Abstract
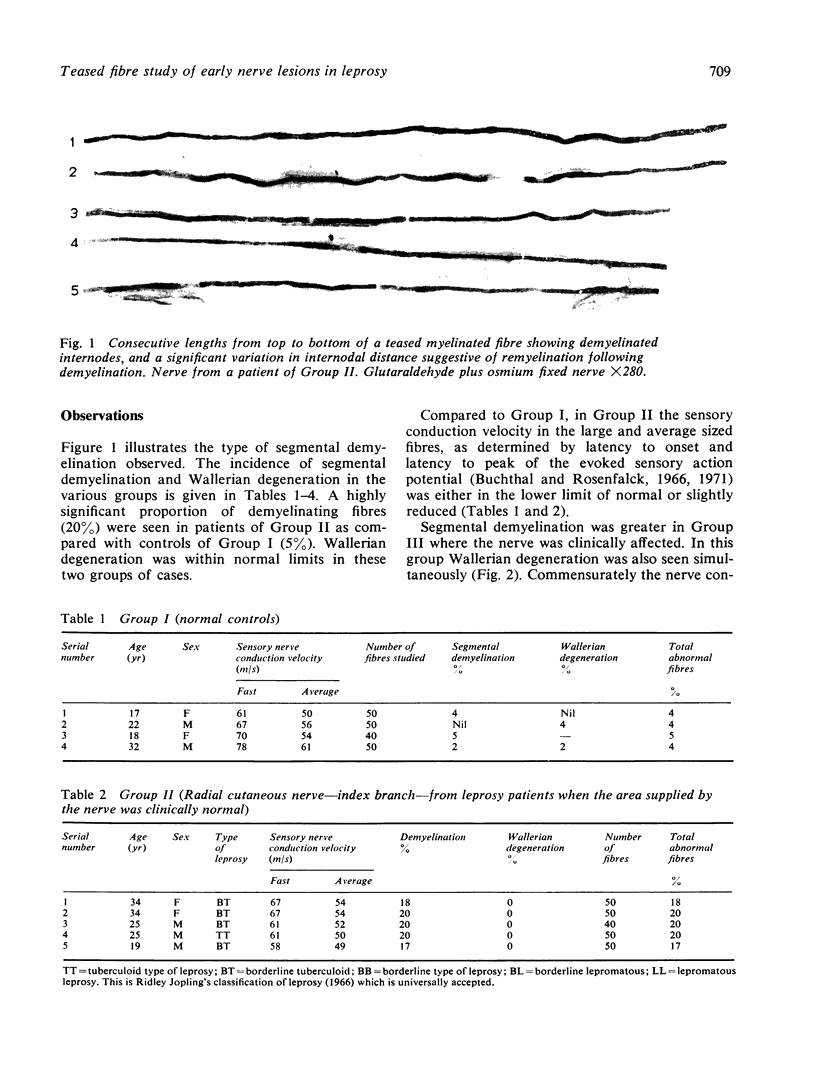
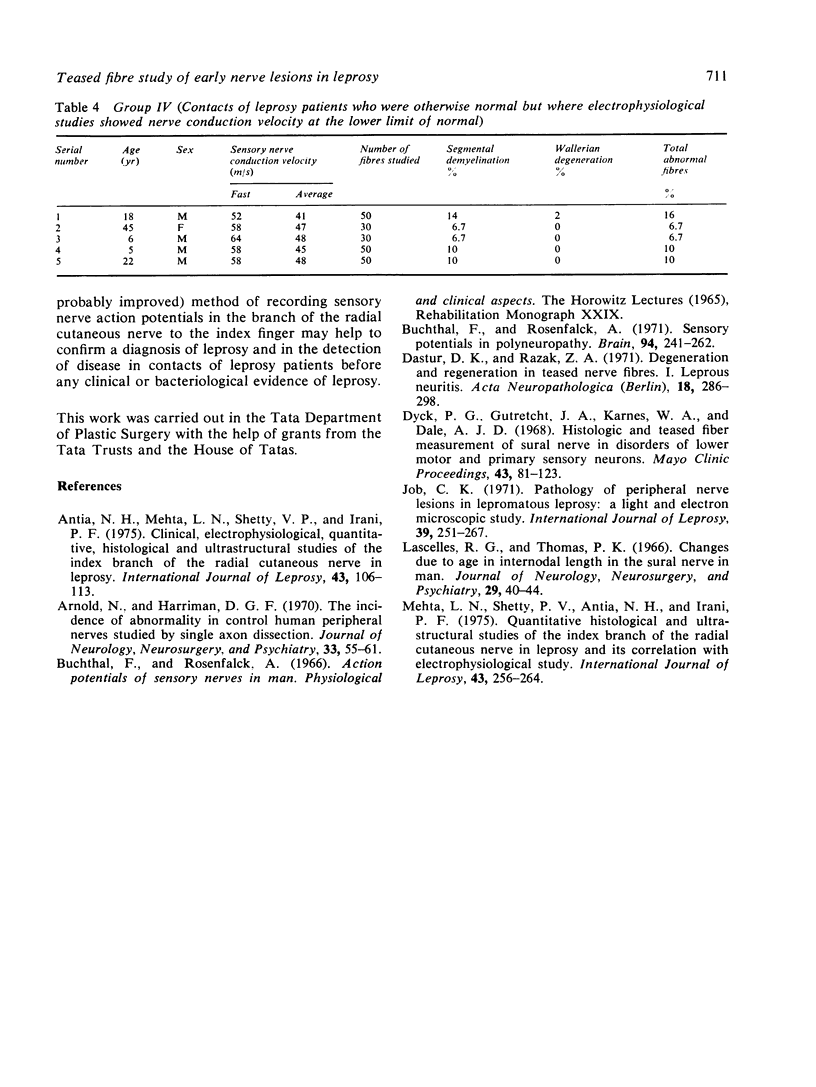
A teased fibre technique was used to study 19 biopsies of the index finger branch of the radial cutaneous nerve of leprosy patients and contacts. These were compared with four normal nerves. Five nerves were from patients with preclinical nerve lesions, five from leprosy patients with minimal sensory nerve impairment, and five from contacts of lepromatous leprosy. The extent of demyelination in preclinical nerve lesions in leprosy and in contacts of leprosy is recorded. The usefulness of nerve conduction velocity studies in early leprosy patients and in contacts is discussed.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Antia N. H., Mehta L., Shetty V., Irani P. F. Clinical, electrophysiological, quantitative, histologic and ultrastructural studies of the index branch of the radial cutaneous nerve in leprosy. I. Preliminary report. Int J Lepr Other Mycobact Dis. 1975 Apr-Jun;43(2):106–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnold N., Harriman D. G. The incidence of abnormality in control human peripheral nerves studied by single axon dissection. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1970 Feb;33(1):55–61. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.33.1.55. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchthal F., Rosenfalck A. Sensory potentials in polyneuropathy. Brain. 1971;94(2):241–262. doi: 10.1093/brain/94.2.241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dastur D. K., Razzak Z. A. Degeneration and regeneration in teased nerve fibres. I. Leprous neuritis. Acta Neuropathol. 1971;18(4):286–298. doi: 10.1007/BF00688442. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyck P. J., Gutrecht J. A., Bastron J. A., Karnes W. E., Dale A. J. Histologic and teased-fiber measurements of sural nerve in disorders of lower motor and primary sensory neurons. Mayo Clin Proc. 1968 Feb;43(2):81–123. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Job C. K. Pathology of peripheral nerve lesions in lepromatous leprosy--a light and electron microscopic study. Int J Lepr Other Mycobact Dis. 1971 Apr-Jun;39(2):251–268. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lascelles R. G., Thomas P. K. Changes due to age in internodal length in the sural nerve in man. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1966 Feb;29(1):40–44. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.29.1.40. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehta L. N., Shetty V. P., Antia N. H., Irani P. F. Quantitative, histologic and ultrastructural studies of the index branch of the radial cutaneous nerve in leprosy and its correlation with electrophysiologic study. Int J Lepr Other Mycobact Dis. 1975 Jul-Sep;43(3):256–264. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




