Abstract
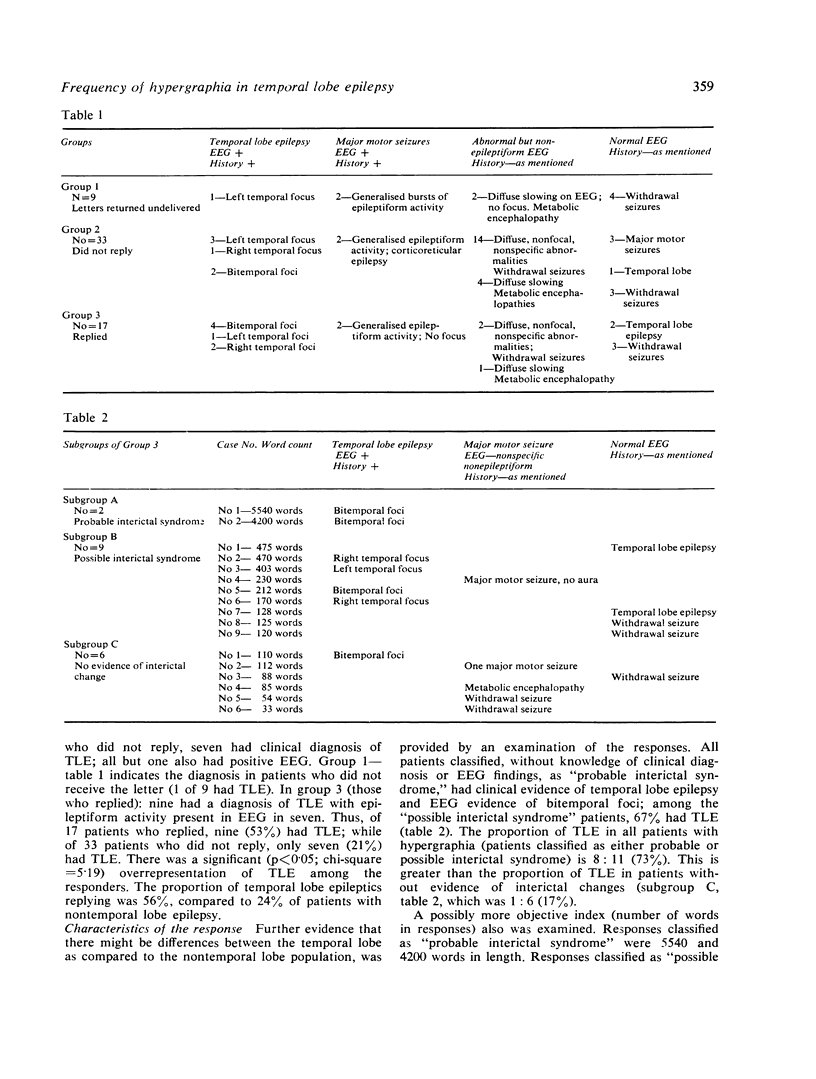
Frequency and degree of hypergraphia were studied in order to assess interictal behaviour change in temporal lobe epilepsy. Patients with temporal lobe epilepsy tended to reply more frequently to a standard questionnaire, and wrote extensively (mean: 1301 words) as compared to others (mean: 106 words). The incidence of temporal lobe epilepsy was 73% in patients exhibiting hypergraphia compared to 17% in patients without this trait. These findings suggest that hypergraphia may be a quantitative index of behaviour change in temporal lobe epilepsy.
Full text
PDF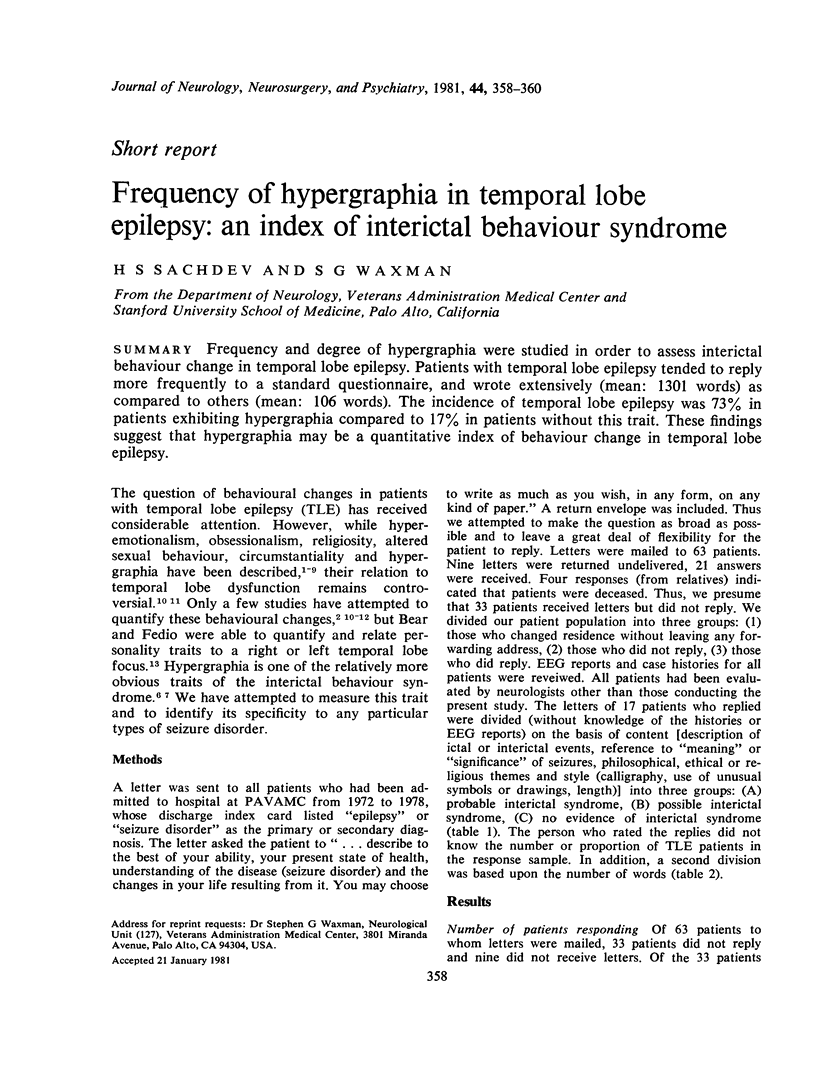

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bear D. M., Fedio P. Quantitative analysis of interictal behavior in temporal lobe epilepsy. Arch Neurol. 1977 Aug;34(8):454–467. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1977.00500200014003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DONGIER S. Statistical study of clinical and electroencephalographic manifestations of 536 psychotic episodes occurring in 516 epileptics between clinical seizures. Epilepsia. 1959 Dec;1:117–142. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1157.1959.tb04255.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIBBS F. A. Ictal and non-ictal psychiatric disorders in temporal lobe epilepsy. J Nerv Ment Dis. 1951 Jun;113(6):522–528. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GLASER G. H. THE PROBLEM OF PSYCHOSIS IN PSYCHOMOTOR TEMPORAL LOBE EPILEPTICS. Epilepsia. 1964 Sep;5:271–278. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1157.1964.tb03333.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geschwind N. Effects of temporal-lobe surgery on behavior. N Engl J Med. 1973 Aug 30;289(9):480–481. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197308302890912. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodin E. A., Katz M., Lennox K. Differences between patients with temporal lobe seizures and those with other forms of epileptic attacks. Epilepsia. 1976 Sep;17(3):313–320. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1157.1976.tb03409.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SLATER E., BEARD A. W., GLITHERO E. The schizophrenialike psychoses of epilepsy. Br J Psychiatry. 1963 Jan;109:95–150. doi: 10.1192/bjp.109.458.95. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Small J. G., Small I. F., Hayden M. P. Further psychiatric investigations of patients with temporal and nontemporal lobe epilepsy. Am J Psychiatry. 1966 Sep;123(3):303–310. doi: 10.1176/ajp.123.3.303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens J. R. Interictal clinical manifestations of complex partial seizures. Adv Neurol. 1975;11:85–112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waxman S. G., Geschwind N. Hypergraphia in temporal lobe epilepsy. Neurology. 1974 Jul;24(7):629–636. doi: 10.1212/wnl.24.7.629. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waxman S. G., Geschwind N. The interictal behavior syndrome of temporal lobe epilepsy. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1975 Dec;32(12):1580–1586. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1975.01760300118011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


