Abstract
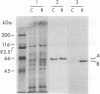
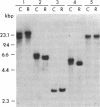
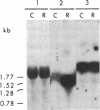
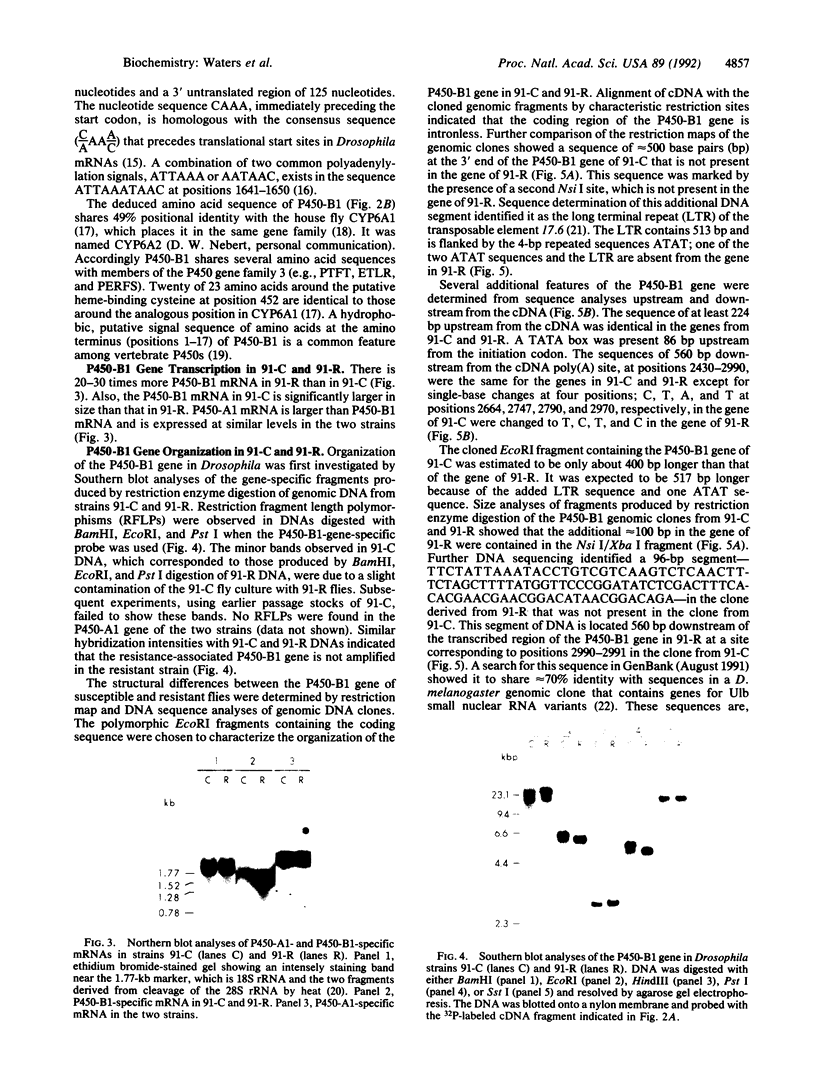
P450-A and P450-B are electrophoretically defined subsets of cytochrome P450 enzymes in Drosophila melanogaster. P450-A is present among all strains tested, whereas expression of P450-B is associated with resistance to insecticides. Monoclonal antibodies were used to obtain cDNA clones for an enzyme from each P450 subset (i.e., P450-A1 and P450-B1). The P450-B1 cDNA was sequenced and shown to code for a P450 of 507 amino acids. Its gene has been named CYP6A2. Comparative molecular analyses of a pair of susceptible, 91-C, and resistant, 91-R, Drosophila strains were made. There was 20-30 times more P450-B1 mRNA in 91-R than in 91-C, and the small amount of P450-B1 mRNA in 91-C was significantly larger in size than that in 91-R. The P450-B1 gene in 91-R was structurally different from that in 91-C but was not amplified. The P450-B1 gene in 91-C contained a solitary long terminal repeat of transposable element 17.6 in its 3' untranslated region. It was absent in the P450-B1 gene of 91-R. On the basis of features of the long terminal repeat and its location in the gene of the susceptible fly, we propose that a posttranscriptional mechanism involving mRNA stability could be involved in regulating P450-B1 gene expression.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bingham P. M., Judd B. H. A copy of the copia transposable element is very tightly linked to the Wa allele at the white locus of D. melanogaster. Cell. 1981 Sep;25(3):705–711. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90177-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnstiel M. L., Busslinger M., Strub K. Transcription termination and 3' processing: the end is in site! Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):349–359. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80007-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brattsten L. B., Holyoke C. W., Jr, Leeper J. R., Raffa K. F. Insecticide resistance: challenge to pest management and basic research. Science. 1986 Mar 14;231(4743):1255–1260. doi: 10.1126/science.231.4743.1255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carbonare B. D., Gehring W. J. Excision of copia element in a revertant of the white-apricot mutation of Drosophila melanogaster leaves behind one long-terminal repeat. Mol Gen Genet. 1985;199(1):1–6. doi: 10.1007/BF00327501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavener D. R. Comparison of the consensus sequence flanking translational start sites in Drosophila and vertebrates. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Feb 25;15(4):1353–1361. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.4.1353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Copeland N. G., Hutchison K. W., Jenkins N. A. Excision of the DBA ecotropic provirus in dilute coat-color revertants of mice occurs by homologous recombination involving the viral LTRs. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):379–387. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90419-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dapkus D., Merrell D. J. Chromosomal analysis of DDT-resistance in a long-term selected population of Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics. 1977 Dec;87(4):685–697. doi: 10.1093/genetics/87.4.685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feyereisen R., Koener J. F., Farnsworth D. E., Nebert D. W. Isolation and sequence of cDNA encoding a cytochrome P-450 from an insecticide-resistant strain of the house fly, Musca domestica. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(5):1465–1469. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.5.1465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field L. M., Devonshire A. L., Forde B. G. Molecular evidence that insecticide resistance in peach-potato aphids (Myzus persicae Sulz.) results from amplification of an esterase gene. Biochem J. 1988 Apr 1;251(1):309–312. doi: 10.1042/bj2510309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inouye S., Yuki S., Saigo K. Sequence-specific insertion of the Drosophila transposable genetic element 17.6. 1984 Jul 26-Aug 1Nature. 310(5975):332–333. doi: 10.1038/310332a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins N. A., Copeland N. G., Taylor B. A., Lee B. K. Dilute (d) coat colour mutation of DBA/2J mice is associated with the site of integration of an ecotropic MuLV genome. Nature. 1981 Oct 1;293(5831):370–374. doi: 10.1038/293370a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kugimiya W., Ikenaga H., Saigo K. Close relationship between the long terminal repeats of avian leukosis-sarcoma virus and copia-like movable genetic elements of Drosophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(11):3193–3197. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.11.3193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lo P. C., Mount S. M. Drosophila melanogaster genes for U1 snRNA variants and their expression during development. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Dec 11;18(23):6971–6979. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.23.6971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mouchès C., Pasteur N., Bergé J. B., Hyrien O., Raymond M., de Saint Vincent B. R., de Silvestri M., Georghiou G. P. Amplification of an esterase gene is responsible for insecticide resistance in a California Culex mosquito. Science. 1986 Aug 15;233(4765):778–780. doi: 10.1126/science.3755546. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nebert D. W., Nelson D. R., Coon M. J., Estabrook R. W., Feyereisen R., Fujii-Kuriyama Y., Gonzalez F. J., Guengerich F. P., Gunsalus I. C., Johnson E. F. The P450 superfamily: update on new sequences, gene mapping, and recommended nomenclature. DNA Cell Biol. 1991 Jan-Feb;10(1):1–14. doi: 10.1089/dna.1991.10.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nickol J. M., Lee K. L., Kenney F. T. Changes in hepatic levels of tyrosine aminotransferase messenger RNA during induction by hydrocortisone. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jun 10;253(11):4009–4015. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paek I., Axel R. Glucocorticoids enhance stability of human growth hormone mRNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Apr;7(4):1496–1507. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.4.1496. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ronis M. J., Hodgson E. Cytochrome P-450 monooxygenases in insects. Xenobiotica. 1989 Oct;19(10):1077–1092. doi: 10.3109/00498258909043163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw G., Kamen R. A conserved AU sequence from the 3' untranslated region of GM-CSF mRNA mediates selective mRNA degradation. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):659–667. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90341-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swartwout S. G., Kinniburgh A. J. c-myc RNA degradation in growing and differentiating cells: possible alternate pathways. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jan;9(1):288–295. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.1.288. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waters L. C., Simms S. I., Nix C. E. Natural variation in the expression of cytochrome P-450 and dimethylnitrosamine demethylase in Drosophila. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Sep 28;123(3):907–913. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(84)80220-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]