Abstract
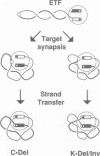
Tn10 transposition is accomplished without extensive replication of the transposon sequences. Replicative cointegrate formation is precluded by efficient separation of transposon sequences from flanking donor DNA at an early stage in the transposition reaction. We report here that excision of Tn10 from its donor site occurs by a pair of flush double-strand breaks. Breaks occur at each end of the element precisely between the terminal base pair of the element and the first base pair of flanking DNA. This observation provides definitive evidence that cleavage of both strands of the element occurs under the direct control of Tn10 transposase protein. It is highly likely that transposase itself is directly responsible for these cleavages. The implications of this possibility are discussed.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bainton R., Gamas P., Craig N. L. Tn7 transposition in vitro proceeds through an excised transposon intermediate generated by staggered breaks in DNA. Cell. 1991 May 31;65(5):805–816. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90388-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bender J., Kleckner N. Genetic evidence that Tn10 transposes by a nonreplicative mechanism. Cell. 1986 Jun 20;45(6):801–815. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90555-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benjamin H. W., Kleckner N. Intramolecular transposition by Tn10. Cell. 1989 Oct 20;59(2):373–383. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90298-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown P. O., Bowerman B., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M. Retroviral integration: structure of the initial covalent product and its precursor, and a role for the viral IN protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2525–2529. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bushman F. D., Fujiwara T., Craigie R. Retroviral DNA integration directed by HIV integration protein in vitro. Science. 1990 Sep 28;249(4976):1555–1558. doi: 10.1126/science.2171144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caparon M. G., Scott J. R. Excision and insertion of the conjugative transposon Tn916 involves a novel recombination mechanism. Cell. 1989 Dec 22;59(6):1027–1034. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90759-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cozzarelli N. R., Krasnow M. A., Gerrard S. P., White J. H. A topological treatment of recombination and topoisomerases. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1984;49:383–400. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1984.049.01.045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craigie R., Mizuuchi K. Mechanism of transposition of bacteriophage Mu: structure of a transposition intermediate. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):867–876. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80067-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujiwara T., Mizuuchi K. Retroviral DNA integration: structure of an integration intermediate. Cell. 1988 Aug 12;54(4):497–504. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90071-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haniford D. B., Benjamin H. W., Kleckner N. Kinetic and structural analysis of a cleaved donor intermediate and a strand transfer intermediate in Tn10 transposition. Cell. 1991 Jan 11;64(1):171–179. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90218-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haniford D. B., Chelouche A. R., Kleckner N. A specific class of IS10 transposase mutants are blocked for target site interactions and promote formation of an excised transposon fragment. Cell. 1989 Oct 20;59(2):385–394. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90299-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katzman M., Katz R. A., Skalka A. M., Leis J. The avian retroviral integration protein cleaves the terminal sequences of linear viral DNA at the in vivo sites of integration. J Virol. 1989 Dec;63(12):5319–5327. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.12.5319-5327.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuuchi K., Craigie R. Mechanism of bacteriophage mu transposition. Annu Rev Genet. 1986;20:385–429. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.20.120186.002125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuuchi K. Mechanism of transposition of bacteriophage Mu: polarity of the strand transfer reaction at the initiation of transposition. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(2 Pt 1):395–404. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90018-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morisato D., Kleckner N. Tn10 transposition and circle formation in vitro. Cell. 1987 Oct 9;51(1):101–111. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90014-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash H. A., Robertson C. A., Flamm E., Weisberg R. A., Miller H. I. Overproduction of Escherichia coli integration host factor, a protein with nonidentical subunits. J Bacteriol. 1987 Sep;169(9):4124–4127. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.9.4124-4127.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Rosenberg A. H., Dunn J. J., Dubendorff J. W. Use of T7 RNA polymerase to direct expression of cloned genes. Methods Enzymol. 1990;185:60–89. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)85008-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugisaki H., Kita K., Takanami M. The FokI restriction-modification system. II. Presence of two domains in FokI methylase responsible for modification of different DNA strands. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 5;264(10):5757–5761. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tullius T. D., Dombroski B. A. Hydroxyl radical "footprinting": high-resolution information about DNA-protein contacts and application to lambda repressor and Cro protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(15):5469–5473. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.15.5469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]