Abstract
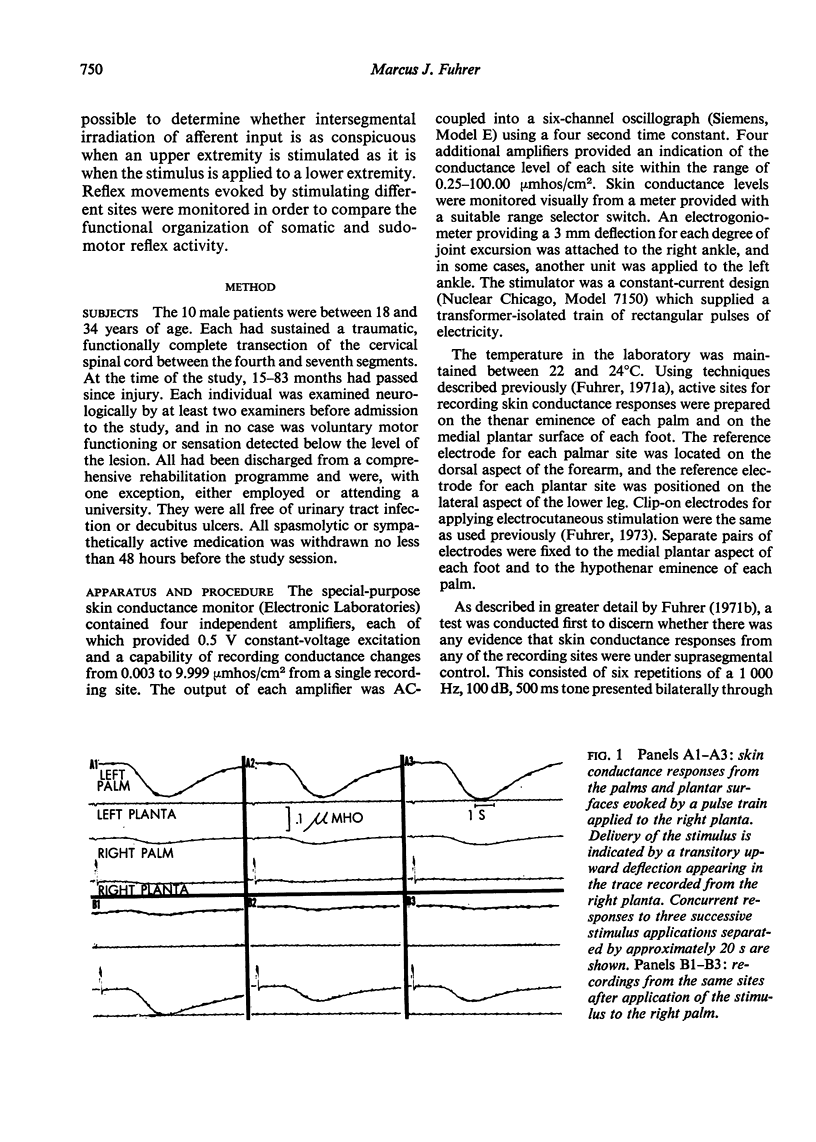
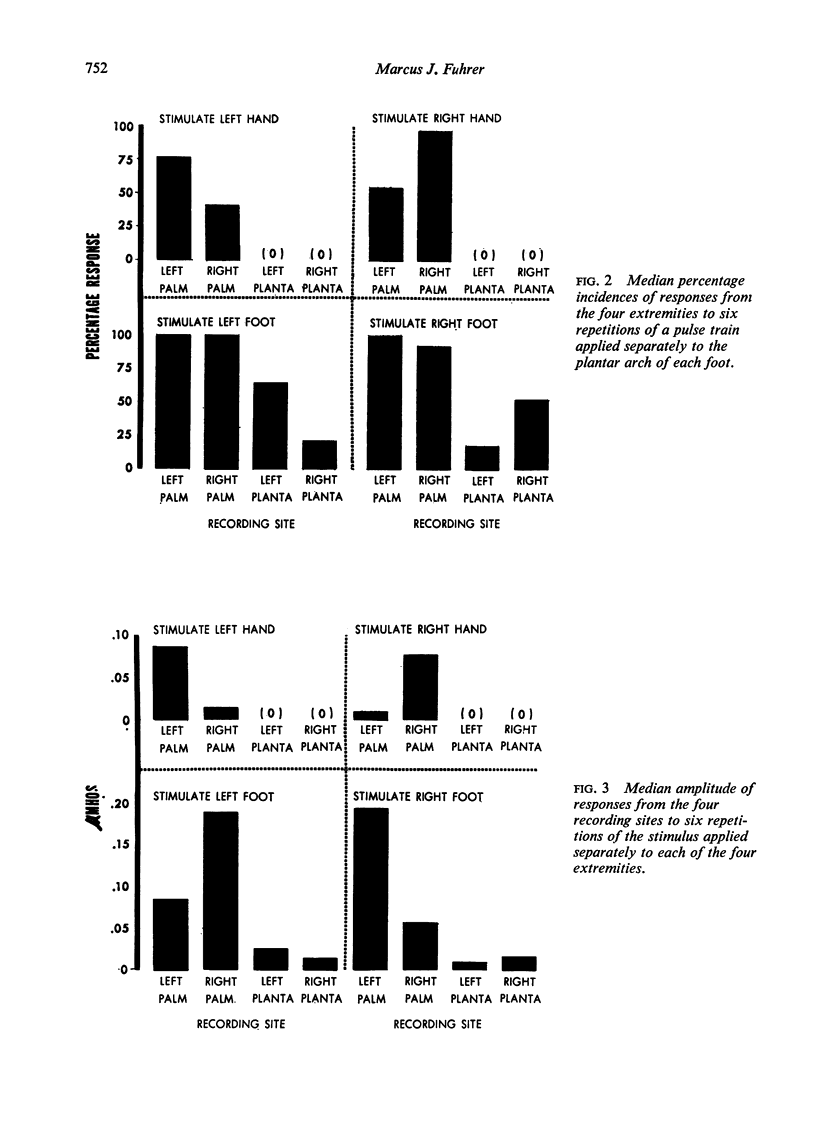
The spatial organization of sudomotor responses mediated by the cervically transected human spinal cord was investigated by recording skin conductance responses from the volar surfaces of the hands and feet of 10 patients after pulse trains applied separately to the skin of each extremity. Each stimulus site tended to be associated with a distinctive pattern of skin conductance responses.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ECCLES R. M., LUNDBERG A. Supraspinal control of interneurones mediating spinal reflexes. J Physiol. 1959 Oct;147:565–584. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006262. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuhrer M. J. Analysis of electrodermal evidence for a paramedullary afferent tract in patients with a transection of the thoracic spinal cord. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1971 Jun;34(3):281–288. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.34.3.281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuhrer M. J. Dishabituation of flexor withdrawal activity mediated by the functionally transected human spinal cord. Brain Res. 1973 Dec 7;63:93–102. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(73)90078-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuhrer M. J., Kilbey M. Effects of spinal-cord transections on electrodermal activity in man. Psychophysiology. 1967 Oct;4(2):176–186. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8986.1967.tb02756.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuhrer M. J. Skin conductance responses mediated by the transected human spinal cord. J Appl Physiol. 1971 May;30(5):663–669. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1971.30.5.663. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LADPLI R. Galvanic skin reactions of chronic spinal cats. Am J Phys Med. 1962 Feb;41:15–22. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LLOYD D. P. The classification of galvanic skin reflex afferent fibers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1962 May 15;48:814–817. doi: 10.1073/pnas.48.5.814. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SOUREK K. DIE BEDEUTUNG DES GALVANISCHEN HAUTREFLEXES FUER DIE LOKALISATION VON LAESIONEN IM NERVENSYSTEM DES MENSCHEN. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 1964;11:518–529. doi: 10.1007/BF01413493. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THOMAS P. E., KORR I. M. Relationship between sweat gland activity and electrical resistance of the skin. J Appl Physiol. 1957 May;10(3):505–510. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1957.10.3.505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


