Abstract
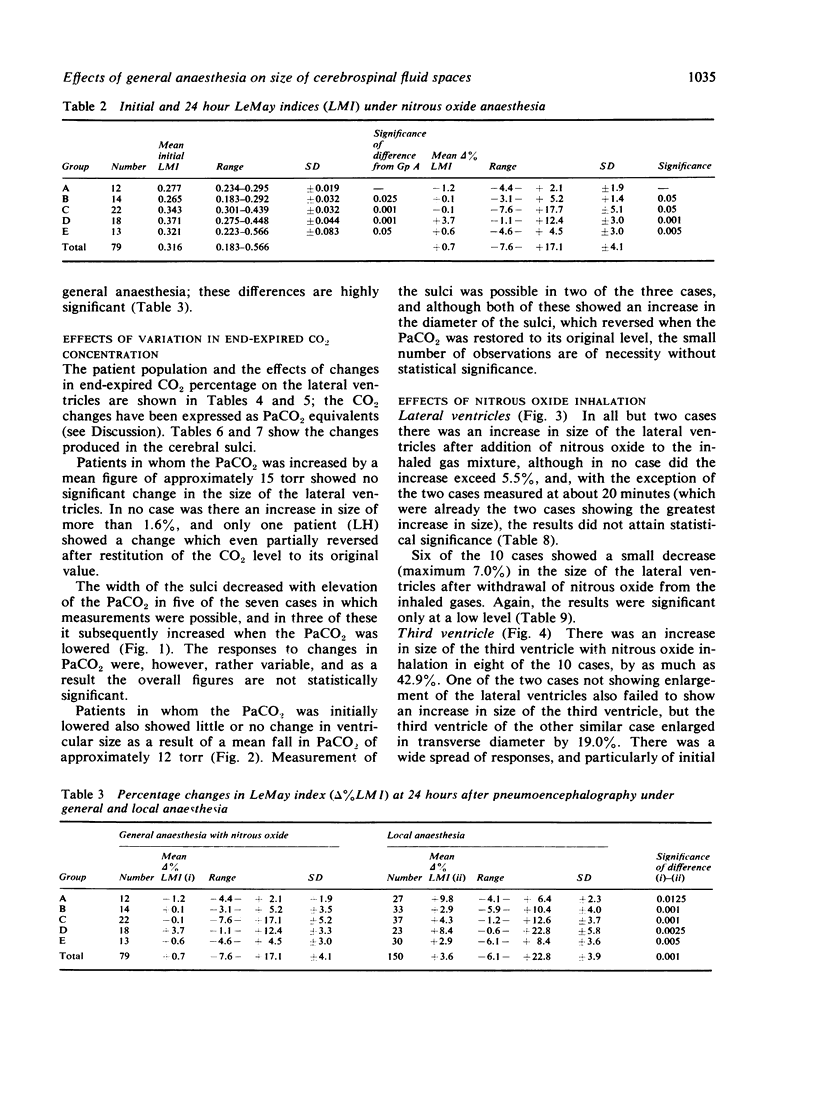
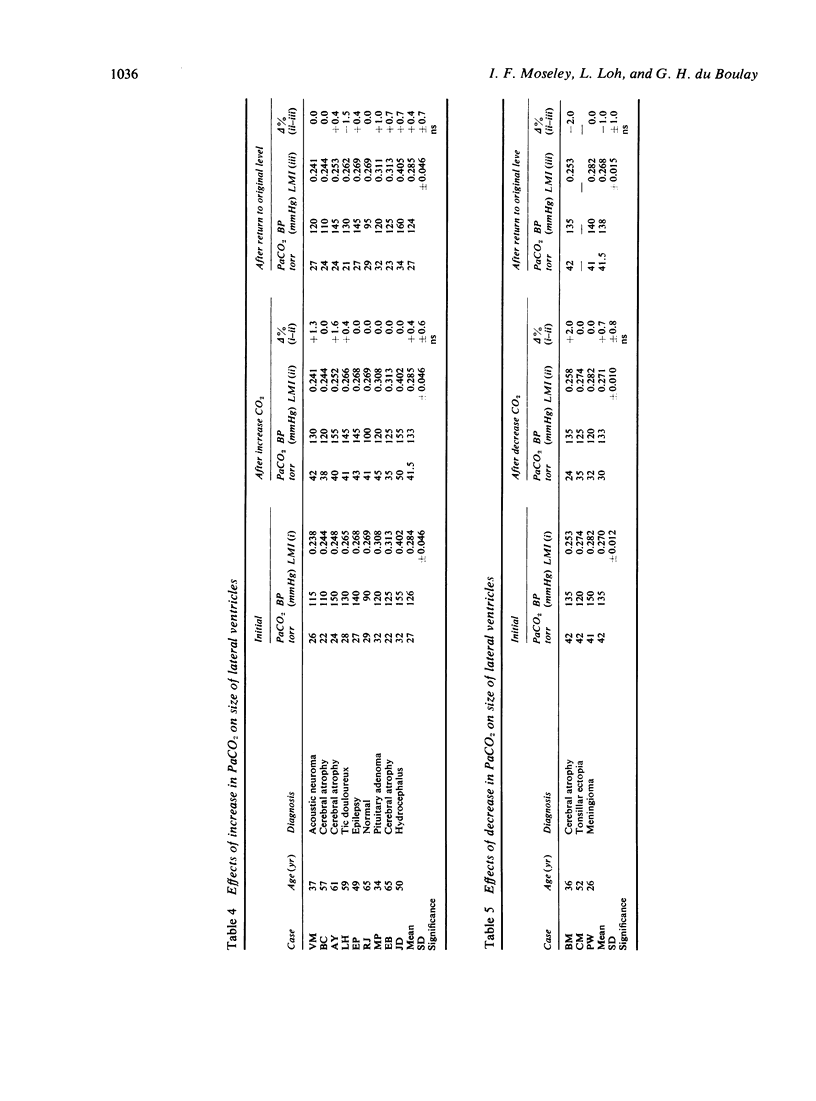
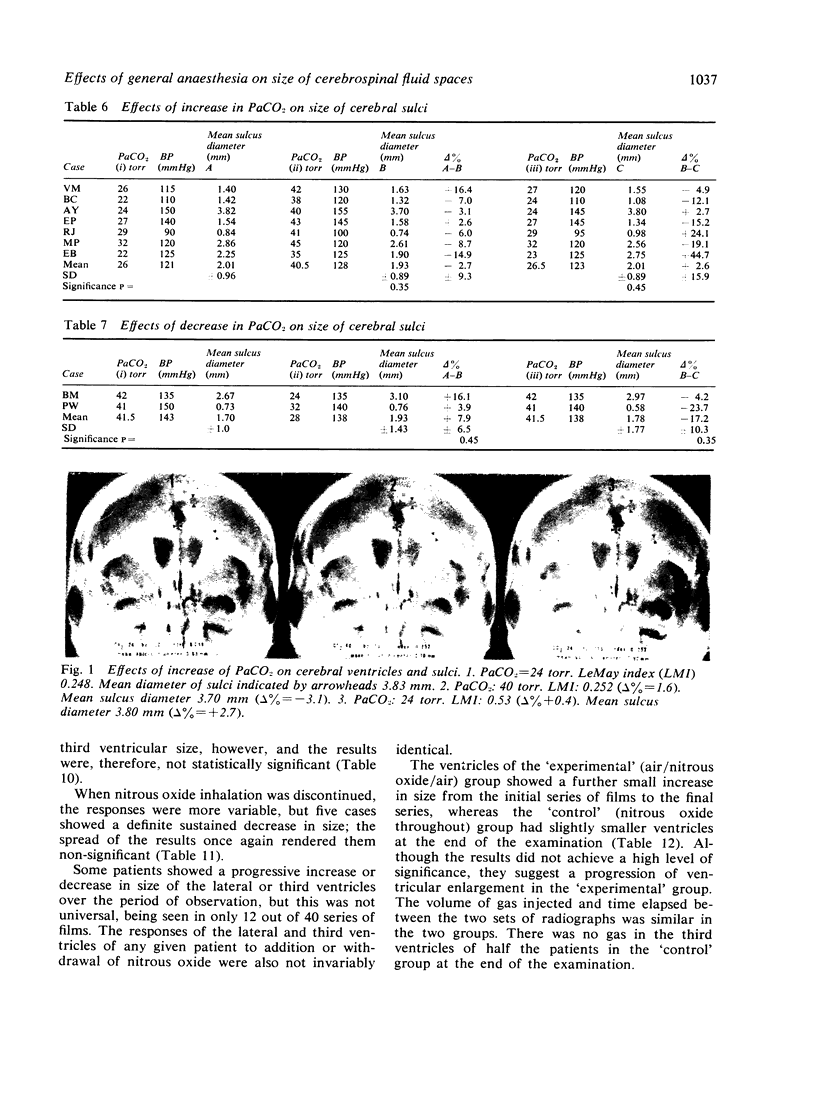
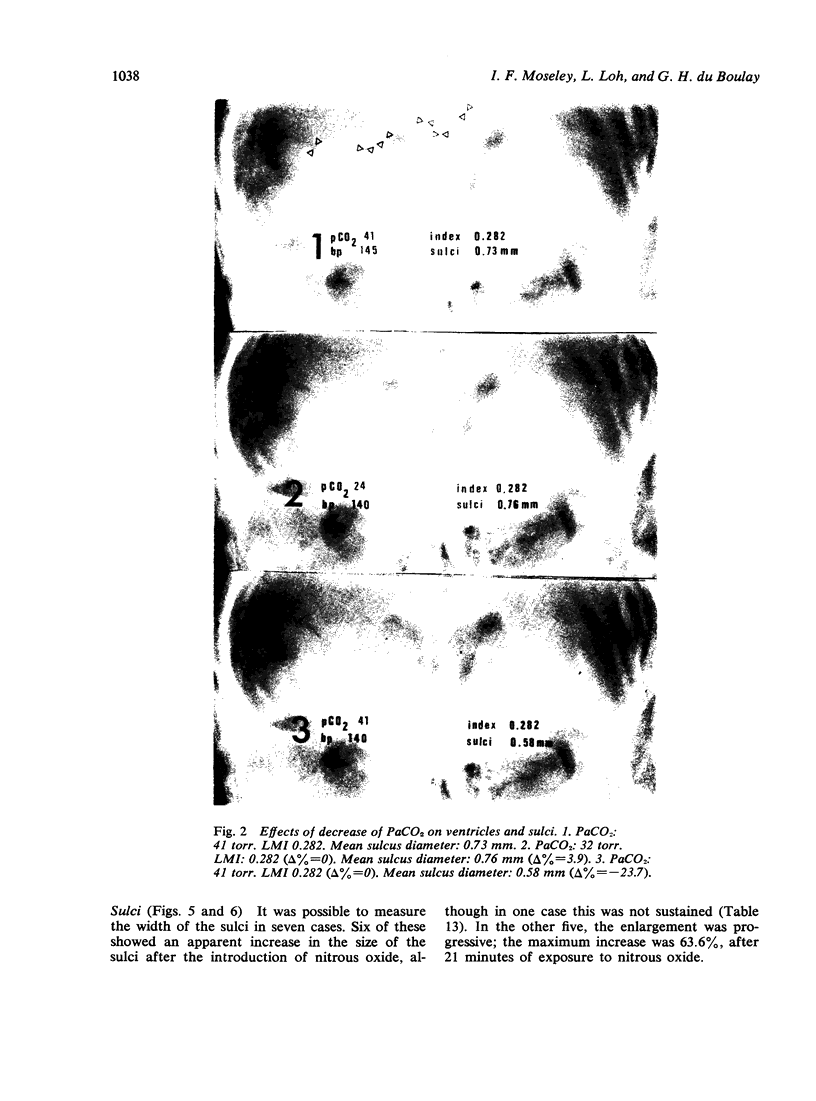
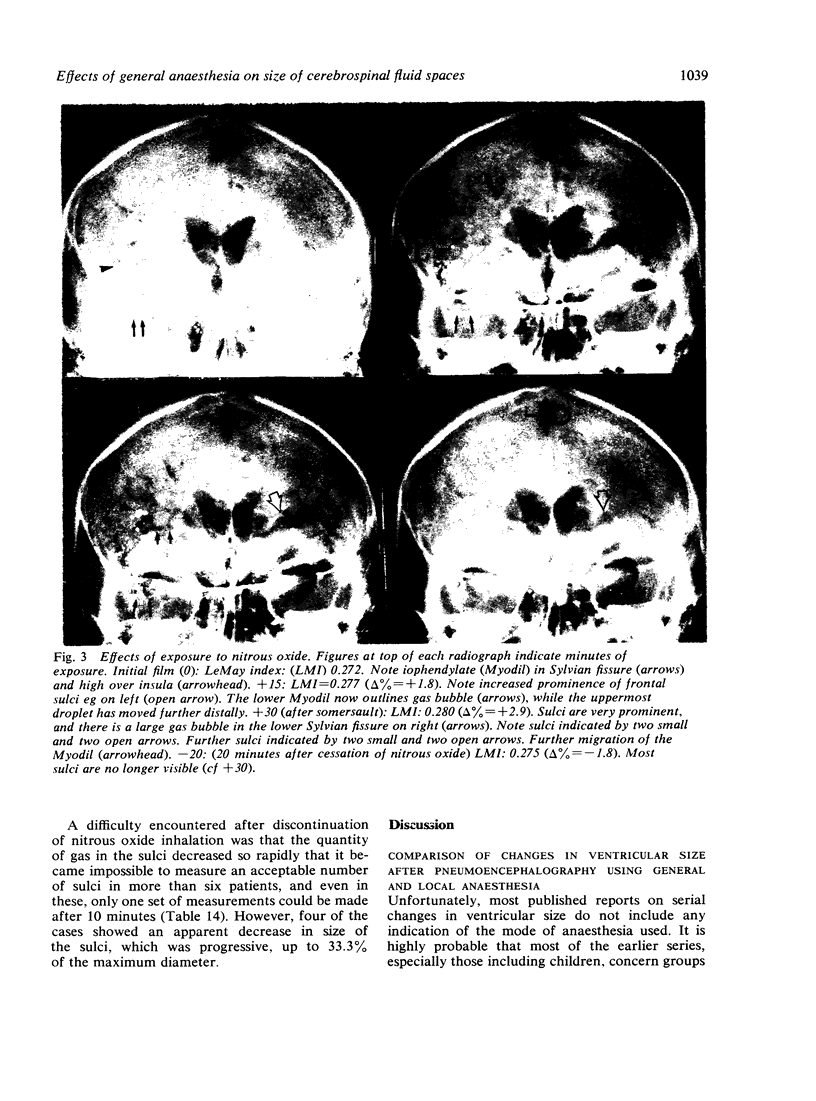
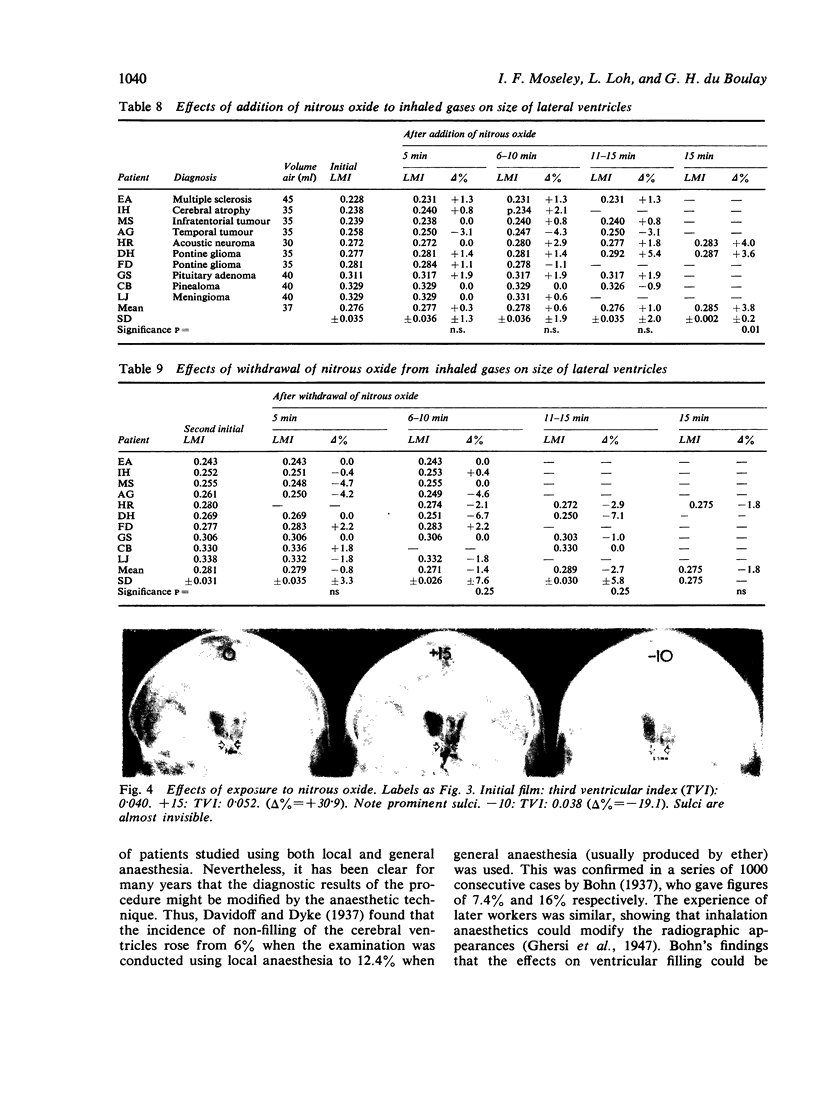
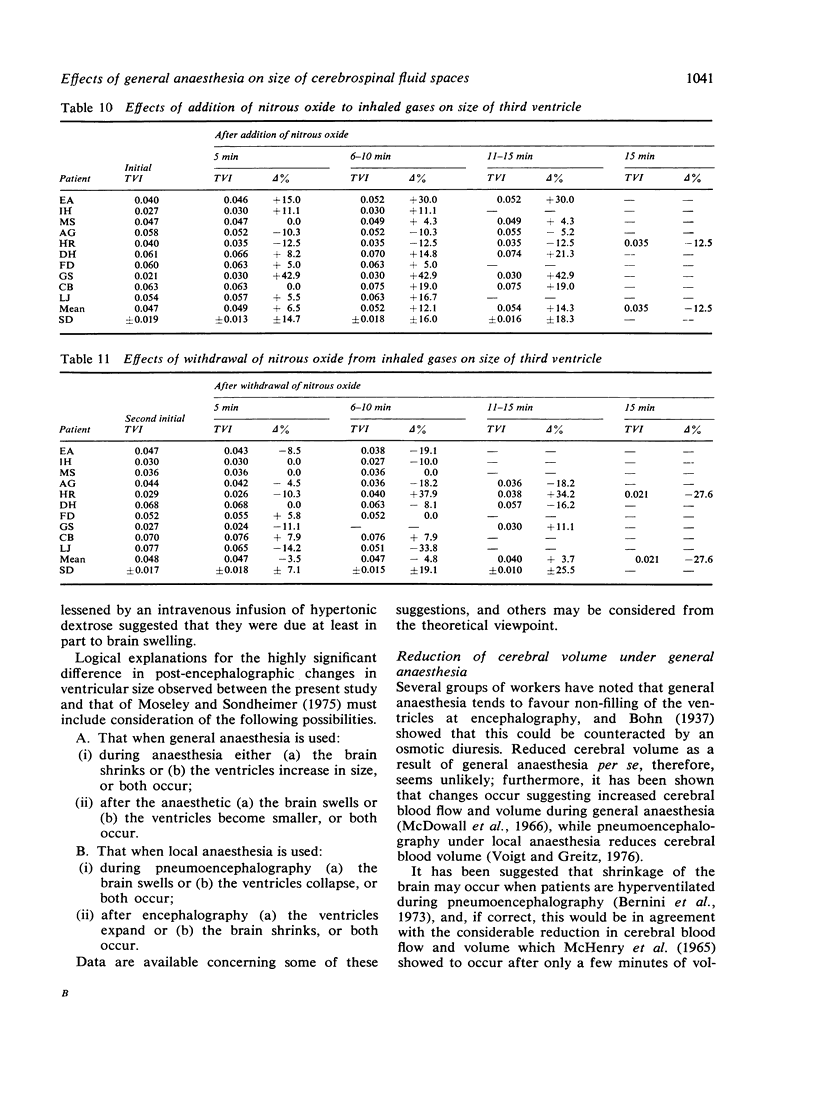
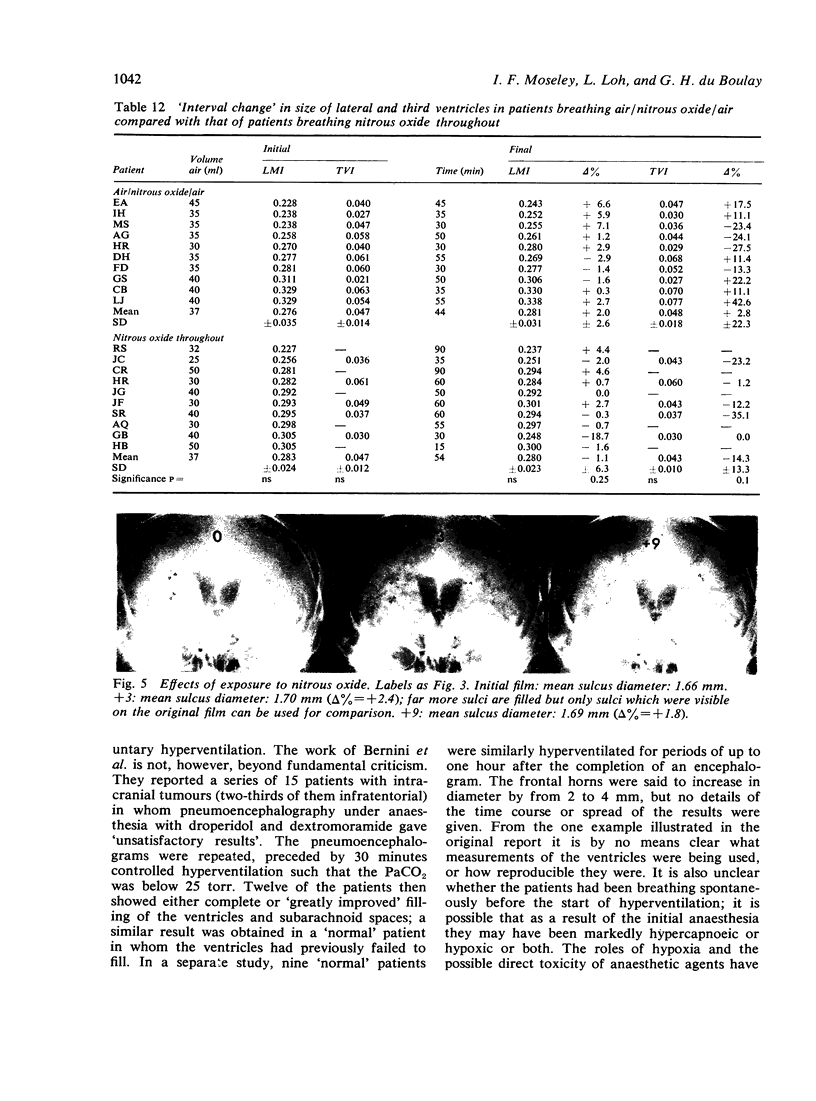
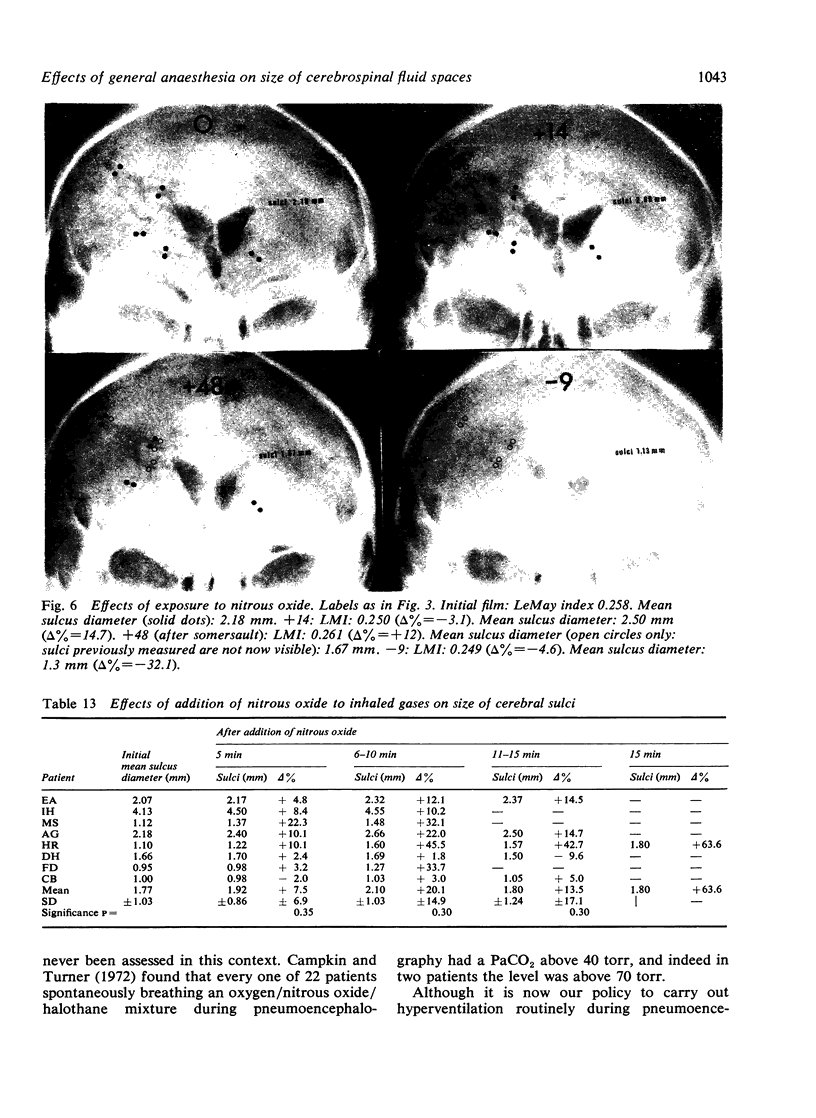
The mode of anaesthesia used during pneumoencephalography has a significant effect on the size of the cerebral ventricles 24 hours after the procedure. Post-encephalographic ventricular enlargement is less marked in patients examined under nitrous oxide anaesthesia. This appears to be related to passage of the gas into the ventricles during the encephalogram, and subsequent diffusion outwards. Variations in arterial carbon dioxide tension during the anaesthesia do not contribute significantly to changes in ventricular size. However, both hyperventilation and inhalation of nitrous oxide may cause apparent increase in size of the cerebral sulci.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AIRD R. B., ZEALEAR D. Pneumoencephalographic study of cerebrospinal fluid absorptive-block mechanisms; a study of the mechanism involved in production of increased intracranial pressure. AMA Arch Neurol Psychiatry. 1951 Aug;66(2):199–212. doi: 10.1001/archneurpsyc.1951.02320080083008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOZZAMARRUBINI M., ROSSANDA M., TRETOLA L. THE ROLE OF ARTIFICIAL HYPERVENTILATION IN THE CONTROL OF BRAIN TENSION DURING NEUROSURGICAL OPERATIONS. Br J Anaesth. 1964 Jul;36:415–431. doi: 10.1093/bja/36.7.415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergström K., Högström S., Lodin H. Experiences with nitrous oxide-oxygen as contrast medium in encephalography and ventriculography performed under general anaesthesia. Ann Radiol (Paris) 1967;10(3):189–191. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernini F. P., Calabro A., Mazzarella B., Smaltino Controlled hyperventilation in fractional encephalography. Preliminary note. Neuroradiology. 1973 Aug;5(4):190–194. doi: 10.1007/BF00394733. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRONQVIST S., LUNDBERG N., PONTEN U. CEREBRAL PNEUMOGRAPHY WITH CONTINUOUS CONTROL OF VENTRICULAR FLUID PRESSURE. Acta Radiol Diagn (Stockh) 1963 May;1:558–564. doi: 10.1177/028418516300100303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campkin T. V., Turner J. M. Blood pressure and cerebrospinal fluid pressure studies during lumbar air encephalography. Br J Anaesth. 1972 Aug;44(8):849–853. doi: 10.1093/bja/44.8.849. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collan R., Iivanainen M. Cardiac arrest caused by rapid elimination of nitrous oxde from cerebral ventricles after encephalography. Can Anaesth Soc J. 1969 Nov;16(6):519–524. doi: 10.1007/BF03004545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gawler J., Du Boulay G. H., Bull J. W., Marshall J. Computerized tomography (the EMI Scanner): a comparison with pneumoencephalography and ventriculography. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1976 Mar;39(3):203–211. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.39.3.203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon E., Greitz T. The effect of nitrous oxide on the cerebrospinal fluid pressure during encephalography. Br J Anaesth. 1970 Jan;42(1):2–8. doi: 10.1093/bja/42.1.2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauke H., Schmitz H. P., Wenner J. Pneumoencephalography: resorption of injected air after oxygen inhalation. Ann Radiol (Paris) 1967;10(3):185–188. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iliff L. D., Zilkha E., Du Boulay G. H., Marshall J., Moseley I. F., Russell R. W., Symon L. Cerebrovascular carbon dioxide reactivity and conductance in patients awake and under general anesthesia. Neurology. 1976 Sep;26(9):835–838. doi: 10.1212/wnl.26.9.835. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iliff L., Zilkha E., Bull J. W., Du Boulay G. H., McAllister V. L., Marshall J., Russell R. W., Symon L. Effect of changes in cerebral blood flow on proportion of high and low flow tissue in the brain. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1974 Jun;37(6):631–635. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.37.6.631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JIROUT J. Changes in the size of the subarachnoid spaces after the insufflation of air. Acta radiol. 1956 Jul-Aug;46(1-2):81–86. doi: 10.3109/00016925609170815. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jährig K., Zöllner H. Veränderungen des Säuren-Basen-Status im Liquor cerebrospinalis unter der Pneumencephalographie. Nervenarzt. 1971 Mar;42(3):152–154. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le May M. Changes in ventricular size during and after pneumoencephalography. Radiology. 1967 Jan;88(1):57–63. doi: 10.1148/88.1.57. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lim S. T., Potts G., Deck M. D. Changes in the ventricular size during fractional pneumoencephalography. Radiology. 1972 Sep;104(3):585–592. doi: 10.1148/104.3.585. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCHENRY L. C., Jr, SLOCUM H. C., BIVENS H. E., MAYES H. A., HAYES G. J. HYPERVENTILATION IN AWAKE AND ANESTHETIZED MAN. EFFECTS ON CEREBRAL BLOOD FLOW AND CEREBRAL METABOLISM. Arch Neurol. 1965 Mar;12:270–277. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1965.00460270046006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mallamo J. R., Hubbard R. B., Boone S. C., Reisner L. S., Pister J. D. Expansion of an air-filled subdural space during nitrous oxide anesthesia. Radiology. 1975 May;115(2):369–372. doi: 10.1148/115.2.369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDowall D. G., Barker J., Jennett W. B. Cerebro-spinal fluid pressure measurements during anaesthesia. Anaesthesia. 1966 Apr;21(2):189–201. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2044.1966.tb02598.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moseley I. F., Sondheimer F. K. The twenty-four hour pneumoencephalogram: with particular reference to ventricular size a series of 150 patients and a review of the literature. Clin Radiol. 1975 Jul;26(3):389–408. doi: 10.1016/s0009-9260(75)80084-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oberson R., Candardjis G., Raad N. Height of fourth ventricle. Normal variability during pneumography. Acta Radiol Diagn (Stockh) 1969;9:193–198. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oigaard A. Changes in ventricular size during pneumoencephalography. Neuroradiology. 1971 Nov;3(1):8–11. doi: 10.1007/BF00346110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pannier J. L., Weyne J., Leusen I. Effects of changes in acid-base composition in the cerebral ventricles on local and general cerebral blood flow. Eur Neurol. 1971;6(1):123–126. doi: 10.1159/000114479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul W. L., Munson E. S. Case history number 88: gas embolism during encephalography. Anesth Analg. 1976 Jan-Feb;55(1):141–145. doi: 10.1213/00000539-197601000-00038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petrov H. Neue Wege in der Pneumencephalographie. Radiologe. 1966 Dec;6(12):503–503. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philippart C., Thibaut A., Bonnal J. Effets de l'inhalation de protoxyde d'azote au cours des explorations neuroradiologiques réalisées avec l'air. Neurochirurgie. 1968 Mar;14(2):97–104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Probst F. P. Gas distension of the lateral ventricles at encephalography. Acta Radiol Diagn (Stockh) 1973 Jan;14(1):1–4. doi: 10.1177/028418517301400101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Probst F. P. Rapid changes in the volume of the lateral ventricles at encephalography. Acta Radiol Diagn (Stockh) 1972 Nov;12(6):757–768. doi: 10.1177/028418517201200609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAIDMAN L. J., EGER E. I., 2nd CHANGE IN CEREBROSPINAL FLUID PRESSURE DURING PNEUMOENCEPHALOGRAPHY UNDER NITROUS OXIDE ANESTHESIA. Anesthesiology. 1965 Jan-Feb;26:67–72. doi: 10.1097/00000542-196501000-00012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley T. H., Kawamura R., Graves C. Effects of nitrous oxide on volume and pressure of endotracheal tube cuffs. Anesthesiology. 1974 Sep;41(3):256–262. doi: 10.1097/00000542-197409000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voigt K., Greitz T. Cerebral blood volume alterations during fractional pneumoencephalography. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1976 Mar;126(3):582–592. doi: 10.2214/ajr.126.3.582. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson I. M., Bull J. W., Duboulay G. H., Marshall J., Russell R. W., Symon L. Regional blood flow in the normal cerebral hemisphere. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1969 Oct;32(5):367–378. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.32.5.367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]