Abstract
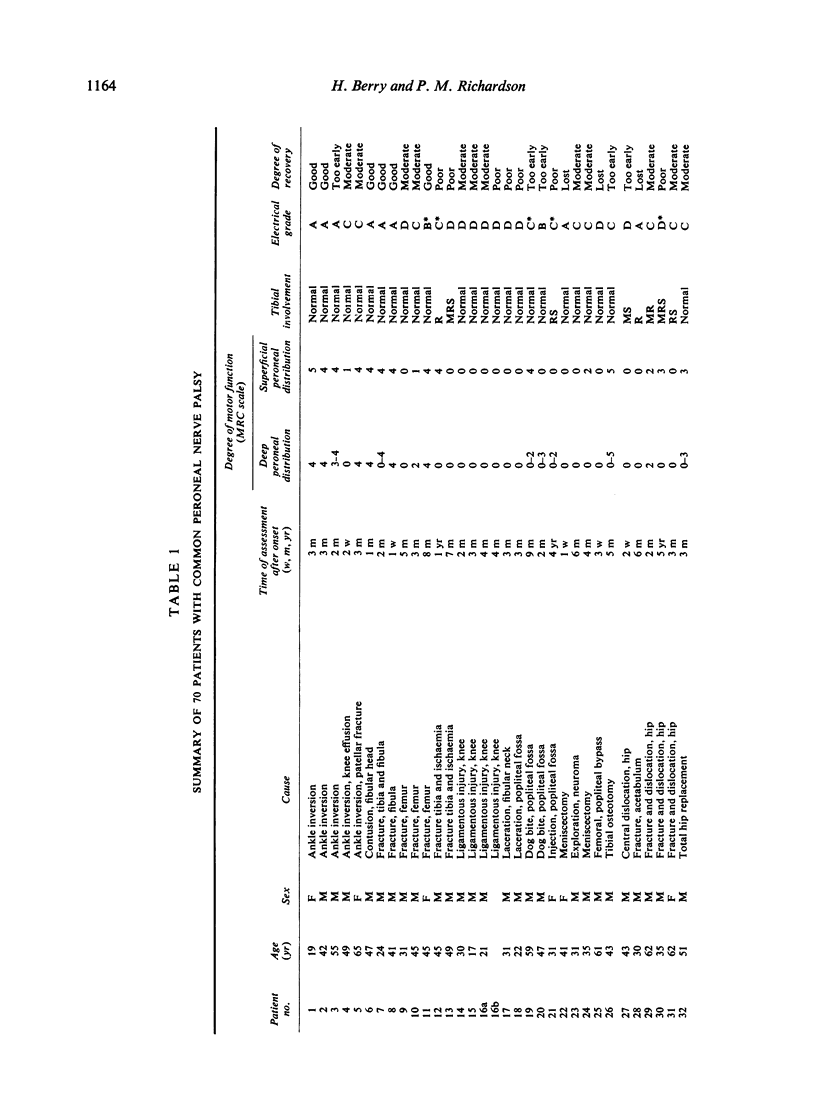
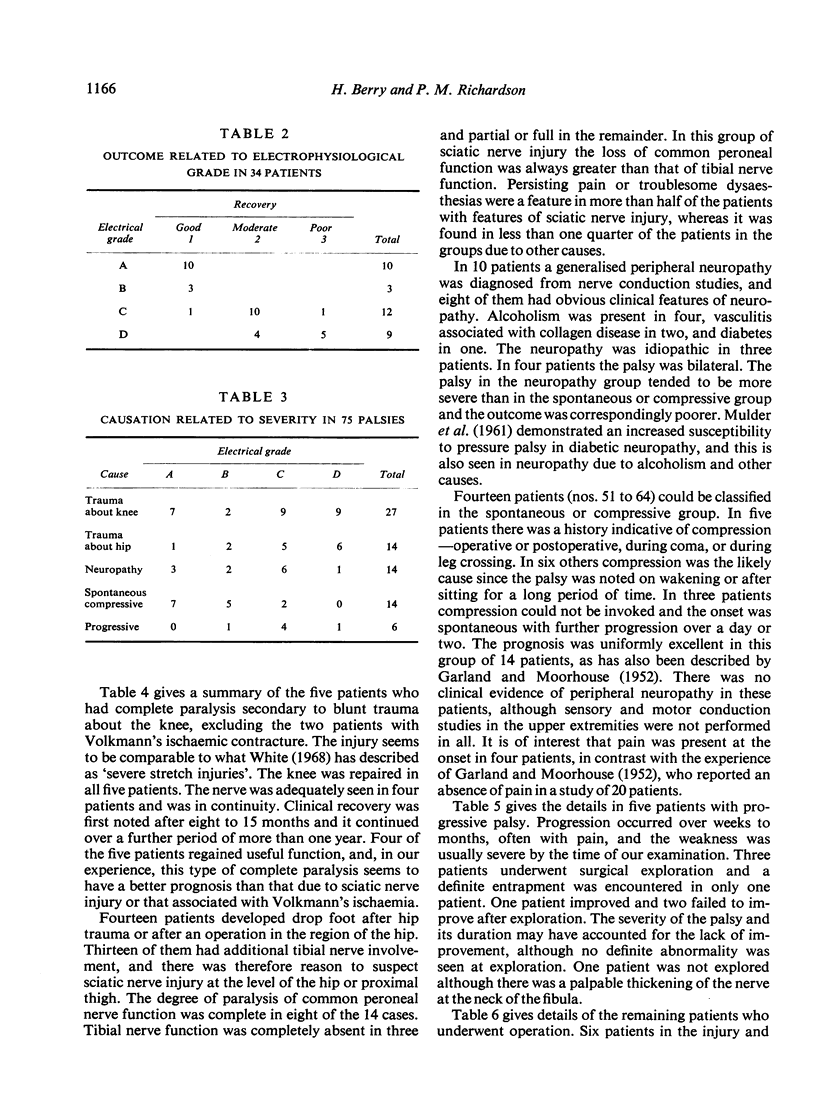
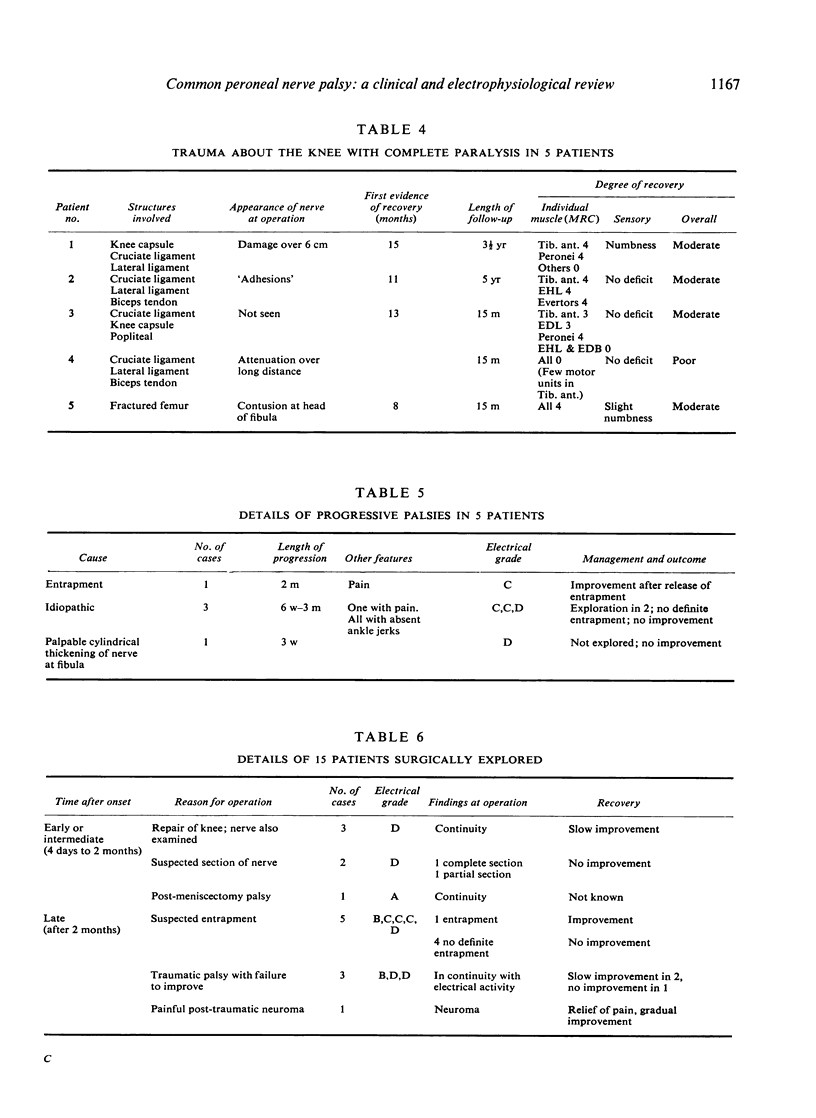
In a series of 70 patients (75 cases of common peroneal nerve palsy) the common causes were trauma about the knee or about the hip, compression, and underlying neuropathy. A few palsies occurred spontaneously for no apparent reason. The prognosis was uniformly good in the compression group; recovery was delayed but usually satisfactory in patients who had suffered stretch injuries. In the acute stage, when clinical paralysis appears to be complete, electrophysiological studies are a useful guide to prognosis. They may also indicate an underlying neuropathy and they detect early evidence of recovery. The anatomical peculiarities of the common peroneal nerve are noted and aspects of the clinical picture, management, and prognosis of palsy are discussed.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BROOKS D. M. Nerve compression by simple ganglia. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1952 Aug;34-B(3):391–400. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.34B3.391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behse F., Buchthal F. Normal sensory conduction in the nerves of the leg in man. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1971 Aug;34(4):404–414. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.34.4.404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLAWSON D. K., SEDDON H. J. The late consequences of sciatic nerve injury. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1960 May;42-B:213–225. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.42B2.213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpendale M. T. The localization of ulnar nerve compression in the hand and arm: an improved method of electroneuromyography. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1966 Jun;47(6):325–330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cobb C. A., 3rd, Moiel R. H. Ganglion of the peroneal nerve. Report of two cases. J Neurosurg. 1974 Aug;41(2):255–259. doi: 10.3171/jns.1974.41.2.0255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FERGUSON F. R., LIVERSEDGE L. A. Ischaemic lateral popliteal nerve palsy. Br Med J. 1954 Aug 7;2(4883):333–335. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.4883.333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GARLAND H., MOORHOUSE D. Compressive lesions of the external popliteal (common peroneal) nerve. Br Med J. 1952 Dec 27;2(4799):1373–1378. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.4799.1373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GASSEL M. M., TROJABORG W. CLINICAL AND ELECTROPHYSIOLOGICAL STUDY OF THE PATTERN OF CONDUCTION TIMES IN THE DISTRIBUTION OF THE SCIATIC NERVE. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1964 Aug;27:351–357. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.27.4.351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutmann L. Atypical deep peroneal neuropathy in presence of accessory deep peroneal nerve. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1970 Aug;33(4):453–456. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.33.4.453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haftek J. Stretch injury of peripheral nerve. Acute effects of stretching on rabbit nerve. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1970 May;52(2):354–365. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kline D. G. Operative management of major nerve lesions of the lower extremity. Surg Clin North Am. 1972 Oct;52(5):1247–1265. doi: 10.1016/s0039-6109(16)39839-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert E. H. The accessory deep peroneal nerve. A common variation in innervation of extensor digitorum brevis. Neurology. 1969 Dec;19(12):1169–1176. doi: 10.1212/wnl.19.12.1169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARWAH V. COMPRESSION OF THE LATERAL POPLITEAL (COMMON PERONEAL) NERVE. Lancet. 1964 Dec 26;2(7374):1367–1369. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(64)91159-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MULDER D. W., LAMBERT E. H., BASTRON J. A., SPRAGUE R. G. The neuropathies associated with diabetes mellitus. A clinical and electromyographic study of 103 unselected diabetic patients. Neurology. 1961 Apr;11(4):275–284. doi: 10.1212/wnl.11.4.275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nobel W. Peroneal palsy due to hematoma in the common peroneal nerve sheath after distal torsional fractures and inversion ankle sprains. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1966 Dec;48(8):1484–1495. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARKES A. Intraneural ganglion of the lateral popliteal nerve. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1961 Nov;43-B:784–790. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.43B4.784. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REDFORD J. B. NERVE CONDUCTION IN MOTOR FIBERS TO THE ANTERIOR TIBIAL MUSCLE IN PERONEAL PALSY. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1964 Oct;45:500–504. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh N., Behse F., Buchthal F. Electrophysical study of peroneal palsy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1974 Nov;37(11):1202–1213. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.37.11.1202. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THOMAS P. K., SEARS T. A., GILLIATT R. W. The range of conduction velocity in normal motor nerve fibers to the small muscles of the hand and foot. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1959 Aug;22:175–181. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.22.3.175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. The results of traction injuries to the common peroneal nerve. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1968 May;50(2):346–350. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


