Abstract
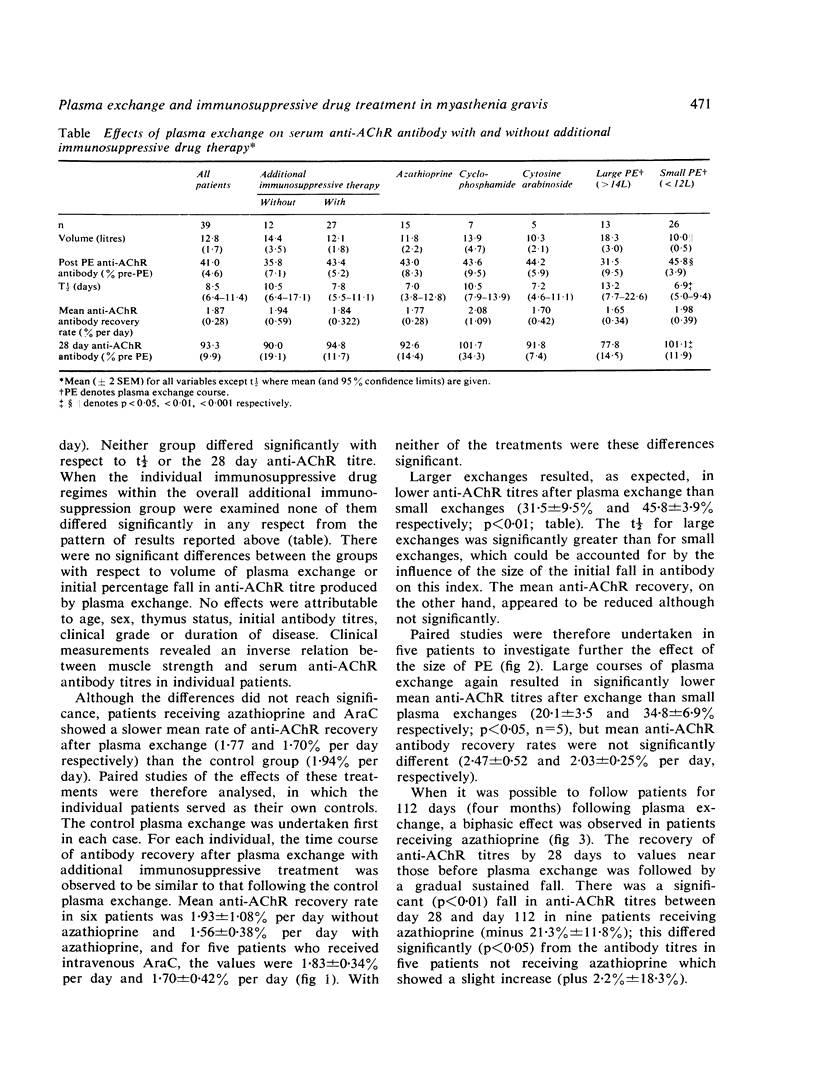
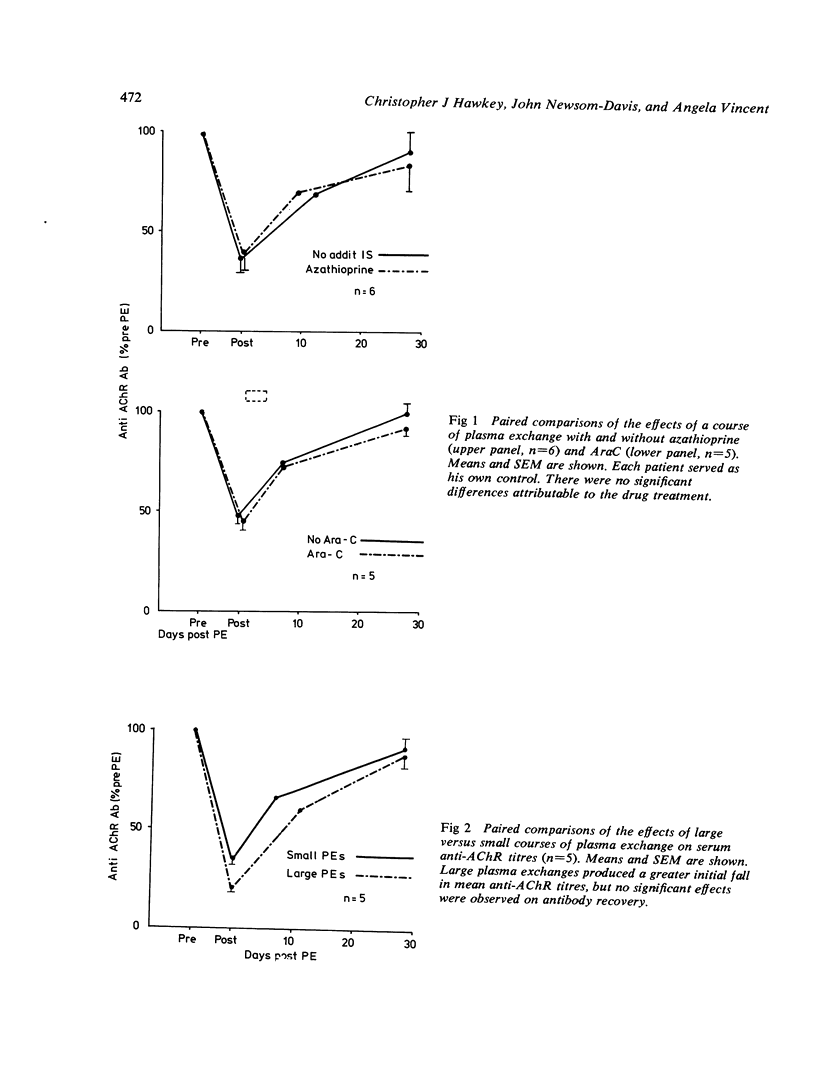
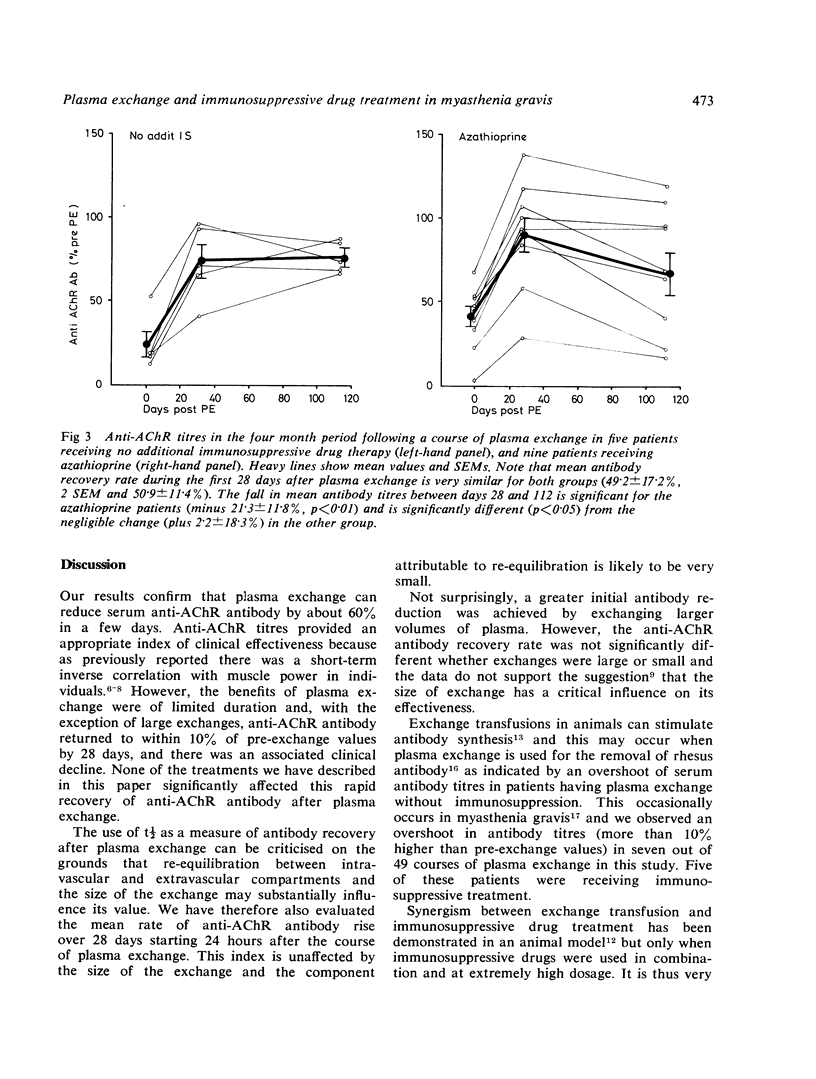
We have investigated whether plasma exchange in myasthenia gravis synergises with additional immunosuppressive drug therapy (azathioprine, cyclophosphamide or cytosine arabinoside). Serum anti-acetylcholine receptor (AChR) antibody titres were followed over 28 days after a course of PE in 20 patients, of whom 17 were taking 20-80 mg prednisone on alternate days. No significant difference was observed in mean anti-AChR antibody recovery following plasma exchange with and without additional immunosuppressive therapy. In paired studies where patients served as their own controls, mean anti-AChR recovery with and without azathioprine or cytosine arabinoside showed no significant differences. Anti-AChR recovery rates after large and small plasma exchange courses also did not differ significantly. Prolonged administration of azathioprine reduced antibody titres independently of plasma exchange. These results fail to demonstrate significant synergy between plasma exchange and the additional immunosuppressive drugs used, and suggest that the effects of plasma exchange were transient.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barclay G. R., Greiss M. A., Urbaniak S. J. Adverse effect of plasma exchange on anti-D production in rhesus immunisation owing to removal of inhibitory factors. Br Med J. 1980 Jun 28;280(6231):1569–1571. doi: 10.1136/bmj.280.6231.1569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behan P. O., Shakir R. A., Simpson J. A., Burnett A. K., Allan T. L., Haase G. Plasma-exchange combined with immunosuppressive therapy in myasthenia gravis. Lancet. 1979 Sep 1;2(8140):438–440. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)91492-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bystryn J. C., Graf M. W., Uhr J. W. Regulation of antibody formation by serum antibody. II. Removal of specific antibody by means of exchange transfusion. J Exp Med. 1970 Dec 1;132(6):1279–1287. doi: 10.1084/jem.132.6.1279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter B., Harrison R., Lunt G. G., Behan P. O., Simpson J. A. Anti-acetylcholine receptor antibody titres in the sera of myasthenia patients treated with plasma exchange combined with immunosuppressive therapy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1980 May;43(5):397–402. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.43.5.397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dau P. C., Lindstrom J. M., Cassel C. K., Denys E. H., Shev E. E., Spitler L. E. Plasmapheresis and immunosuppressive drug therapy in myasthenia gravis. N Engl J Med. 1977 Nov 24;297(21):1134–1140. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197711242972102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engel A. G., Lambert E. H., Howard F. M. Immune complexes (IgG and C3) at the motor end-plate in myasthenia gravis: ultrastructural and light microscopic localization and electrophysiologic correlations. Mayo Clin Proc. 1977 May;52(5):267–280. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fambrough D. M., Drachman D. B., Satyamurti S. Neuromuscular junction in myasthenia gravis: decreased acetylcholine receptors. Science. 1973 Oct 19;182(4109):293–295. doi: 10.1126/science.182.4109.293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito Y., Miledi R., Vincent A., Newsom-Davis J. Acetylcholine receptors and end-plate electrophysiology in myasthenia gravis. Brain. 1978 Jun;101(2):345–368. doi: 10.1093/brain/101.2.345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mertens H. G., Balzereit F., Leipert M. The treatment of severe myasthenia gravis with immunosuppressive agents. Eur Neurol. 1969;2(6):321–339. doi: 10.1159/000113809. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newsom-Davis J., Pinching A. J., Vincent A., Wilson S. G. Function of circulating antibody to acetylcholine receptor in myasthenia gravis: investigation by plasma exchange. Neurology. 1978 Mar;28(3):266–272. doi: 10.1212/wnl.28.3.266. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newsom-Davis J., Wilson S. G., Vincent A., Ward C. D. Long-term effects of repeated plasma exchange in myasthenia gravis. Lancet. 1979 Mar 3;1(8114):464–468. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)90823-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osserman K. E., Genkins G. Studies in myasthenia gravis: review of a twenty-year experience in over 1200 patients. Mt Sinai J Med. 1971 Nov-Dec;38(6):497–537. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinching A. J., Peters D. K. Remission of myasthenia gravis following plasma-exchange. Lancet. 1976 Dec 25;2(8000):1373–1376. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)91917-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturgill B. C., Worzniak M. J. Stimulation of proliferation of 19S antibody-forming cells in the spleens of immunized guinea pigs after exchange transfusion. Nature. 1970 Dec 26;228(5278):1304–1305. doi: 10.1038/2281304a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toyka K. V., Drachman D. B., Griffin D. E., Pestronk A., Winkelstein J. A., Fishbeck K. H., Kao I. Myasthenia gravis. Study of humoral immune mechanisms by passive transfer to mice. N Engl J Med. 1977 Jan 20;296(3):125–131. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197701202960301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


