Abstract
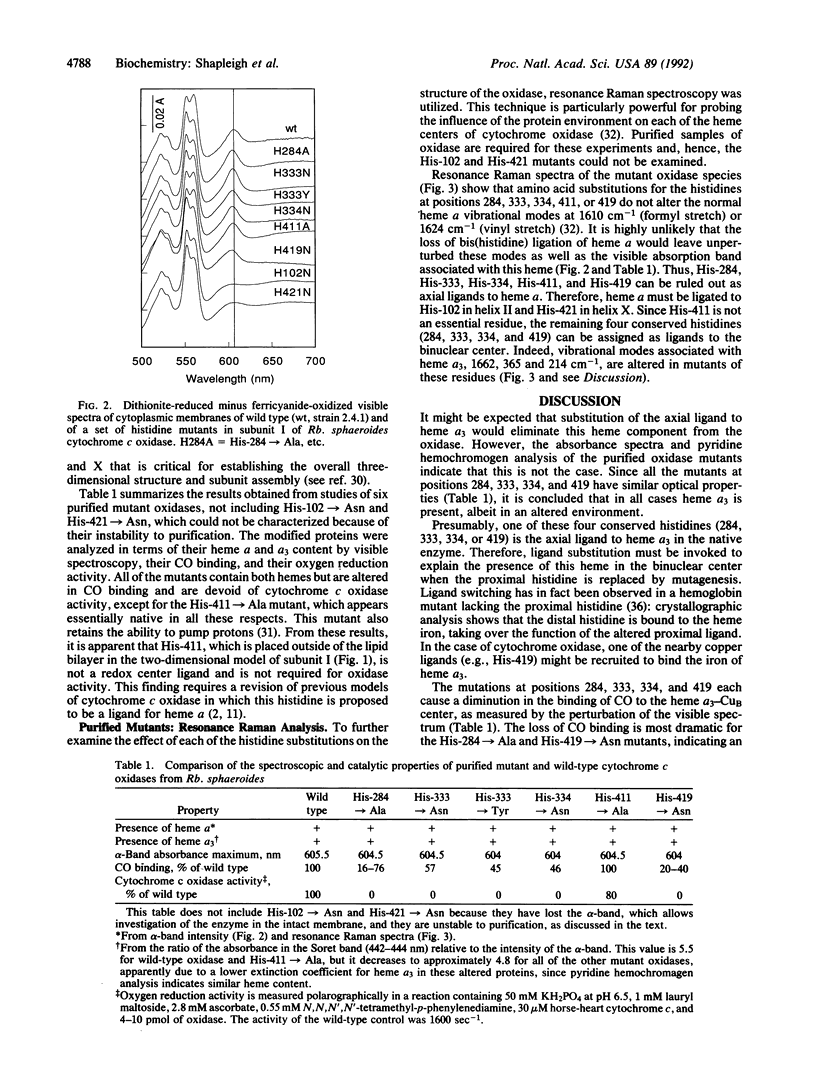
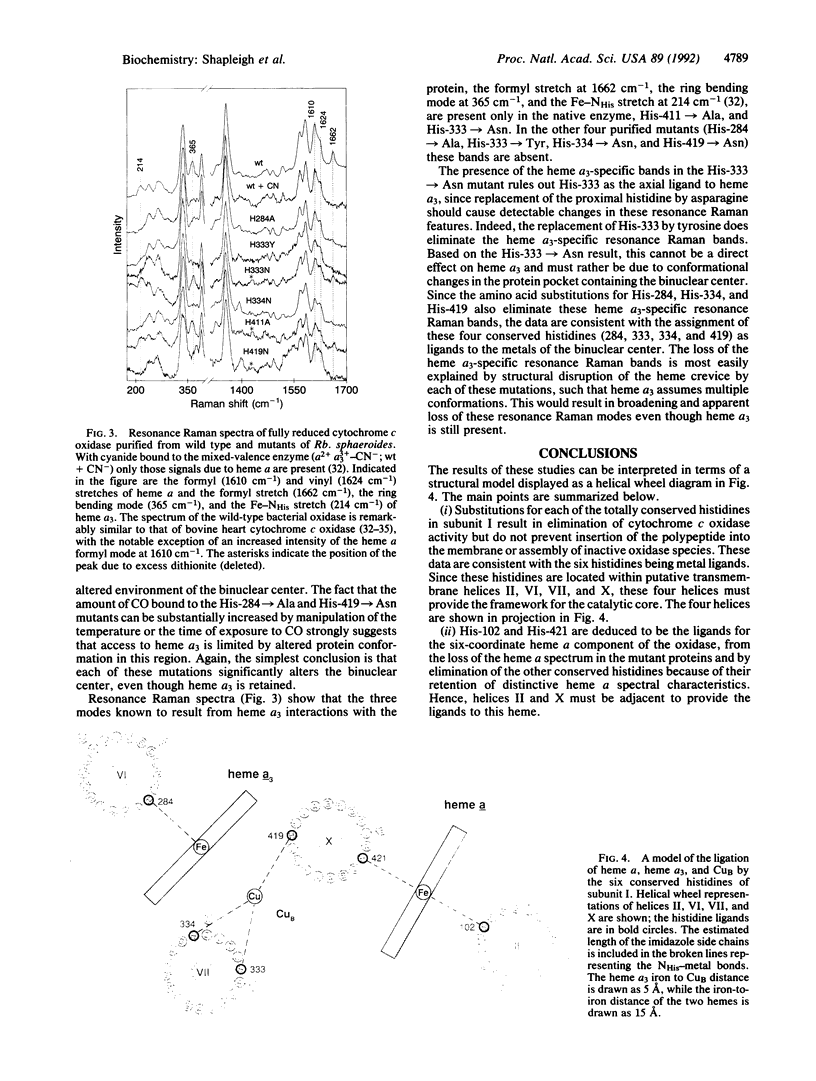
The three-subunit aa3-type cytochrome c oxidase (EC 1.9.3.1) of Rhodobacter sphaeroides is structurally and functionally homologous to the more complex mitochondrial oxidase. The largest subunit, subunit I, is highly conserved and predicted to contain 12 transmembrane segments that provide all the ligands for three of the four metal centers: heme a, heme a3, and CuB. A variety of spectroscopic techniques identify these ligands as histidines. We have used site-directed mutagenesis to change all the conserved histidines within subunit I of cytochrome c oxidase from Rb. sphaeroides. Analysis of the membrane-bound and purified mutant proteins by optical absorption and resonance Raman spectroscopy indicates that His-102 and His-421 are the ligands of heme a, while His-284, His-333, His-334, and His-419 ligate the heme a3-CuB center. To satisfy this ligation assignment, helices II, VI, VII, and X, which contain these histidine residues, must be in close proximity. These data provide empirical evidence regarding the three-dimensional protein structure at the catalytic core of cytochrome c oxidase.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Babcock G. T., Callahan P. M., Ondrias M. R., Salmeen I. Coordination geometries and vibrational properties of cytochromes alpha and alpha 3 in cytochrome oxidase from Soret excitation Raman spectroscopy. Biochemistry. 1981 Feb 17;20(4):959–966. doi: 10.1021/bi00507a049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berry E. A., Trumpower B. L. Simultaneous determination of hemes a, b, and c from pyridine hemochrome spectra. Anal Biochem. 1987 Feb 15;161(1):1–15. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90643-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bott M., Bolliger M., Hennecke H. Genetic analysis of the cytochrome c-aa3 branch of the Bradyrhizobium japonicum respiratory chain. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Dec;4(12):2147–2157. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00576.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHEN-BAZIRE G., SISTROM W. R., STANIER R. Y. Kinetic studies of pigment synthesis by non-sulfur purple bacteria. J Cell Physiol. 1957 Feb;49(1):25–68. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1030490104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cao J., Shapleigh J., Gennis R., Revzin A., Ferguson-Miller S. The gene encoding cytochrome c oxidase subunit II from Rhodobacter sphaeroides; comparison of the deduced amino acid sequence with sequences of corresponding peptides from other species. Gene. 1991 May 15;101(1):133–137. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(91)90235-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter K., Palmer G. Models of the two heme centers in cytochrome oxidase. The optical properties of cytochrome a and a3. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 25;257(22):13507–13514. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan S. I., Li P. M. Cytochrome c oxidase: understanding nature's design of a proton pump. Biochemistry. 1990 Jan 9;29(1):1–12. doi: 10.1021/bi00453a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ching Y. C., Argade P. V., Rousseau D. L. Resonance raman spectra of CN--bound cytochrome oxidase: spectral isolation of cytochromes a2+, a3(2+), and a3(2+)(CN-). Biochemistry. 1985 Aug 27;24(18):4938–4946. doi: 10.1021/bi00339a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cline J., Reinhammar B., Jensen P., Venters R., Hoffman B. M. Coordination environment for the type 3 copper center of tree laccase and CuB of cytochrome c oxidase as determined by electron nuclear double resonance. J Biol Chem. 1983 Apr 25;258(8):5124–5128. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Copeland R. A. Conformational switching at cytochrome a during steady-state turnover of cytochrome c oxidase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 15;88(16):7281–7283. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.16.7281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fee J. A., Kuila D., Mather M. W., Yoshida T. Respiratory proteins from extremely thermophilic, aerobic bacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986;853(2):153–185. doi: 10.1016/0304-4173(86)90009-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabel C., Maier R. J. Nucleotide sequence of the coxA gene encoding subunit I of cytochrome aa3 of Bradyrhizobium japonicum. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Oct 25;18(20):6143–6143. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.20.6143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holm L., Saraste M., Wikström M. Structural models of the redox centres in cytochrome oxidase. EMBO J. 1987 Sep;6(9):2819–2823. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02578.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keen N. T., Tamaki S., Kobayashi D., Trollinger D. Improved broad-host-range plasmids for DNA cloning in gram-negative bacteria. Gene. 1988 Oct 15;70(1):191–197. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90117-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemieux L. J., Calhoun M. W., Thomas J. W., Ingledew W. J., Gennis R. B. Determination of the ligands of the low spin heme of the cytochrome o ubiquinol oxidase complex using site-directed mutagenesis. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 25;267(3):2105–2113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li P. M., Gelles J., Chan S. I., Sullivan R. J., Scott R. A. Extended X-ray absorption fine structure of copper in CuA-depleted, p-(hydroxymercuri)benzoate-modified, and native cytochrome c oxidase. Biochemistry. 1987 Apr 21;26(8):2091–2095. doi: 10.1021/bi00382a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin C. T., Scholes C. P., Chan S. I. The identification of histidine ligands to cytochrome a in cytochrome c oxidase. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 10;260(5):2857–2861. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minagawa J., Mogi T., Gennis R. B., Anraku Y. Identification of heme and copper ligands in subunit I of the cytochrome bo complex in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 25;267(3):2096–2104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagai M., Yoneyama Y., Kitagawa T. Unusual CO bonding geometry in abnormal subunits of hemoglobin M Boston and hemoglobin M Saskatoon. Biochemistry. 1991 Jul 2;30(26):6495–6503. doi: 10.1021/bi00240a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohnishi T., LoBrutto R., Salerno J. C., Bruckner R. C., Frey T. G. Spatial relationship between cytochrome a and a3. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 25;257(24):14821–14825. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliveberg M., Malmström B. G. Internal electron transfer in cytochrome c oxidase: evidence for a rapid equilibrium between cytochrome a and the bimetallic site. Biochemistry. 1991 Jul 23;30(29):7053–7057. doi: 10.1021/bi00243a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powers L., Chance B., Ching Y., Angiolillo P. Structural features and the reaction mechanism of cytochrome oxidase: iron and copper X-ray absorption fine structure. Biophys J. 1981 Jun;34(3):465–498. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(81)84863-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raitio M., Jalli T., Saraste M. Isolation and analysis of the genes for cytochrome c oxidase in Paracoccus denitrificans. EMBO J. 1987 Sep;6(9):2825–2833. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02579.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raitio M., Pispa J. M., Metso T., Saraste M. Are there isoenzymes of cytochrome c oxidase in Paracoccus denitrificans? FEBS Lett. 1990 Feb 26;261(2):431–435. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80609-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saraste M. Structural features of cytochrome oxidase. Q Rev Biophys. 1990 Nov;23(4):331–366. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500005588. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott R. A., Schwartz J. R., Cramer S. P. Structural aspects of the copper sites in cytochrome c oxidase. An X-ray absorption spectroscopic investigation of the resting-state enzyme. Biochemistry. 1986 Sep 23;25(19):5546–5555. doi: 10.1021/bi00367a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapleigh J. P., Gennis R. B. Cloning, sequencing and deletion from the chromosome of the gene encoding subunit I of the aa3-type cytochrome c oxidase of Rhodobacter sphaeroides. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Mar;6(5):635–642. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01511.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens T. H., Chan S. I. Histidine is the axial ligand to cytochrome alpha 3 in cytochrome c oxidase. J Biol Chem. 1981 Feb 10;256(3):1069–1071. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandeyar M. A., Weiner M. P., Hutton C. J., Batt C. A. A simple and rapid method for the selection of oligodeoxynucleotide-directed mutants. Gene. 1988 May 15;65(1):129–133. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90425-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanneste W. H. The stoichiometry and absorption spectra of components a and a-3 in cytochrome c oxidase. Biochemistry. 1966 Mar;5(3):838–848. doi: 10.1021/bi00867a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wielburski A., Nelson B. D. Heme a induces assembly of rat liver cytochrome c oxidase subunits I--III in isolated mitochondria. FEBS Lett. 1984 Nov 19;177(2):291–294. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)81302-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wikstrom M. K. Proton pump coupled to cytochrome c oxidase in mitochondria. Nature. 1977 Mar 17;266(5599):271–273. doi: 10.1038/266271a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodruff W. H., Dallinger R. F., Antalis T. M., Palmer G. Resonance Raman spectroscopy of cytochrome oxidase using Soret excitation: selective enhancement, indicator bands, and structural significance for cytochromes a and a3. Biochemistry. 1981 Mar 3;20(5):1332–1338. doi: 10.1021/bi00508a045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yun C. H., Crofts A. R., Gennis R. B. Assignment of the histidine axial ligands to the cytochrome bH and cytochrome bL components of the bc1 complex from Rhodobacter sphaeroides by site-directed mutagenesis. Biochemistry. 1991 Jul 9;30(27):6747–6754. doi: 10.1021/bi00241a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]