Abstract
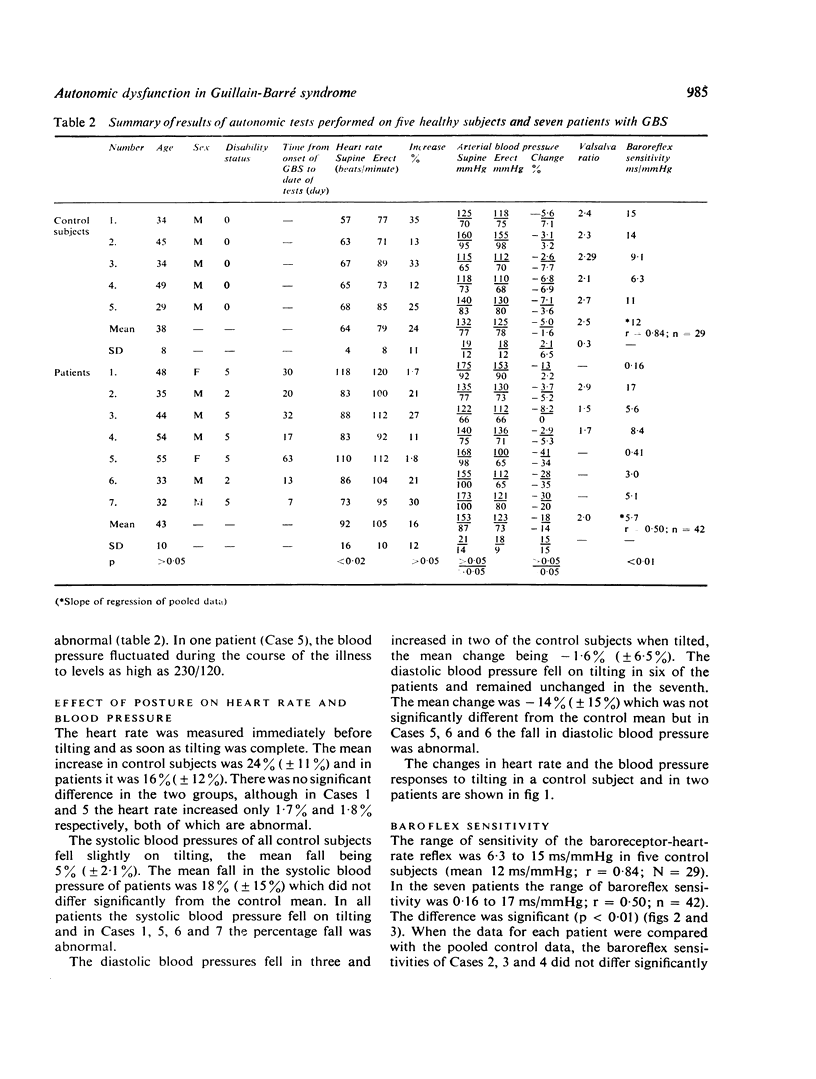
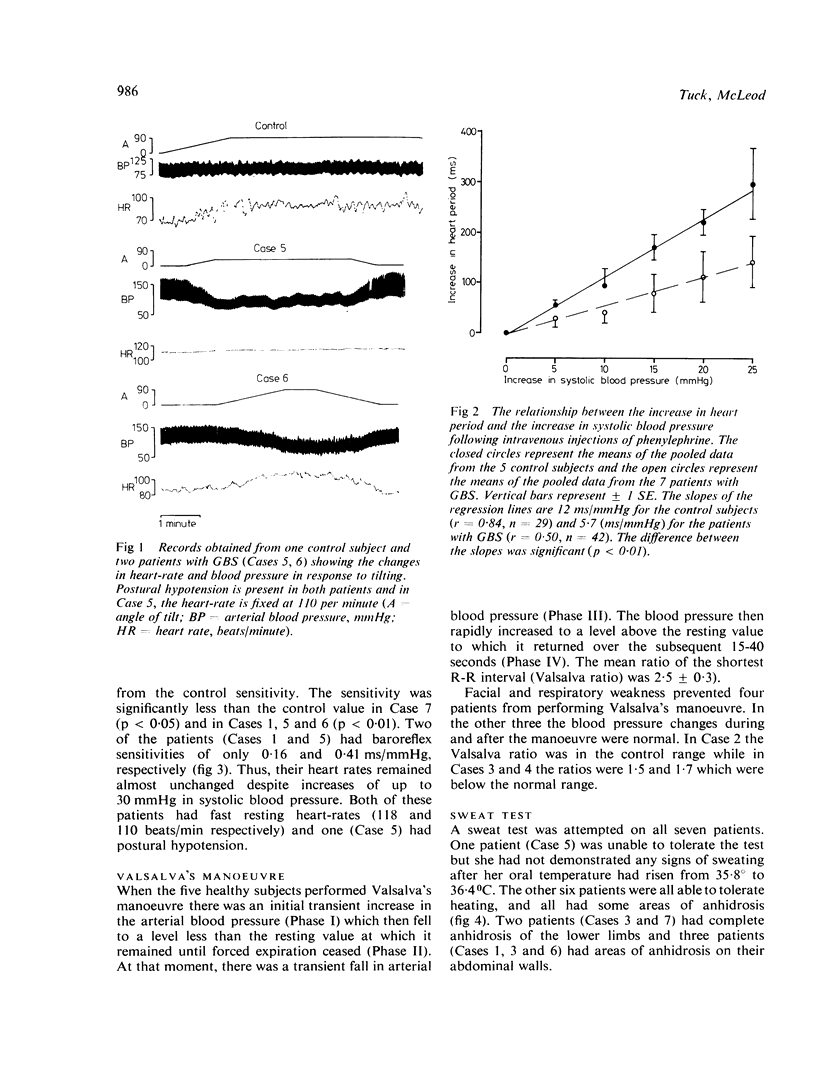
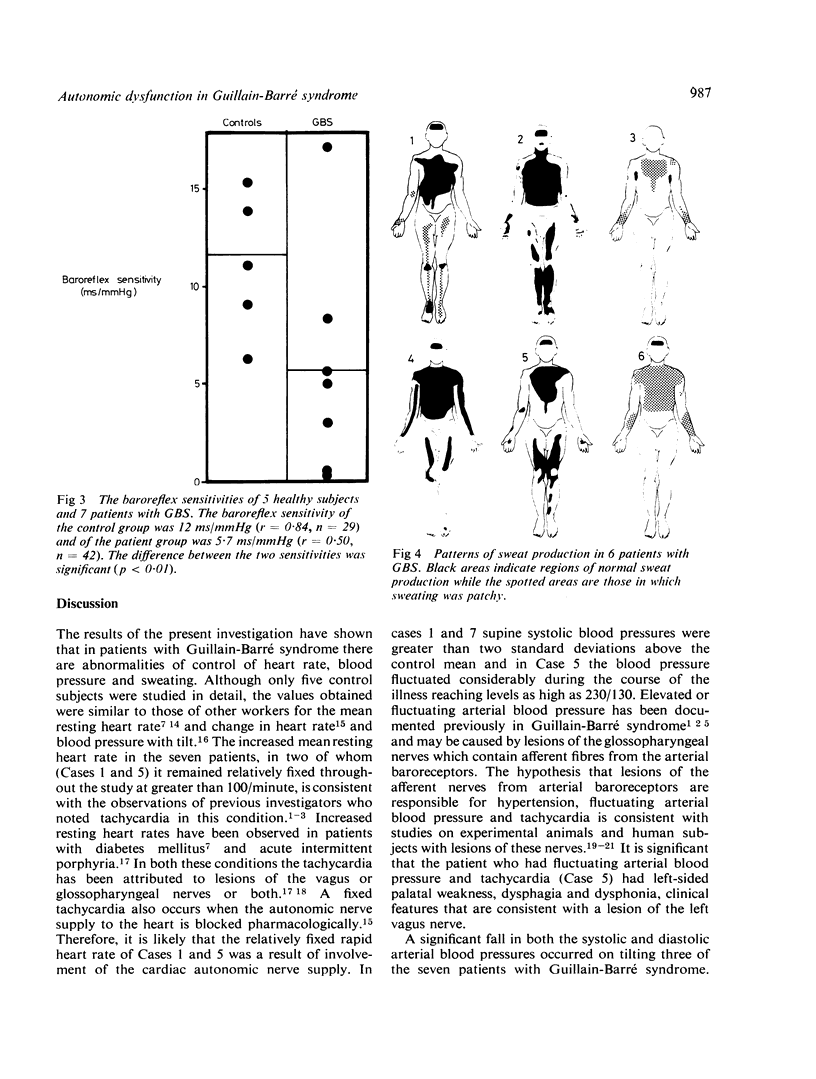
The following tests of autonomic function were performed on seven patients with the Guillain-Barré syndrome and compared with controls: (1) measurement of heart rate and blood pressure in the supine and erect positions, (2) measurement of baroreflex sensitivity, (3) Valsalva's manoeuvre, (4) sweat test. In two patients the heart rates were fixed and greater than 100/min and in three there was postural hypotension. The baroflex sensitivity of four patients was abnormal and heart rate response to Valsalva's manoeuvre was impaired in two of the three patients who were able to perform the manoeuvre. Areas of anhidrosis were found in all seven patients. These abnormalities probably reflect pathological alterations of the sympathetic and parasympathetic components of the autonomic nervous system of patients with Guillain-Barré syndrome. The severity of autonomic involvement is not related to the degree of sensory and motor disturbance which is consistent with the patchy distribution of lesions throughout the peripheral and autonomic nervous systems.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- APPENZELLER O., MARSHALL J. VASOMOTOR DISTURBANCE IN LANDRY-GUILLIAN-BARR'E SYNDROME. Arch Neurol. 1963 Oct;9:368–372. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1963.00460100056006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asbury A. K., Arnason B. G., Adams R. D. The inflammatory lesion in idiopathic polyneuritis. Its role in pathogenesis. Medicine (Baltimore) 1969 May;48(3):173–215. doi: 10.1097/00005792-196905000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARRACLOUGH M. A., SHARPEY-SCHAFER E. P. Hypotension from absent circulatory reflexes. Effects of alcohol, barbiturates, psychotherapeutic drugs, and other mechanisms. Lancet. 1963 May 25;1(7291):1121–1126. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(63)91799-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BIRCHFIELD R. I., SHAW C. M. POSTURAL HYPOTENSION IN THE GUILLAIN-BARR'E SYNDROME. Arch Neurol. 1964 Feb;10:149–157. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1964.00460140035006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett T., Hosking D. J., Hampton J. R. Baroreflex sensitivity and responses to the Valsalva manoeuvre in subjects with diabetes mellitus. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1976 Feb;39(2):178–183. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.39.2.178. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bredin C. P. Guillain-Barré syndrome: the unsolved cardiovascular problems. Ir J Med Sci. 1977 Sep;146(9):273–279. doi: 10.1007/BF03030974. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke D., Sundlöf G., Wallin G. Postural effects on muscle nerve sympathetic activity in man. J Physiol. 1977 Nov;272(2):399–414. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp012051. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson D. L., Jellinek E. H. Hypertension and papilloedema in the Guillain-Barré syndrome. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1977 Feb;40(2):144–148. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.40.2.144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guz A., Noble M. I., Widdicombe J. G., Trenchard D., Mushin W. W., Makey A. R. The role of vagal and glossopharyngeal afferent nerves in respiratory sensation, control of breathing and arterial pressure regulation in conscious man. Clin Sci. 1966 Feb;30(1):161–170. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirchheim H. R. Systemic arterial baroreceptor reflexes. Physiol Rev. 1976 Jan;56(1):100–177. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1976.56.1.100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korner P. I., West M. J., Shaw J., Uther J. B. "Steady-state" properties of the baroreceptor-heart rate reflex in essential hypertension in man. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 1974 Jan-Feb;1(1):65–76. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1681.1974.tb00528.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin A. B. A simple test of cardiac function based upon the heart rate changes induced by the Valsalva maneuver. Am J Cardiol. 1966 Jul;18(1):90–99. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(66)90200-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichtenfeld P. Autonomic dysfunction in the Guillain-Barré syndrome. Am J Med. 1971 Jun;50(6):772–780. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(71)90185-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low P. A., Walsh J. C., Huang C. Y., McLeod J. G. The sympathetic nervous system in alcoholic neuropathy. A clinical and pathological study. Brain. 1975 Sep;98(3):357–364. doi: 10.1093/brain/98.3.357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low P. A., Walsh J. C., Huang C. Y., McLeod J. G. The sympathetic nervous system in diabetic neuropathy. A clinical and pathological study. Brain. 1975 Sep;98(3):341–356. doi: 10.1093/brain/98.3.341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuyama H., Haymaker W. Distribution of lesions in the Landry-Guillain-Barré syndrome, with emphasis on involvement of the sympathetic system. Acta Neuropathol. 1967 May 5;8(3):230–241. doi: 10.1007/BF00688825. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Page M. M., Watkins P. J. Cardiorespiratory arrest and diabetic autonomic neuropathy. Lancet. 1978 Jan 7;1(8054):14–16. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)90360-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perel A., Reches A., Davidson J. T. Anaesthesia in the Guillian-Barré syndrome. A case report and recommendations. Anaesthesia. 1977 Mar;32(3):257–260. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2044.1977.tb11604.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridley A., Hierons R., Cavanagh J. B. Tachycardia and the neuropathy of porphyria. Lancet. 1968 Sep 28;2(7570):708–710. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(68)90751-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ripley R. C., Hollifield J. W., Nies A. S. Sustained hypertension after section of the glossopharyngeal nerve. Am J Med. 1977 Feb;62(2):297–302. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(77)90326-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson B. F., Epstein S. E., Beiser G. D., Braunwald E. Control of heart rate by the autonomic nervous system. Studies in man on the interrelation between baroreceptor mechanisms and exercise. Circ Res. 1966 Aug;19(2):400–411. doi: 10.1161/01.res.19.2.400. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowell L. B., Detry J. M., Blackmon J. R., Wyss C. Importance of the splanchnic vascular bed in human blood pressure regulation. J Appl Physiol. 1972 Feb;32(2):213–220. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1972.32.2.213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepherd J. T. Role of the veins in the circulation. Circulation. 1966 Mar;33(3):484–491. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.33.3.484. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smyth H. S., Sleight P., Pickering G. W. Reflex regulation of arterial pressure during sleep in man. A quantitative method of assessing baroreflex sensitivity. Circ Res. 1969 Jan;24(1):109–121. doi: 10.1161/01.res.24.1.109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart P. M., Hensley W. J. An acute attack of variegate porphyria complicated by severe autonomic neuropathy. Aust N Z J Med. 1981 Feb;11(1):82–83. doi: 10.1111/j.1445-5994.1981.tb03745.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuck R. R., McLeod J. G. Autonomic dysfunction in the Landry-Guillain-Barre syndrome. Clin Exp Neurol. 1978;15:197–203. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WATSON W. E. Some circulatory responses to Valsalva's manoeuvre in patients with polyneuritis and spinal cord disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1962 Feb;25:19–23. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.25.1.19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WATSON W. E. Venous distensibility of the hand during Valsalva's manoeuvre. Br Heart J. 1962 Jan;24:26–30. doi: 10.1136/hrt.24.1.26. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheeler T., Watkins P. J. Cardiac denervation in diabetes. Br Med J. 1973 Dec 8;4(5892):584–586. doi: 10.1136/bmj.4.5892.584. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


