Abstract
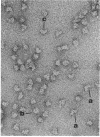
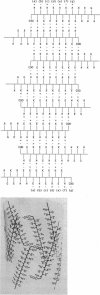
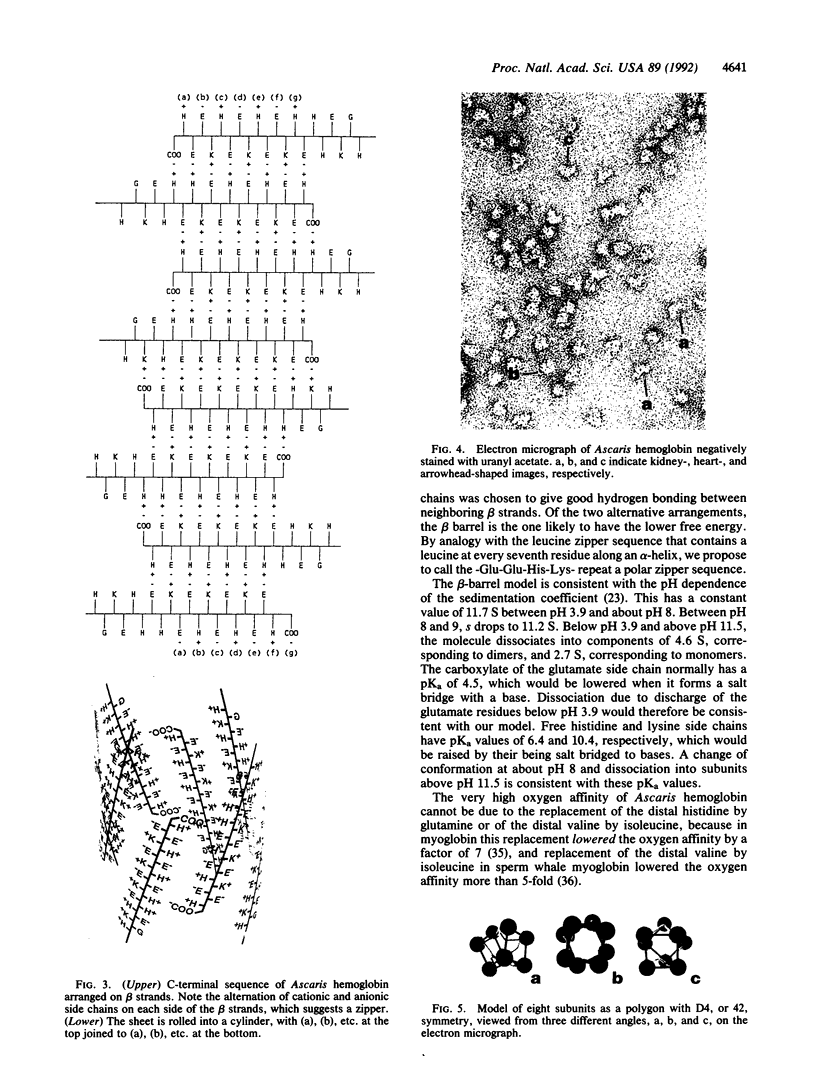
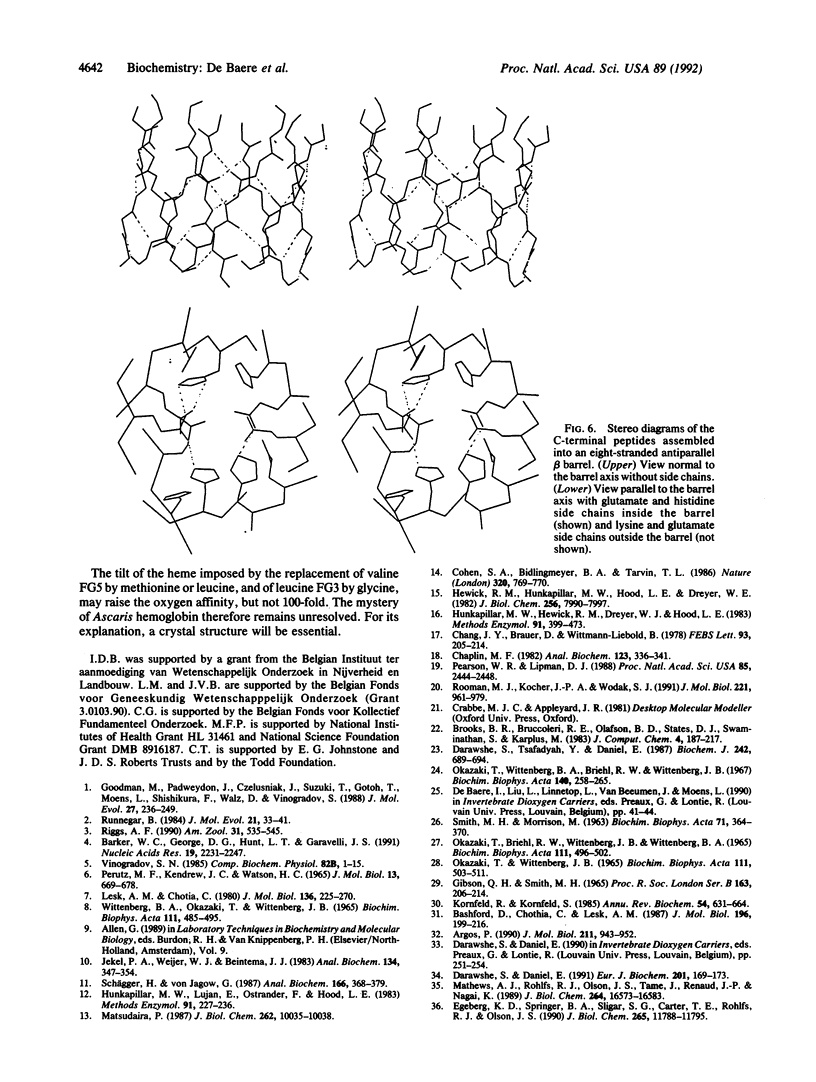
The extracellular hemoglobin of Ascaris has an extremely high oxygen affinity (P50 = 0.004 mmHg). It consists of eight identical subunits of molecular weight 40,600. Their sequence, determined by protein chemistry, shows two tandemly linked globin-like sequences and an 18-residue C-terminal extension. Two N-linked glycosylation sites contain equal ratios of mannose/glucosamine/fucose of 3:2:1. Electron micrographs suggest that the eight subunits form a polyhedron of point symmetry D4, or 42. The C-terminal extension contains a repeat of the sequence Glu-Glu-His-Lys, which would form a pattern of alternate glutamate and histidine side chains on one side and of glutamate and lysine side chains on the other side of a beta strand. We propose that this represents a polar zipper sequence and that the C-terminal extensions are joined in an eight-stranded beta barrel at the center of the molecule, with histidine and glutamate side chains inside and lysine and glutamate side chains outside the barrel compensating each other's charges. The amino acid sequence of Ascaris hemoglobin fails to explain its high oxygen affinity.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Argos P. An investigation of oligopeptides linking domains in protein tertiary structures and possible candidates for general gene fusion. J Mol Biol. 1990 Feb 20;211(4):943–958. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90085-Z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker W. C., George D. G., Hunt L. T., Garavelli J. S. The PIR protein sequence database. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Apr 25;19 (Suppl):2231–2236. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.suppl.2231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bashford D., Chothia C., Lesk A. M. Determinants of a protein fold. Unique features of the globin amino acid sequences. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jul 5;196(1):199–216. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90521-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaplin M. F. A rapid and sensitive method for the analysis of carbohydrate components in glycoproteins using gas-liquid chromatography. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jul 1;123(2):336–341. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90455-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S. A., Bidlingmeyer B. A., Tarvin T. L. PITC derivatives in amino acid analysis. Nature. 1986 Apr 24;320(6064):769–770. doi: 10.1038/320769a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darawshe S., Daniel E. Molecular symmetry and arrangement of subunits in extracellular hemoglobin from the nematode Ascaris suum. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Oct 1;201(1):169–173. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb16270.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darawshe S., Tsafadyah Y., Daniel E. Quaternary structure of erythrocruorin from the nematode Ascaris suum. Evidence for unsaturated haem-binding sites. Biochem J. 1987 Mar 15;242(3):689–694. doi: 10.1042/bj2420689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egeberg K. D., Springer B. A., Sligar S. G., Carver T. E., Rohlfs R. J., Olson J. S. The role of Val68(E11) in ligand binding to sperm whale myoglobin. Site-directed mutagenesis of a synthetic gene. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 15;265(20):11788–11795. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson Q. H., Smith M. H. Rates of reaction of Ascaris haemoglobins with ligands. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1965 Oct 12;163(991):206–214. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1965.0067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman M., Pedwaydon J., Czelusniak J., Suzuki T., Gotoh T., Moens L., Shishikura F., Walz D., Vinogradov S. An evolutionary tree for invertebrate globin sequences. J Mol Evol. 1988;27(3):236–249. doi: 10.1007/BF02100080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hewick R. M., Hunkapiller M. W., Hood L. E., Dreyer W. J. A gas-liquid solid phase peptide and protein sequenator. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 10;256(15):7990–7997. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunkapiller M. W., Hewick R. M., Dreyer W. J., Hood L. E. High-sensitivity sequencing with a gas-phase sequenator. Methods Enzymol. 1983;91:399–413. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)91038-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunkapiller M. W., Lujan E., Ostrander F., Hood L. E. Isolation of microgram quantities of proteins from polyacrylamide gels for amino acid sequence analysis. Methods Enzymol. 1983;91:227–236. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)91019-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jekel P. A., Weijer W. J., Beintema J. J. Use of endoproteinase Lys-C from Lysobacter enzymogenes in protein sequence analysis. Anal Biochem. 1983 Oct 15;134(2):347–354. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90308-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornfeld R., Kornfeld S. Assembly of asparagine-linked oligosaccharides. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:631–664. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.003215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lesk A. M., Chothia C. How different amino acid sequences determine similar protein structures: the structure and evolutionary dynamics of the globins. J Mol Biol. 1980 Jan 25;136(3):225–270. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90373-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathews A. J., Rohlfs R. J., Olson J. S., Tame J., Renaud J. P., Nagai K. The effects of E7 and E11 mutations on the kinetics of ligand binding to R state human hemoglobin. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 5;264(28):16573–16583. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsudaira P. Sequence from picomole quantities of proteins electroblotted onto polyvinylidene difluoride membranes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 25;262(21):10035–10038. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okazaki T., Briehl R. W., Wittenberg J. B., Wittenberg B. A. The hemoglobin of Ascaris perienteric fluid. II. Molecular weight and subunits. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Dec 16;111(2):496–502. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(65)90059-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okazaki T., Wittenberg B. A., Briehl R. W., Wittenberg J. B. The hemoglobin of Ascaris body walls. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Jun 27;140(2):258–265. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(67)90466-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okazaki T., Wittenberg J. B. The hemoglobin of Ascaris perienteric fluid. 3. Equilibria with oxygen and carbon monoxide. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Dec 16;111(2):503–511. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(65)90060-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson W. R., Lipman D. J. Improved tools for biological sequence comparison. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2444–2448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rooman M. J., Kocher J. P., Wodak S. J. Prediction of protein backbone conformation based on seven structure assignments. Influence of local interactions. J Mol Biol. 1991 Oct 5;221(3):961–979. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)80186-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Runnegar B. Derivation of the globins from type b cytochromes. J Mol Evol. 1984;21(1):33–41. doi: 10.1007/BF02100625. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH M. H., MORRISON M. Isolation of Ascaris haemoglobins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 May 14;71:364–370. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schägger H., von Jagow G. Tricine-sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis for the separation of proteins in the range from 1 to 100 kDa. Anal Biochem. 1987 Nov 1;166(2):368–379. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90587-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vinogradov S. N. The structure of invertebrate extracellular hemoglobins (erythrocruorins and chlorocruorins). Comp Biochem Physiol B. 1985;82(1):1–15. doi: 10.1016/0305-0491(85)90120-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wittenberg B. A., Okazaki T., Wittenberg J. B. The hemoglobin of Ascaris perienteric fluid. I. Purification and spectra. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Dec 16;111(2):485–495. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(65)90058-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]