Abstract
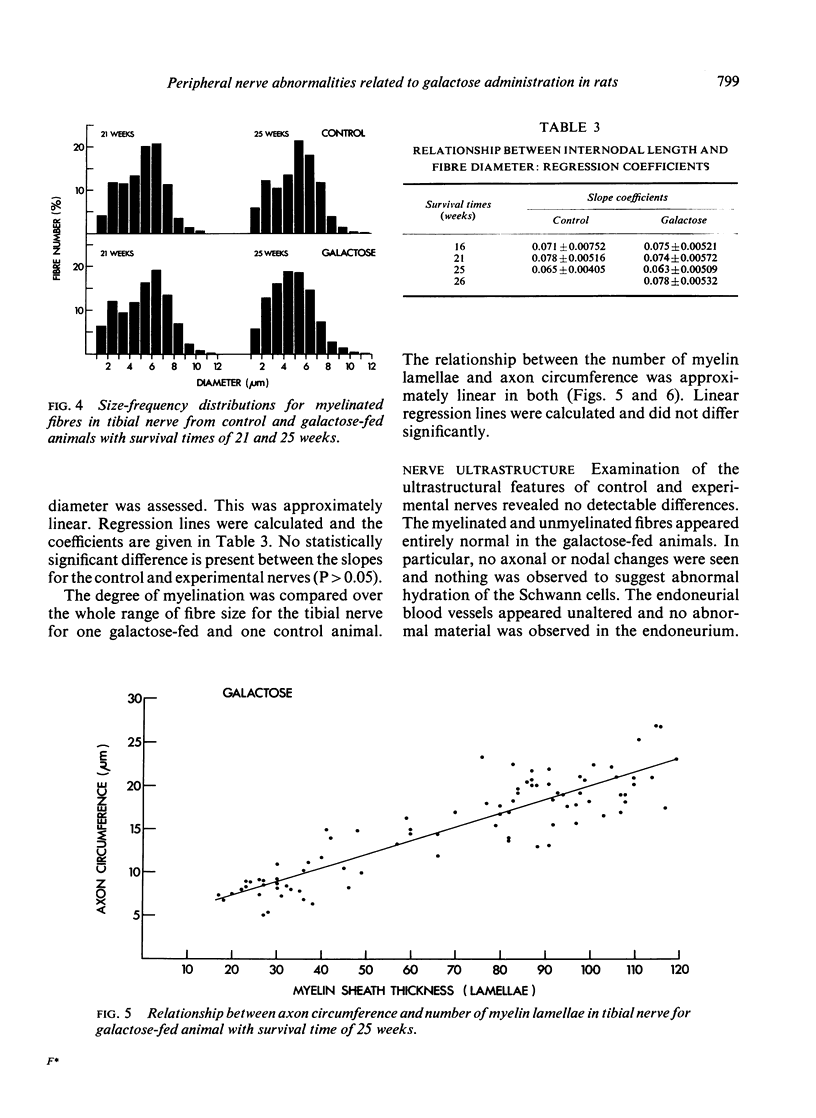
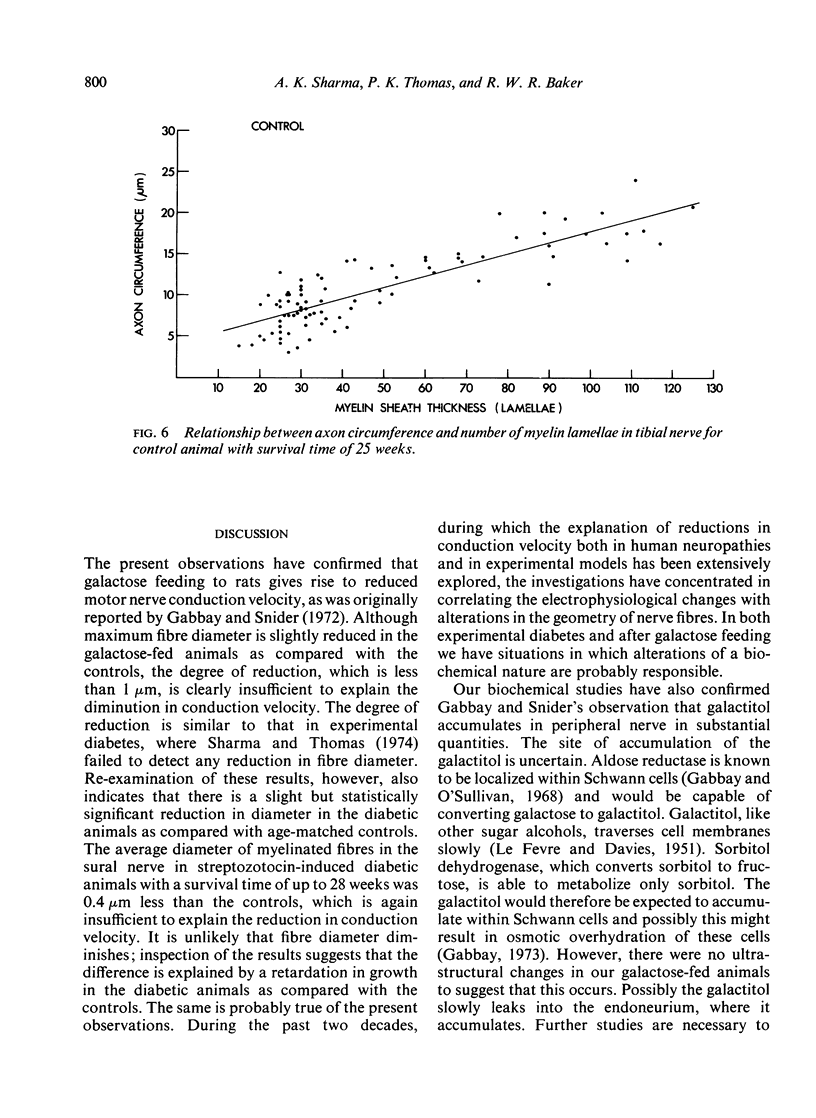
Electrophysiological, biochemical, and morphometric observations were made on the peripheral nerves of rats after galactose feeding. Motor nerve conduction velocity was found to be reduced. This was associated with an accumulation of galactitol in the peripheral nerves and a diminution in their myoinositol content. An increased water content and fascicular area, taken in conjunction with a probable increase in the area of the endoneurial spaces, indicated overhydration of the peripheral nerves. Morphometric observations on the myelinated fibre population in the tibial nerve showed no loss of fibres and although both the maximal and the average diameter of the myelinated fibres was slightly less than in age-matched controls, this was insufficient to explain the reduction in conduction velocity. Segmental demyelination was not detected and the relationship between myelin thickness and axon circumference was not altered. Electron microscope observations revealed no ultrastructural changes in the myelinated fibres and, in particular, no abnormalities at the nodes of Ranvier or indication of abnormal hydration of the Schwann cells. The relevance of these findings to the peripheral nerve changes in human and experimental diabetes is discussed.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cotran R. S., Karnovsky M. J. Ultrastructural studies on the permeability of the mesothelium to horseradish peroxidase. J Cell Biol. 1968 Apr;37(1):123–137. doi: 10.1083/jcb.37.1.123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeJesus P. V., Jr, Clements R. S., Jr, Winegrad A. I. Hypermyoinositolemic polyneuropathy in rats. A possible mechanism for uremic polyneuropathy. J Neurol Sci. 1974 Mar;21(3):237–249. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(74)90170-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eichberg J., Hauser G. The subcellular distribution of polyphosphoinositides in myelinated and unmyelinated rat brain. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Nov 29;326(2):210–223. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(73)90247-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eliasson S. G. Properties of isolated nerve fibres from alloxanized rats. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1969 Dec;32(6):525–529. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.32.6.525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabbay K. H., O'Sullivan J. B. The sorbitol pathway. Enzyme localization and content in normal and diabetic nerve and cord. Diabetes. 1968 May;17(5):239–243. doi: 10.2337/diab.17.5.239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabbay K. H. The sorbitol pathway and the complications of diabetes. N Engl J Med. 1973 Apr 19;288(16):831–836. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197304192881609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gitzelmann R., Curtius H. C., Schneller I. Galactitol and galactose-1-phosphate in the lens of a galactosemic infant. Exp Eye Res. 1967 Jan;6(1):1–3. doi: 10.1016/s0014-4835(67)80047-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene D. A., De Jesus P. V., Jr, Winegrad A. I. Effects of insulin and dietary myoinositol on impaired peripheral motor nerve conduction velocity in acute streptozotocin diabetes. J Clin Invest. 1975 Jun;55(6):1326–1336. doi: 10.1172/JCI108052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendrickson H. S., Reinertsen J. L. Comparison of metal-binding properties of trans-1,2-cyclohexanediol diphosphate and deacylated phosphoinositides. Biochemistry. 1969 Dec;8(12):4855–4858. doi: 10.1021/bi00840a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendrickson H. S., Reinertsen J. L. Phosphoinositide interconversion: a model for control of Na + and K + permeability in the nerve axon membrane. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Sep;44(5):1258–1264. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(71)80221-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KINOSHITA J. H., MEROLA L. O., SATOH K., DIKMAK E. Osmotic changes caused by the accumulation of dulcitol in the lenses of rats fed with galactose. Nature. 1962 Jun 16;194:1085–1087. doi: 10.1038/1941085a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kai M., Hawthorne J. N. Physiological significance of polyphosphoinositides in brain. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1969 Oct 17;165(2):761–773. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinoshita J. H. Cataracts in galactosemia. The Jonas S. Friedenwald Memorial Lecture. Invest Ophthalmol. 1965 Oct;4(5):786–799. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeFEVRE P. G., DAVIES R. I. Active transport into the human erythrocyte; evidence from comparative kinetics and competition among monosaccharides. J Gen Physiol. 1951 May;34(5):515–524. doi: 10.1085/jgp.34.5.515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michell R. H. Inositol phospholipids and cell surface receptor function. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Mar 25;415(1):81–47. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(75)90017-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma A. K., Thomas P. K. Peripheral nerve structure and function in experimental diabetes. J Neurol Sci. 1974 Sep;23(1):1–15. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(74)90136-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart M. A., Sherman W. R., Kurien M. M., Moonsammy G. I., Wisgerhof M. Polyol accumulations in nervous tissue of rats with experimental diabetes and galactosaemia. J Neurochem. 1967 Nov;14(11):1057–1066. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1967.tb09516.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward J. D., Baker R. W., Davis B. H. Effect of blood sugar control on the accumulation of sorbitol and fructose in nervous tissues. Diabetes. 1972 Dec;21(12):1173–1178. doi: 10.2337/diab.21.12.1173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White G. L., Larrabee M. G. Phosphoinositides and other phospholipids in sympathetic ganglia and nerve trunks of rats. Effects of neuronal activity and inositol analogs ( - and -hexachlorocyclohexane (lindane)) on ( 32 P)-labelling, synaptic transmission and axonal conduction. J Neurochem. 1973 Mar;20(3):783–798. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1973.tb00039.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yagihara Y., Salway J. G., Hawthorne J. N. Incorporation of 32P in vitro into triphosphoinositide and related lipids of rat superior cervical ganglia and vagus nerves. J Neurochem. 1969 Jul;16(7):1133–1139. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1969.tb05958.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


