Abstract
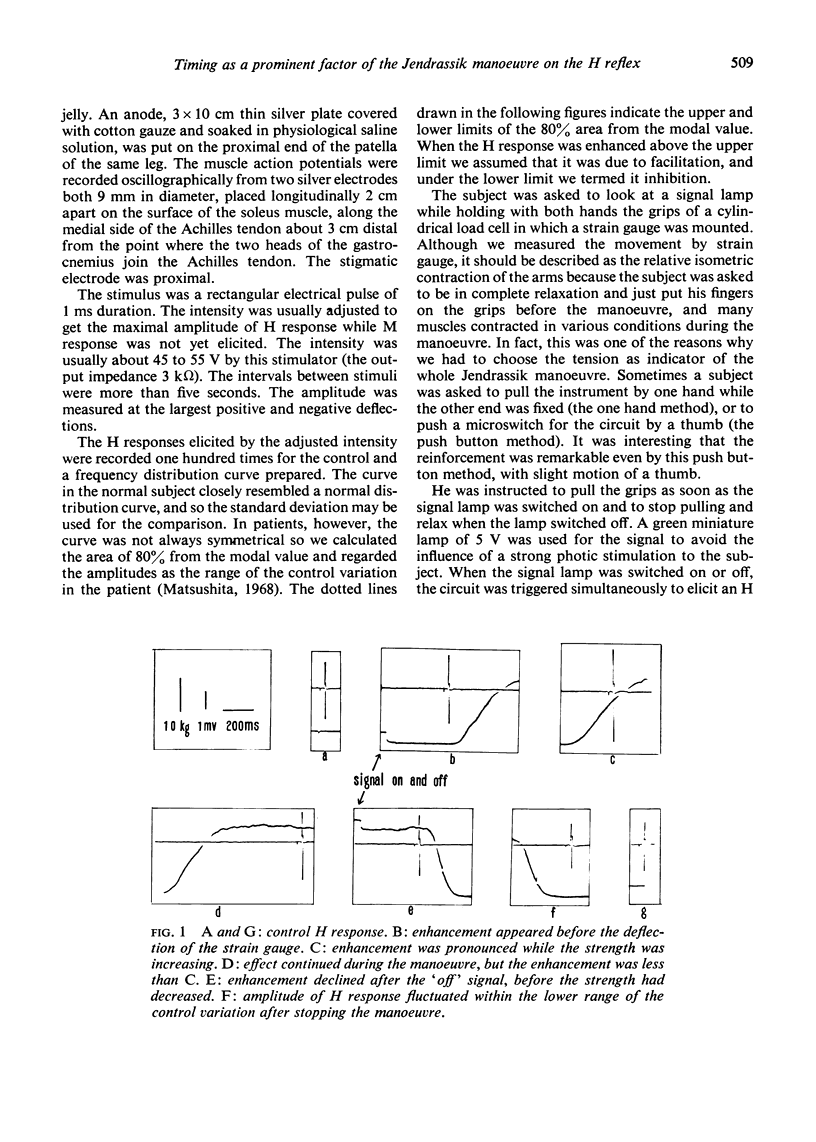
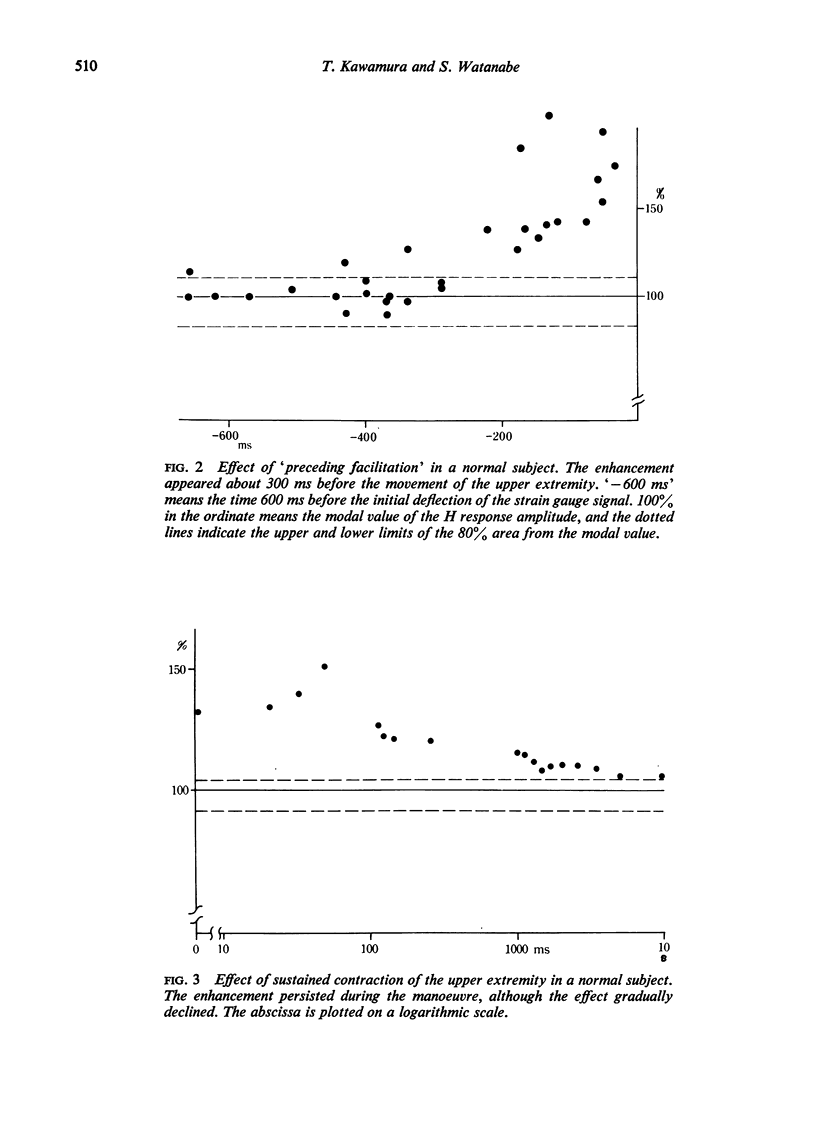
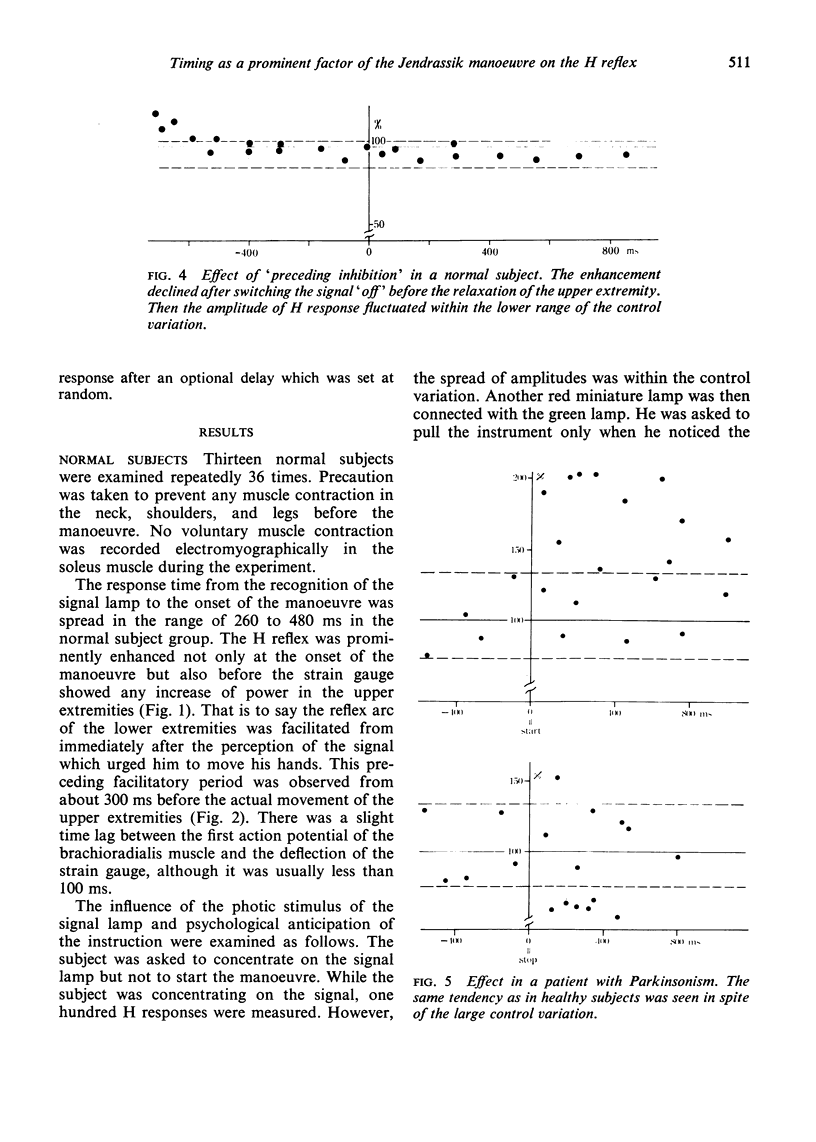
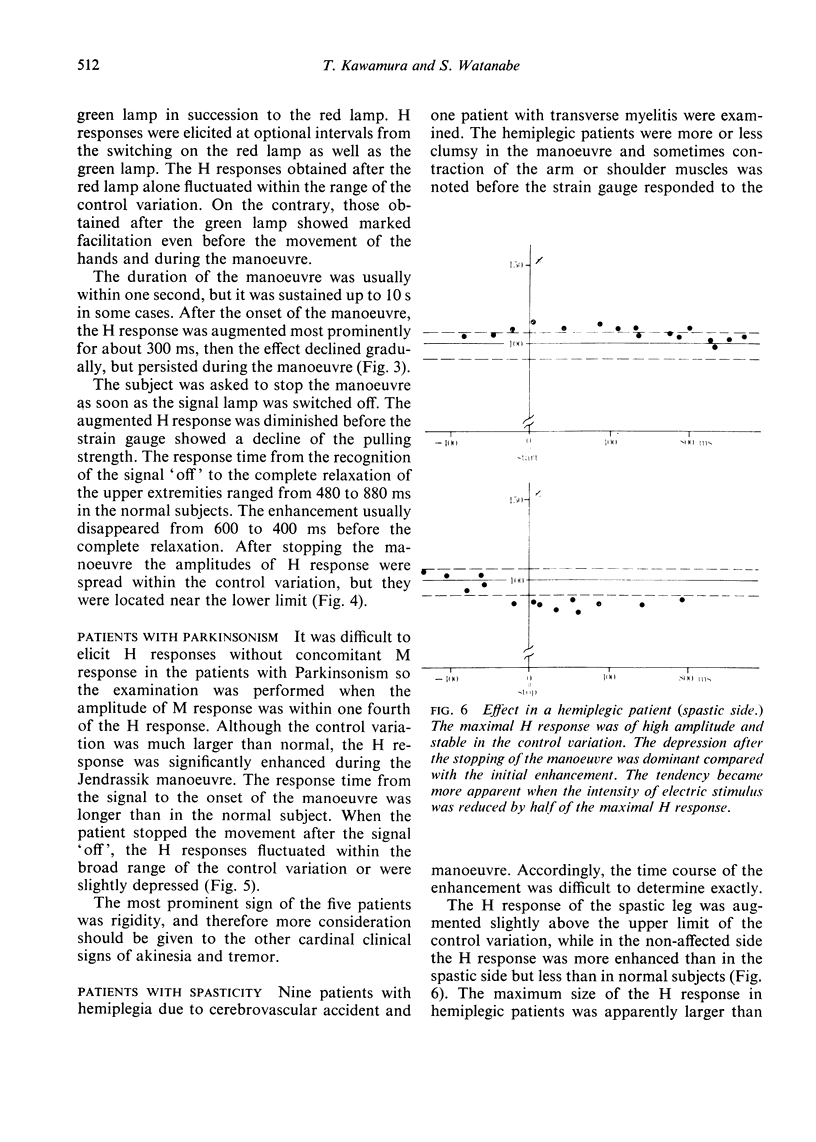
The influence of the Jendrassik manoeuvre on the myotatic reflex was analysed using a strain gauge as an indicator of the upper extremity movement and the H reflex of the soleus muscle as the test reflex. The most prominent factor responsible for the enhancement was not the speed or the strength of the manoeuvre but the timing from the instruction.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BIANCONI R., van der MEULEN J. The response to vibration of the end organs of mammalian muscle spindles. J Neurophysiol. 1963 Jan;26:177–190. doi: 10.1152/jn.1963.26.1.177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BULLER A. J., DORNHORST A. C. The reinforcement of tendon-reflexes. Lancet. 1957 Dec 21;273(7008):1260–1262. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(57)91542-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowditch H. P., Warren J. W. The Knee-jerk and its Physiological Modifications. J Physiol. 1890 Jan;11(1-2):25–64. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1890.sp000318. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLARE M. H., LANDAU W. M. FUSIMOTOR FUNCTION. V. REFLEX REINFORCEMENT UNDER FUSIMOTOR BLOCK IN NORMAL SUBJECTS. Arch Neurol. 1964 Feb;10:123–127. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1964.00460140009002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Gail P., Lance J. W., Neilson P. D. Differential effects on tonic and phasic reflex mechanisms produced by vibration of muscles in man. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1966 Feb;29(1):1–11. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.29.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GASSEL M. M., DIAMTOPOULOS E. THE JENDRASSIK MANEUVER. II. AN ANALYSIS OF THE MECHANISM. Neurology. 1964 Jul;14:640–642. doi: 10.1212/wnl.14.7.640. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRANIT R., HENATSCH H. D. Gamma control of dynamic properties of muscle spindles. J Neurophysiol. 1956 Jul;19(4):356–366. doi: 10.1152/jn.1956.19.4.356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HASSLER R. Die extrapyramidalen Rindensysteme und die zentrale Regelung der Motorik. Dtsch Z Nervenheilkd. 1956;175(3):233–258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOFFMANN P. Die Aufklärung der Wirkung des Jendrassikschen Handgriffs durch die Arbeiten von Sommer und Kuffler. Dtsch Z Nervenheilkd. 1951;166(1):60–64. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANDAU W. M., CLARE M. H. FUSIMOTOR FUNCTION. IV. REINFORCEMENT OF THE H REFLEX IN NORMAL SUBJECTS. Arch Neurol. 1964 Feb;10:117–122. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1964.00460140003001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANDAU W. M., CLARE M. H. FUSIMOTOR FUNCTION. VI. H REFLEX, TENDON JERK, AND REINFORCEMENT IN HEMIPLEGIA. Arch Neurol. 1964 Feb;10:128–134. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1964.00460140014003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STERN J., WARD A., Jr Inhibition of the muscle spindle discharge by ventrolateral thalamic stimulation. Its relation to parkinsonism. Arch Neurol. 1960 Aug;3:193–204. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1960.00450020073011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STRUPPLER A., PREUSS R. Untersuchungen über periphere und zentrale Faktoren der Eigenreflexerregbarkeit am Menschen mit Hilfe des Jendrassikschen Handgriffes. Pflugers Arch. 1959;268(5):425–434. doi: 10.1007/BF00362945. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yajima K. [Clinical study on evoked EMG]. No To Shinkei. 1965 Nov;17(11):1145–1157. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


