Abstract
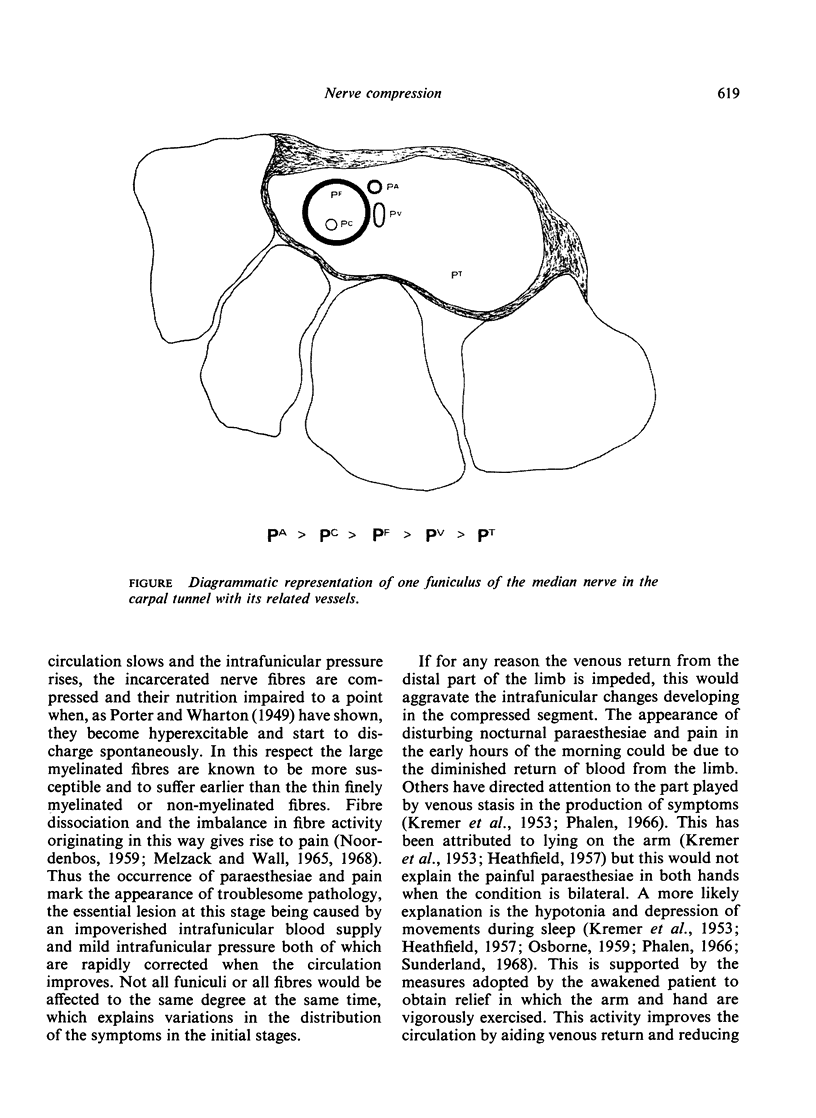
The relative roles of pressure deformation and ischaemia in the production of compression nerve lesions remain a controversial issue. This paper concerns the genesis of the structural changes which follow compression of the median nerve in the carpal tunnel. The initial lesion is an intrafunicular anoxia caused by obstruction to the venous return from the funiculi as the result of increased pressure in the tunnel. This leads to intrafunicular oedema and an increase in intrafunicular pressure which imperil and finally destroy nerve fibres by impairing their blood supply and by compression. The final outcome is the fibrous tissue replacement of the contents of the funiculi.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aguayo A., Nair C. P., Midgley R. Experimental progressive compression neuropathy in the rabbit. Histologic and electrophysiologic studies. Arch Neurol. 1971 Apr;24(4):358–364. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1971.00480340090010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen F. M. EFFECTS OF LIGATIONS ON NERVES OF THE EXTREMITIES. Ann Surg. 1938 Dec;108(6):1088–1093. doi: 10.1097/00000658-193812000-00011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson M. H., Fullerton P. M., Gilliatt R. W., Hern J. E. Changes in the forearm associated with median nerve compression at the wrist in the guinea-pig. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1970 Feb;33(1):70–79. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.33.1.70. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLUNT M. J. The vascular anatomy of the median nerve in the forearm and hand. J Anat. 1959 Jan;93(1):15–22. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bentley F. H., Schlapp W. The effects of pressure on conduction in peripheral nerve. J Physiol. 1943 Jun 30;102(1):72–82. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1943.sp004016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CAUSEY G., PALMER E. The effect of pressure on nerve conduction and nerve-fibre size. J Physiol. 1949 Aug;109(1-2):220–231. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1949.sp004386. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Causey G. The effect of pressure on nerve fibres. J Anat. 1948 Oct;82(Pt 4):262–270.1. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FULLERTON P. M. THE EFFECT OF ISCHAEMIA ON NERVE CONDUCTION IN THE CARPAL TUNNEL SYNDROME. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1963 Oct;26:385–397. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.26.5.385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fowler T. J., Danta G., Gilliatt R. W. Recovery of nerve conduction after a pneumatic tourniquet: observations on the hind-limb of the baboon. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1972 Oct;35(5):638–647. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.35.5.638. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fullerton P. M., Gilliatt R. W. Median and ulnar neuropathy in the guinea-pig. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1967 Oct;30(5):393–402. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.30.5.393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GARLAND H., BRADSHAW J. P., CLARK J. M. Compression of median nerve in carpal tunnel and its relation to acroparaesthesiae. Br Med J. 1957 Mar 30;1(5021):730–734. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5021.730. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GELFAN S., TARLOV I. M. Physiology of spinal cord, nerve root and peripheral nerve compression. Am J Physiol. 1956 Apr;185(1):217–229. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1956.185.1.217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GILLIATT R. W., WILSON T. G. A pneumatic-tourniquet test in the carpal-tunnel syndrome. Lancet. 1953 Sep 19;265(6786):595–597. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(53)90327-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GILLIATT R. W., WILSON T. G. Ischaemic sensory loss in patients with peripheral nerve lesions. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1954 May;17(2):104–114. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.17.2.104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilliatt R. W., McDonald W. I., Rudge P. Proceeding: The site of conduction block in peripheral nerves compressed by a pneumatic tourniquet. J Physiol. 1974 Apr;238(1):31P–32P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEATHFIELD K. W. Acroparaesthesiae and the carpal-tunnel syndrome. Lancet. 1957 Oct 5;273(6997):663–666. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(57)92107-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KENDALL D. Aetiology, diagnosis, and treatment of paraesthesiae in the hands. Br Med J. 1960 Dec 3;2(5213):1633–1640. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5213.1633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KREMER M., GILLIATT R. W., GOLDING J. S., WILSON T. G. Acroparaesthesiae in the carpal-tunnel syndrome. Lancet. 1953 Sep 19;265(6786):590–595. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(53)90326-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOLDAVER J. Tourniquet paralysis syndrome. AMA Arch Surg. 1954 Feb;68(2):136–144. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1954.01260050138002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marotte L. R. An electron microscope study of chronic median nerve compression in the guinea pig. Acta Neuropathol. 1974 Feb 7;27(1):69–82. doi: 10.1007/BF00687242. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melzack R., Wall P. D. Pain mechanisms: a new theory. Science. 1965 Nov 19;150(3699):971–979. doi: 10.1126/science.150.3699.971. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neary D., Ochoa J., Gilliatt R. W. Sub-clinical entrapment neuropathy in man. J Neurol Sci. 1975 Mar;24(3):283–298. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(75)90248-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ochoa J., Fowler T. J., Gilliatt R. W. Anatomical changes in peripheral nerves compressed by a pneumatic tourniquet. J Anat. 1972 Dec;113(Pt 3):433–455. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ochoa J., Marotte L. The nature of the nerve lesion caused by chronic entrapment in the guinea-pig. J Neurol Sci. 1973 Aug;19(4):491–495. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(73)90045-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsson Y. Studies on vascular permeability in peripheral nerves. I. Distribution of circulating fluorescent serum albumin in normal, crushed and sectioned rat sciatic nerve. Acta Neuropathol. 1966 Sep 1;7(1):1–15. doi: 10.1007/BF00686605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phalen G. S. The carpal-tunnel syndrome. Seventeen years' experience in diagnosis and treatment of six hundred fifty-four hands. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1966 Mar;48(2):211–228. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RICHARDS R. L. Ischaemic lesions of peripheral nerves: a review. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1951 May;14(2):76–87. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.14.2.76. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudge P., Ochoa J., Gilliatt R. W. Acute peripheral nerve compression in the baboon. J Neurol Sci. 1974 Nov;23(3):403–420. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(74)90158-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SUNDERLAND S., BRADLEY K. C. Denervation atrophy of the distal stump of a severed nerve. J Comp Neurol. 1950 Dec;93(3):401–409. doi: 10.1002/cne.900930304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SUNDERLAND S., BRADLEY K. C. Endoneurial tube shrinkage in the distal segment of a severed nerve. J Comp Neurol. 1950 Dec;93(3):411–420. doi: 10.1002/cne.900930305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SUNDERLAND S., BRADLEY K. C. The cross-sectional area of peripheral nerve trunks devoted to nerve fibers. Brain. 1949 Sep;72(3):428–449. doi: 10.1093/brain/72.3.428. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SUNDERLAND S., BRADLEY K. C. The perineurium of peripheral nerves. Anat Rec. 1952 Jun;113(2):125–141. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091130202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spinner M., Spencer P. S. Nerve compression lesions of the upper extremity. A clinical and experimental review. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1974 Oct;(104):46–67. doi: 10.1097/00003086-197410000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sunderland S. The connective tissues of peripheral nerves. Brain. 1965 Nov;88(4):841–854. doi: 10.1093/brain/88.4.841. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TANZER R. C. The carpal-tunnel syndrome; a clinical and anatomical study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1959 Jun;41-A(4):626–634. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THOMAS P. K., FULLERTON P. M. NERVE FIBRE SIZE IN THE CARPAL TUNNEL SYNDROME. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1963 Dec;26:520–527. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.26.6.520. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEISL H., OSBORNE G. V. THE PATHOLOGICAL CHANGES IN RATS' NERVES SUBJECT TO MODERATE COMPRESSION. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1964 May;46:297–306. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]