39ΔciaR mutant was less than that of the wild type at elevated temperature. The CiaR/H system is also involved in the control of bacterial lysis (11, 16, 24, 29); in particular, Lange and coworkers (24) reported that a ciaR mutant of the strain R6 had an increased rate of autolysis when grown in Todd-Hewitt medium at 37°C. In contrast to this report, our D39ΔciaR mutant showed a decreased rate of autolysis, as judged by viable counts at stationary and decline phases of growth at both normal and elevated temperatures. This may reflect differences in the genetic content of R6 and D39, which are now known to differ at several loci (41). We also studied the in vitro growth phenotype of the serotype 3 ciaR mutant. The effect of ciaR deletion in this strain was more dramatic, as the growth of this mutant was prevented at elevated temperature; however, it showed a rate of autolysis similar to that of the parent strain at 37°C. These findings highlight the differences of the effects of mutations in different strains. The growth phenotype of strain D39ΔciaR was restored to that of the wild type by introducing pAL2-HtrA plasmid in the complemented strain, suggesting that the strain D39ΔciaR growth phenotype is due to the low level of HtrA expressed by this strain.
As we have previously shown that deletion of HtrA is associated with increased sensitivity to oxidative stress (18), we predicted that reduced levels of HtrA in strain D39ΔciaR would also result in reduced resistance to oxidative stress. The sensitivity to oxidative stress of D39ΔciaR was increased, although not to the same extent as found previously for the D39ΔhtrA mutant. After 5 min of exposure to 40 mM hydrogen peroxide, the survival of strain D39ΔciaR was similar to that of the wild type (Fig. 5) whereas the survival of strain D39ΔhtrA was significantly reduced at this time (18). This probably reflects the expression of low levels of HtrA in strain D39ΔciaR. Resistance of strain D39ΔciaR to hydrogen peroxide could be restored to wild-type levels by complementation with HtrA, which again confirms that the D39ΔciaR phenotype could be explained by down-regulation of HtrA in this mutant.
In summary, we have confirmed that the CiaR/H system is involved in controlling the levels of HtrA within the cell and have shown that up-regulation of HtrA in response to heat is dependent on the CiaR/H system. As the response regulator CiaR has been shown to physically bind to DNA in the region of HtrA, this regulation is proposed to be direct (29). We have shown that a number of the phenotypes associated with deficiency in CiaR/H are due to the alterations in levels of HtrA. Thus, the resistance of cells to autolysis, the increased sensitivity to oxidative stress, and the decreased virulence of strain D39ΔciaR can all be explained by alterations in levels of HtrA. We have also shown that transformation efficiency is also altered by HtrA (18). While the CiaR/H regulon is obviously very complex, many of the phenotypes observed with mutants of this regulon can be explained by changes in HtrA. The exact mechanism by which HtrA controls these processes is still unclear and is the subject of ongoing studies.
Acknowledgments
Yasser Musa Ibrahim is the recipient of a scholarship from the Egyptian government.
We thank J.-P. Claverys and Bernard Martin (CNRS-Université Paul Sabatier, Toulouse, France) for provision of strain R6 carrying a mariner mutation in CiaR and Mark Roberts (University of Glasgow) for provision of HtrA antiserum. We thank V. Salisbury (University of the West of England) for providing plasmid pAL2. We are also grateful to Martin Burnham (GlaxoSmithKline) for provision of type 3 strain 0100993 with a CiaR mutation.
REFERENCES
- 1.Alloing, G., M. C. Trombe, and J. P. Claverys. 1990. The ami locus of the gram-positive bacterium Streptococcus pneumoniae is similar to binding protein-dependent transport operons of gram-negative bacteria. Mol. Microbiol. 4:633-644. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 1a.Avery, O. T., C. M. Macleod, and M. McCarty. 1944. Studies on the chemical nature of the sustance inducing transformation of pneumococcal types: induction of transformation by desoxyribonucleic acid fraction isolated from pneumococcus type III. J. Exp. Med. 79:137-158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Baumler, A. J., J. G. Kusters, I. Stojiljkovic, and F. Heffron. 1994. Salmonella typhimurium loci involved in survival within macrophages. Infect. Immun. 62:1623-1630. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Beard, S. J., V. Salisbury, R. J. Lewis, J. A. Sharpe, and A. P. MacGowan. 2002. Expression of lux genes in a clinical isolate of Streptococcus pneumoniae: using bioluminescence to monitor gemifloxacin activity. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 46:538-542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Blue, C. E., and T. J. Mitchell. 2003. Contribution of a response regulator to the virulence of Streptococcus pneumoniae is strain dependent. Infect. Immun. 71:4405-4413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Bradford, M. M. 1976. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 72:248-254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Bukau, B., and A. L. Horwich. 1998. The Hsp70 and Hsp60 chaperone machines. Cell 92:351-366. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Choi, I. H., J. H. Shim, S. W. Kim, S. N. Kim, S. N. Pyo, and D. K. Rhee. 1997. Characterization of the stress response in Streptococcus pneumoniae. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 418:1007-1009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Echenique, J. R., S. Chapuy-Regaud, and M. C. Trombe. 2000. Competence regulation by oxygen in Streptococcus pneumoniae: involvement of ciaRH and comCDE. Mol. Microbiol. 36:688-696. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Elzer, P. H., R. W. Phillips, G. T. Robertson, and R. M. Roop 2nd. 1996. The HtrA stress response protease contributes to resistance of Brucella abortus to killing by murine phagocytes. Infect. Immun. 64:4838-4841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Gasc, A. M., P. Giammarinaro, S. Richter, and M. Sicard. 1998. Organization around the dnaA gene of Streptococcus pneumoniae. Microbiology 144:433-439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Giammarinaro, P., M. Sicard, and A. M. Gasc. 1999. Genetic and physiological studies of the CiaH-CiaR two-component signal-transducing system involved in cefotaxime resistance and competence of Streptococcus pneumoniae. Microbiology 145:1859-1869. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Gottesman, S., S. Wickner, and M. R. Maurizi. 1997. Protein quality control: triage by chaperones and proteases. Genes Dev. 11:815-823. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Gray, C. W., R. V. Ward, E. Karran, S. Turconi, A. Rowles, D. Viglienghi, C. Southan, A. Barton, K. G. Fantom, A. West, J. Savopoulos, N. J. Hassan, H. Clinkenbeard, C. Hanning, B. Amegadzie, J. B. Davis, C. Dingwall, G. P. Livi, and C. L. Creasy. 2000. Characterization of human HtrA2, a novel serine protease involved in the mammalian cellular stress response. Eur. J. Biochem. 267:5699-5710. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Guenzi, E., A. M. Gasc, M. A. Sicard, and R. Hakenbeck. 1994. A two-component signal-transducing system is involved in competence and penicillin susceptibility in laboratory mutants of Streptococcus pneumoniae. Mol. Microbiol. 12:505-515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Guenzi, E., and R. Hakenbeck. 1995. Genetic competence and susceptibility to beta-lactam antibiotics in Streptococcus pneumoniae R6 are linked via a two-component signal-transducing system cia. Dev. Biol. Stand. 85:125-128. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Hakenbeck, R., T. Grebe, D. Zahner, and J. B. Stock. 1999. Beta-lactam resistance in Streptococcus pneumoniae: penicillin-binding proteins and non-penicillin-binding proteins. Mol. Microbiol. 33:673-678. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Hava, D. L., and A. Camilli. 2002. Large-scale identification of serotype 4 Streptococcus pneumoniae virulence factors. Mol. Microbiol. 45:1389-1406. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Ibrahim, Y. M., A. R. Kerr, J. McCluskey, and T. J. Mitchell. 2004. Role of HtrA in the virulence and competence of Streptococcus pneumoniae. Infect. Immun. 72:3584-3591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Johnson, S. R., B. M. Steiner, D. D. Cruce, G. H. Perkins, and R. J. Arko. 1993. Characterization of a catalase-deficient strain of Neisseria gonorrhoeae: evidence for the significance of catalase in the biology of N. gonorrhoeae. Infect. Immun. 61:1232-1238. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Jones, C. H., T. C. Bolken, K. F. Jones, G. O. Zeller, and D. E. Hruby. 2001. Conserved DegP protease in gram-positive bacteria is essential for thermal and oxidative tolerance and full virulence in Streptococcus pyogenes. Infect. Immun. 69:5538-5545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Kadioglu, A., N. A. Gingles, K. Grattan, A. Kerr, T. J. Mitchell, and P. W. Andrew. 2000. Host cellular immune response to pneumococcal lung infection in mice. Infect. Immun. 68:492-501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Kerr, A. R., J. J. Irvine, J. J. Search, N. A. Gingles, A. Kadioglu, P. W. Andrew, W. L. McPheat, C. G. Booth, and T. J. Mitchell. 2002. Role of inflammatory mediators in resistance and susceptibility to pneumococcal infection. Infect. Immun. 70:1547-1557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Lacks, S., and R. D. Hotchkiss. 1960. A study of the genetic material determining an enzyme activity in the pneumococcus. Biochem. Biophys. Acta 39:508-517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Lange, R., C. Wagner, A. de Saizieu, N. Flint, J. Molnos, M. Stieger, P. Caspers, M. Kamber, W. Keck, and K. E. Amrein. 1999. Domain organization and molecular characterization of 13 two-component systems identified by genome sequencing of Streptococcus pneumoniae. Gene 237:223-234. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Li, S. R., N. Dorrell, P. H. Everest, G. Dougan, and B. W. Wren. 1996. Construction and characterization of a Yersinia enterocolitica O:8 high-temperature requirement (htrA) isogenic mutant. Infect. Immun. 64:2088-2094. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Lindquist, S., and E. A. Craig. 1988. The heat-shock proteins. Annu. Rev. Genet. 22:631-677. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Marra, A., J. Asundi, M. Bartilson, S. Lawson, F. Fang, J. Christine, C. Wiesner, D. Brigham, W. P. Schneider, and A. E. Hromockyj. 2002. Differential fluorescence induction analysis of Streptococcus pneumoniae identifies genes involved in pathogenesis. Infect. Immun. 70:1422-1433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Martin, B., M. Prudhomme, G. Alloing, C. Granadel, and J. P. Claverys. 2000. Cross-regulation of competence pheromone production and export in the early control of transformation in Streptococcus pneumoniae. Mol. Microbiol. 38:867-878. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Mascher, T., D. Zähner, M. Merai, N. Balmelle, A. B. de Saizieu, and R. Hakenbeck. 2003. The Streptococcus pneumoniae cia regulon: CiaR target sites and transcription profile analysis. J. Bacteriol. 185:60-70. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Parkinson, J. S. 1993. Signal transduction schemes of bacteria. Cell 73:857-871. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Ponting, C. P. 1997. Evidence for PDZ domains in bacteria, yeast, and plants. Protein Sci. 6:464-468. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Porter, R. D., and W. R. Guild. 1976. Characterization of some pneumococcal bacteriophages. J. Virol. 19:659-667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Pozzi, G., L. Masala, F. Iannelli, R. Manganelli, L. S. Havarstein, L. Piccoli, D. Simon, and D. A. Morrison. 1996. Competence for genetic transformation in encapsulated strains of Streptococcus pneumoniae: two allelic variants of the peptide pheromone. J. Bacteriol. 178:6087-6090. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Sambrook, J., E. F. Fritsch, and T. Maniatis. 1989. Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, 2nd ed. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, N.Y.
- 35.Sebert, M. E., L. M. Palmer, M. Rosenberg, and J. N. Weiser. 2002. Microarray-based identification of htrA, a Streptococcus pneumoniae gene that is regulated by the CiaRH two-component system and contributes to nasopharyngeal colonization. Infect. Immun. 70:4059-4067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Seol, J. H., S. K. Woo, E. M. Jung, S. J. Yoo, C. S. Lee, K. J. Kim, K. Tanaka, A. Ichihara, D. B. Ha, and C. H. Chung. 1991. Protease Do is essential for survival of Escherichia coli at high temperature: its identity with the htrA gene product. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 176:730-736. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Spiess, C., A. Beil, and M. Ehrmann. 1999. A temperature-dependent switch from chaperone to protease in a widely conserved heat shock protein. Cell 97:339-347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Stock, J. B., M. G. Surette, M. Levit, and P. Park. 1995. Two-component signal transduction systems: structure-function relationships and mechanisms of catalysis, p. 25-51. In J. A. Hoch and T. J. Silhavy (ed.), Two-component signal transduction. American Society for Microbiology, Washington, D.C.
- 39.Strauch, K. L., K. Johnson, and J. Beckwith. 1989. Characterization of degP, a gene required for proteolysis in the cell envelope and essential for growth of Escherichia coli at high temperature. J. Bacteriol. 171:2689-2696. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Talbot, U. M., A. W. Paton, and J. C. Paton. 1996. Uptake of Streptococcus pneumoniae by respiratory epithelial cells. Infect. Immun. 64:3772-3777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Tettelin, H., K. E. Nelson, I. T. Paulsen, J. A. Eisen, T. D. Read, S. Peterson, J. Heidelberg, R. T. DeBoy, D. H. Haft, R. J. Dodson, A. S. Durkin, M. Gwinn, J. F. Kolonay, W. C. Nelson, J. D. Peterson, L. A. Umayam, O. White, S. L. Salzberg, M. R. Lewis, D. Radune, E. Holtzapple, H. Khouri, A. M. Wolf, T. R. Utterback, C. L. Hansen, L. A. McDonald, T. V. Feldblyum, S. Angiuoli, T. Dickinson, E. K. Hickey, I. E. Holt, B. J. Loftus, F. Yang, H. O. Smith, J. C. Venter, B. A. Dougherty, D. A. Morrison, S. K. Hollingshead, and C. M. Fraser. 2001. Complete genome sequence of a virulent isolate of Streptococcus pneumoniae. Science 293:498-506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Throup, J. P., K. K. Koretke, A. P. Bryant, K. A. Ingraham, A. F. Chalker, Y. Ge, A. Marra, N. G. Wallis, J. R. Brown, D. J. Holmes, M. Rosenberg, and M. K. Burnham. 2000. A genomic analysis of two-component signal transduction in Streptococcus pneumoniae. Mol. Microbiol. 35:566-576. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Tuomanen, E. I., R. Austrian, and H. R. Masure. 1995. Pathogenesis of pneumococcal infection. N. Engl. J. Med. 332:1280-1284. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Watson, D. A., D. M. Musher, and J. Verhoef. 1995. Pneumococcal virulence factors and host immune responses to them. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 14:479-490. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Zugel, U., and S. H. Kaufmann. 1999. Role of heat shock proteins in protection from and pathogenesis of infectious diseases. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 12:19-39. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Zumbrunn, J., and B. Trueb. 1996. Primary structure of a putative serine protease specific for IGF-binding proteins. FEBS Lett. 398:187-192. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]