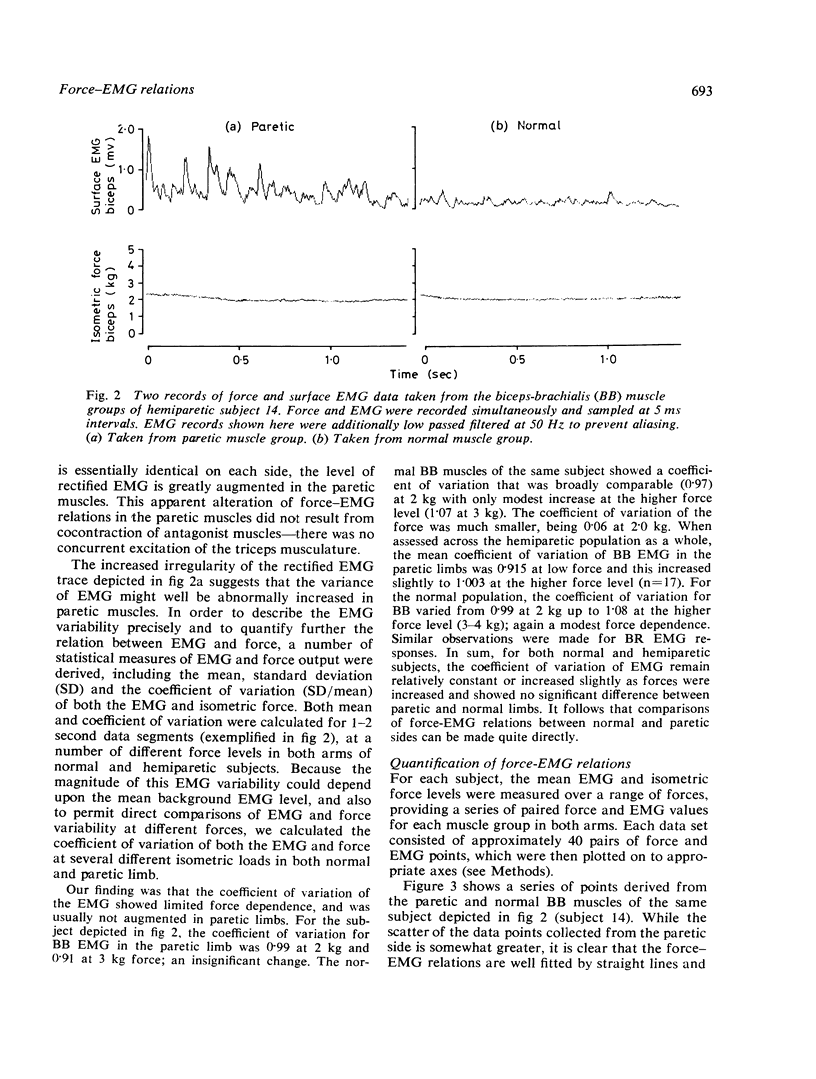
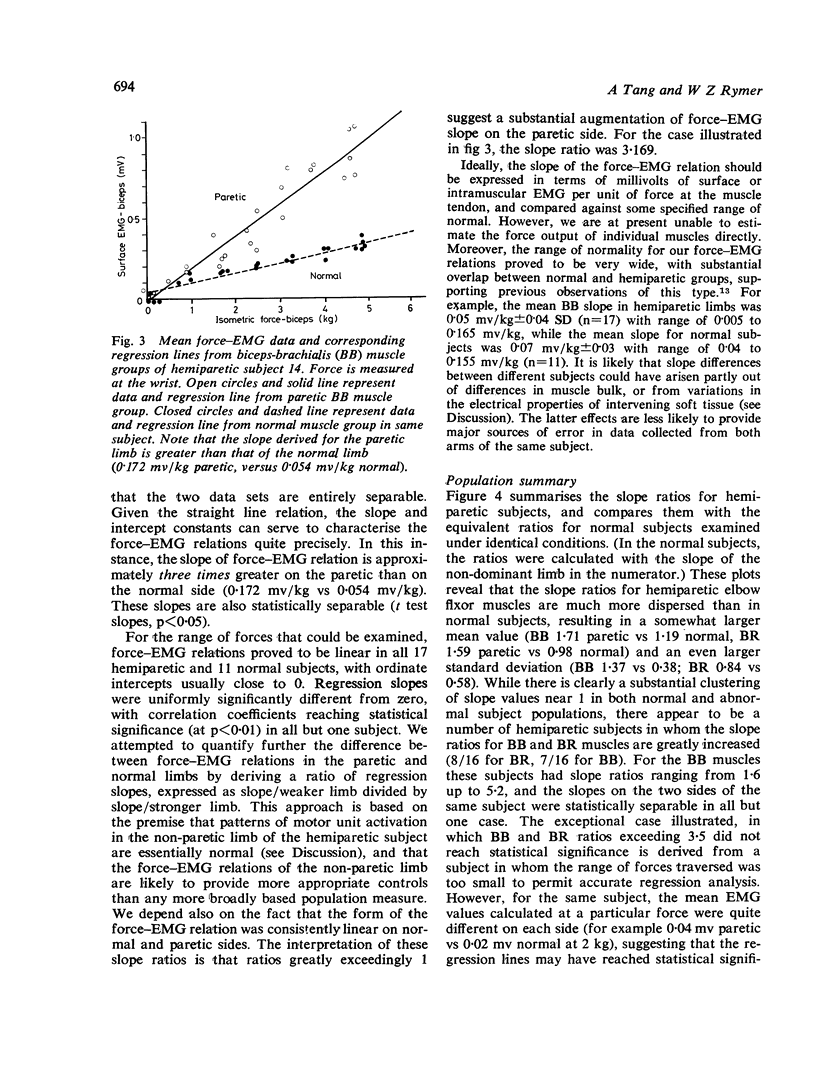
Abstract
The relations between surface EMG and isometric force generated by elbow flexor muscles were compared in normal and paretic limbs of 17 hemiparetic human subjects. Similar analyses were performed on both arms of 11 normal subjects. In almost half of the hemiparetic subjects examined (8/17), the slope of the relation between elbow flexion force and surface EMG, measured over the biceps-brachialis and brachioradialis muscle groups was increased in the paretic limb. A mechanism based on anomalous reductions in mean motor unit discharge rate in paretic muscles is advanced as the most likely cause of the findings.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alpert S., Jarrett S., Lerner I. M., Rosenthal A. M. Electromyographic findings in early hemiplegia. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1973 Oct;54(10):464–465. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke D., Knowles L., Andrews C., Ashby P. Spasticity, decerebrate rigidity and the clasp-knife phenomenon: an experimental study in the cat. Brain. 1972;95(1):31–48. doi: 10.1093/brain/95.1.31. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Luca C. J., Forrest W. J. Some properties of motor unit action potential trains recorded during constant force isometric contractions in man. Kybernetik. 1973 Mar;12(3):160–168. doi: 10.1007/BF00289169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietz V., Hillesheimer W., Freund H. J. Correlation between tremor, voluntary contraction, and firing pattern of motor units in Parkinson's disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1974 Aug;37(8):927–937. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.37.8.927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gandevia S. C., McCloskey D. I. Sensations of heaviness. Brain. 1977 Jun;100(2):345–354. doi: 10.1093/brain/100.2.345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadefors R., Kaiser E., Petersén I. Dynamic spectrum analysis of myo-potentials and with special reference to muscle fatigue. Electromyography. 1968 Jan-Apr;8(1):39–74. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindstrom L., Magnusson R., Petersén I. Muscular fatigue and action potential conduction velocity changes studied with frequency analysis of EMG signals. Electromyography. 1970 Nov-Dec;10(4):341–356. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milner-Brown H. S., Stein R. B. The relation between the surface electromyogram and muscular force. J Physiol. 1975 Apr;246(3):549–569. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010904. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rack P. M., Westbury D. R. The effects of length and stimulus rate on tension in the isometric cat soleus muscle. J Physiol. 1969 Oct;204(2):443–460. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008923. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfalck A., Andreassen S. Impaired regulation of force and firing pattern of single motor units in patients with spasticity. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1980 Oct;43(10):907–916. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.43.10.907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rymer W. Z., Houk J. C., Crago P. E. Mechanisms of the clasp-knife reflex studied in an animal model. Exp Brain Res. 1979 Sep;37(1):93–113. doi: 10.1007/BF01474257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


