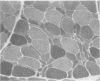
Abstract
Polyneuropathy is a rare but possible manifestation of severe hyperthyroidism. The patient reported here developed a polyneuropathy affecting mostly leg muscles (Basedow's paraplegia) during the course of severe thyrotoxicosis. The polyneuropathy was confirmed with sequential electrophysiological studies of nerves and muscles and by muscle biopsy. The involvement of the proximal leg muscle is also interpreted as a neuropathic or nerve-mediated process rather than a concomitant thyrotoxic myopathy.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CRILE G., Jr, McCULLAGH E. P. The treatment of hyperthyroidism; an evaluation of thyroidectomy, of prolonged administration of propyl thiouracil, and of radioactive iodine. Ann Surg. 1951 Jul;134(1):18–28. doi: 10.1097/00000658-195107000-00004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chollet P., Rigal J. P., Pignide L. Une complication méconnue de l'hyperthyroïdie: la neuropathie périphérique. Presse Med. 1971 Jan 23;79(4):145–145. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fridberg D. I., Egart F. M. Sluchai bazedovicheskoi paraplegii. Probl Endokrinol (Mosk) 1970 Sep-Oct;16(5):38–40. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAVARD C. W., CAMPBELL E. D., ROSS H. B., SPENCE A. W. Electromyographic and histological findings in the muscles of patients with thyrotoxicosis. Q J Med. 1963 Apr;32:145–163. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludin H. P., Spiess H., Koenig M. P. Neuromuscular dysfunction associated with thyrotoxicosis. Eur Neurol. 1969;2(5):269–278. doi: 10.1159/000113803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILLIKAN C. H., HAINES S. F. The thyroid gland in relation to neuromuscular disease. AMA Arch Intern Med. 1953 Jul;92(1):5–39. doi: 10.1001/archinte.1953.00240190017002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGAVACK T. H., CHEVALLEY J. Untoward hematologic responses to the antithyroid compounds. Am J Med. 1954 Jul;17(1):36–40. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(54)90141-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pleasure D. E., Lovelace R. E., Duvoisin R. C. The prognosis of acute polyradiculoneuritis. Neurology. 1968 Dec;18(12):1143–1148. doi: 10.1212/wnl.18.12.1143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramsay I. D. Electromyography in thyrotoxicosis. Q J Med. 1965 Jul;34(135):255–267. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramsay I. Thyrotoxic muscle disease. Postgrad Med J. 1968 May;44(511):385–397. doi: 10.1136/pgmj.44.511.385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SANGHVI L. M., GUPTA K. D., BANERJEE K., BOSE K. Paraplegia, hypokalemia and nephropathy, with muscle lesions of potassium deficiency, associated with thyrotoxicosis. Am J Med. 1959 Nov;27:817–823. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(59)90198-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VANDERLAAN W. P., STORRIE V. M. A survey of the factors controlling thyroid function, with especial reference to newer views on antithyroid substances. Pharmacol Rev. 1955 Sep;7(3):301–334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warmolts J. R., Engel W. K. A critique of the "myopathic" electromyogram. Trans Am Neurol Assoc. 1970;95:173–177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]