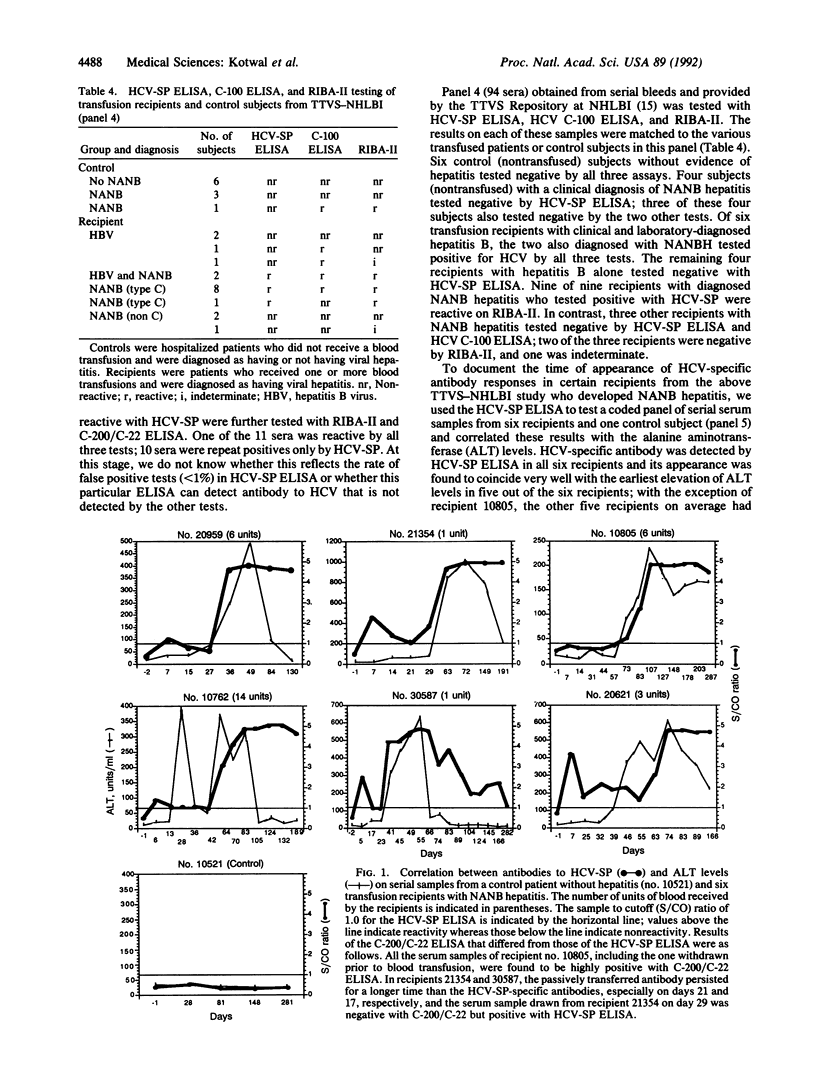
Abstract
An enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) was developed by using a synthetic polypeptide (SP) whose sequence was derived from the structural region of hepatitis C virus (HCV). Results of several coded panels of sera obtained from volunteer blood donors and patients with apparent non-A, non-B hepatitis and/or hepatitis B virus used in this ELISA were compared with those of a commercially available first-generation C-100 ELISA (using nonstructural HCV antigens), an experimental second-generation C-200/C-22 ELISA (using both structural and nonstructural HCV antigens), and recombinant immunoblot assays RIBA-I and RIBA-II. In the majority of cases, the results obtained with the HCV-SP ELISA correlated well with those obtained by RIBA-II and C-200/C-22 ELISA. In contrast, many samples that were repeatedly reactive in the C-100 ELISA results were nonreactive with RIBA and HCV-SP ELISA. In addition, HCV-SP detected HCV-specific antibody that appeared within a month of infection and coincided with the earliest increase in alanine aminotransferase. In summary, we have developed an ELISA based on a structural HCV synthetic polypeptide, HCV-SP, that has high specificity and sensitivity and is capable of detecting specific antibodies in the acute phase of HCV infection.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Choo Q. L., Kuo G., Weiner A. J., Overby L. R., Bradley D. W., Houghton M. Isolation of a cDNA clone derived from a blood-borne non-A, non-B viral hepatitis genome. Science. 1989 Apr 21;244(4902):359–362. doi: 10.1126/science.2523562. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choo Q. L., Weiner A. J., Overby L. R., Kuo G., Houghton M., Bradley D. W. Hepatitis C virus: the major causative agent of viral non-A, non-B hepatitis. Br Med Bull. 1990 Apr;46(2):423–441. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a072408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotton P. Tests help nail down HCV--but not entirely. JAMA. 1991 Jan 16;265(3):312–312. doi: 10.1001/jama.265.3.312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebeling F., Naukkarinen R., Leikola J. Recombinant immunoblot assay for hepatitis C virus antibody as predictor of infectivity. Lancet. 1990 Apr 21;335(8695):982–983. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)91055-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garson J. A., Tedder R. S., Briggs M., Tuke P., Glazebrook J. A., Trute A., Parker D., Barbara J. A., Contreras M., Aloysius S. Detection of hepatitis C viral sequences in blood donations by "nested" polymerase chain reaction and prediction of infectivity. Lancet. 1990 Jun 16;335(8703):1419–1422. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)91446-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hosein B., Fang C. T., Popovsky M. A., Ye J., Zhang M., Wang C. Y. Improved serodiagnosis of hepatitis C virus infection with synthetic peptide antigen from capsid protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 1;88(9):3647–3651. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.9.3647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kubo Y., Takeuchi K., Boonmar S., Katayama T., Choo Q. L., Kuo G., Weiner A. J., Bradley D. W., Houghton M., Saito I. A cDNA fragment of hepatitis C virus isolated from an implicated donor of post-transfusion non-A, non-B hepatitis in Japan. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Dec 25;17(24):10367–10372. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.24.10367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo G., Choo Q. L., Alter H. J., Gitnick G. L., Redeker A. G., Purcell R. H., Miyamura T., Dienstag J. L., Alter M. J., Stevens C. E. An assay for circulating antibodies to a major etiologic virus of human non-A, non-B hepatitis. Science. 1989 Apr 21;244(4902):362–364. doi: 10.1126/science.2496467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto H., Munekata E., Tsuda F., Takahashi K., Yotsumoto S., Tanaka T., Tachibana K., Akahane Y., Sugai Y., Miyakawa Y. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for antibodies against the capsid protein of hepatitis C virus with a synthetic oligopeptide. Jpn J Exp Med. 1990 Aug;60(4):223–233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto H., Okada S., Sugiyama Y., Yotsumoto S., Tanaka T., Yoshizawa H., Tsuda F., Miyakawa Y., Mayumi M. The 5'-terminal sequence of the hepatitis C virus genome. Jpn J Exp Med. 1990 Jun;60(3):167–177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto H., Tsuda F., Machida A., Munekata E., Akahane Y., Sugai Y., Mashiko K., Mitsui T., Tanaka T., Miyakawa Y. Antibodies against synthetic oligopeptides deduced from the putative core gene for the diagnosis of hepatitis virus infection. Hepatology. 1992 Feb;15(2):180–186. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840150203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulrich P. P., Romeo J. M., Lane P. K., Kelly I., Daniel L. J., Vyas G. N. Detection, semiquantitation, and genetic variation in hepatitis C virus sequences amplified from the plasma of blood donors with elevated alanine aminotransferase. J Clin Invest. 1990 Nov;86(5):1609–1614. doi: 10.1172/JCI114882. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van der Poel C. L., Cuypers H. T., Reesink H. W., Weiner A. J., Quan S., Di Nello R., Van Boven J. J., Winkel I., Mulder-Folkerts D., Exel-Oehlers P. J. Confirmation of hepatitis C virus infection by new four-antigen recombinant immunoblot assay. Lancet. 1991 Feb 9;337(8737):317–319. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)90942-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner A. J., Kuo G., Bradley D. W., Bonino F., Saracco G., Lee C., Rosenblatt J., Choo Q. L., Houghton M. Detection of hepatitis C viral sequences in non-A, non-B hepatitis. Lancet. 1990 Jan 6;335(8680):1–3. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)90134-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuck T. F., Rose G. A., Dumaswala U. J., Geer N. J. Experience with a transfusion recipient education program about hepatitis C. Transfusion. 1990 Oct;30(8):759–761. doi: 10.1046/j.1537-2995.1990.30891020339.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Poel C. L., Reesink H. W., Schaasberg W., Leentvaar-Kuypers A., Bakker E., Exel-Oehlers P. J., Lelie P. N. Infectivity of blood seropositive for hepatitis C virus antibodies. Lancet. 1990 Mar 10;335(8689):558–560. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)90347-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


