Abstract
The case histories of four patients who developed choreoathetoid movements during intoxication with phenytoin are presented. Drug intoxication was confirmed in each case by measuring the serum phenytoin concentration. Drug interactions were, in part, responsible for the occurrence of intoxication in three of them. Phenytoin intoxication is not always easy to recognize, particularly when nystagmus is minimal or absent, as in these four patients. The estimation of the serum phenytoin concentration is invaluable in this situation.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnold K., Gerber N. The rate of decline of diphenylhydantoin in human plasma. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1970 Jan-Feb;11(1):121–134. doi: 10.1002/cpt1970111121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atkinson A. J., Jr, Shaw J. M. Pharmacokinetic study of a patient with diphenylhydantoin toxicity. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1973 Jul-Aug;14(4):521–528. doi: 10.1002/cpt1973144part1521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERGIN J. T., FISCHER E., MORRIS J. V. Rare complication of phenytoin sodium treatment. Br Med J. 1956 Dec 29;2(5008):1529–1529. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5008.1529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bochner F., Hooper W. D., Tyrer J. H., Eadie M. J. Effect of dosage increments on blood phenytoin concentrations. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1972 Dec;35(6):873–876. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.35.6.873. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engel, Cruz M. E., Shapiro B. Phenytoin encephalopathy? Lancet. 1971 Oct 9;2(7728):824–825. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)92787-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerber N., Wagner J. G. Explanation of dose-dependent decline of diphenylhydantoin plasma levels by fitting to the integrated form of the Michaelis-Menten equation. Res Commun Chem Pathol Pharmacol. 1972 May;3(3):455–466. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibberd F. B., Dunne J. F., Handley A. J., Hazleman B. L. Supervision of epileptic patients taking phenytoin. Br Med J. 1970 Jan 17;1(5689):147–149. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5689.147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen J. M., Kristensen M., Skovsted L. Sulthiame (Ospolot) as inhibitor of diphenylhydatoin metabolism. Epilepsia. 1968 Mar;9(1):17–22. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1157.1968.tb04954.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houghton G. W., Richens A. Phenytoin intoxication induced by sulthiame in epileptic patients. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1974 Mar;37(3):275–281. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.37.3.275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huisman J. W., van Heycop ten Ham M. W., van Zijl C. H. Influence of ethylphenacemide on serum levels of other anti-epileptic drugs. Epilepsia. 1970 Jun;11(2):207–215. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1157.1970.tb03882.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kooiker J. C., Sumi S. M. Movement disorder as a manifestation of diphenylhydantoin intoxication. Neurology. 1974 Jan;24(1):68–71. doi: 10.1212/wnl.24.1.68. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kutt H., Winters W., McDowell F. H. Depression of prahydroxylation of diphenylhydantoin by antituberculosis chemotherapy. Neurology. 1966 Jun;16(6):594–602. doi: 10.1212/wnl.16.6.594. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVY L. L., FENICHEL G. M. DIPHENYLHYDANTOIN ACTIVATED SEIZURES. Neurology. 1965 Aug;15:716–722. doi: 10.1212/wnl.15.8.719. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Logan W. J., Freeman J. M. Pseudodegenerative disease due to diphenylhydantoin intoxication. Arch Neurol. 1969 Dec;21(6):631–637. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1969.00480180087008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLellan D. L., Swash M. Choreo-athetosis and encephalopathy induced by phenytoin. Br Med J. 1974 Apr 27;2(5912):204–205. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5912.204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSEMAN E. Dilantin toxicity. A clinical and electroence-phalographic study. Neurology. 1961 Oct;11:912–921. doi: 10.1212/wnl.11.10.912. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
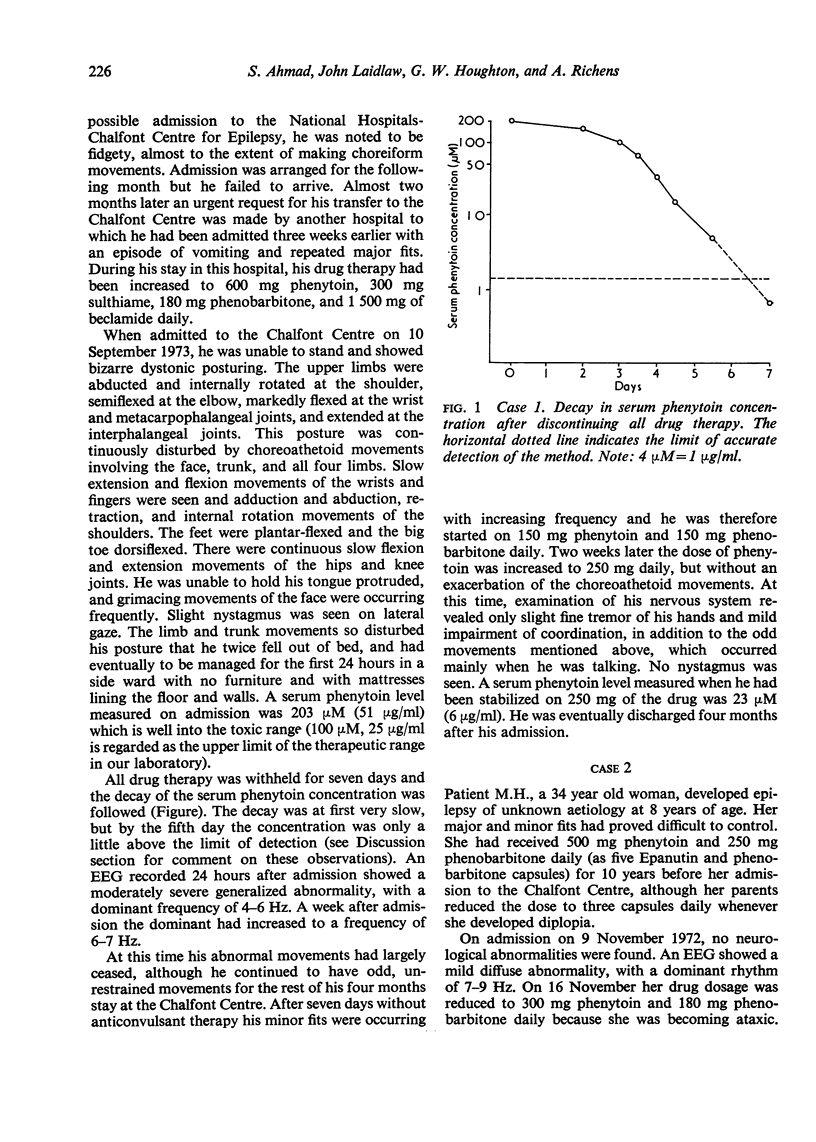
- Richens A. Drug estimation in the treatment of epilepsy. Proc R Soc Med. 1974 Dec;67(12 Pt 1):1227–1229. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


