Abstract
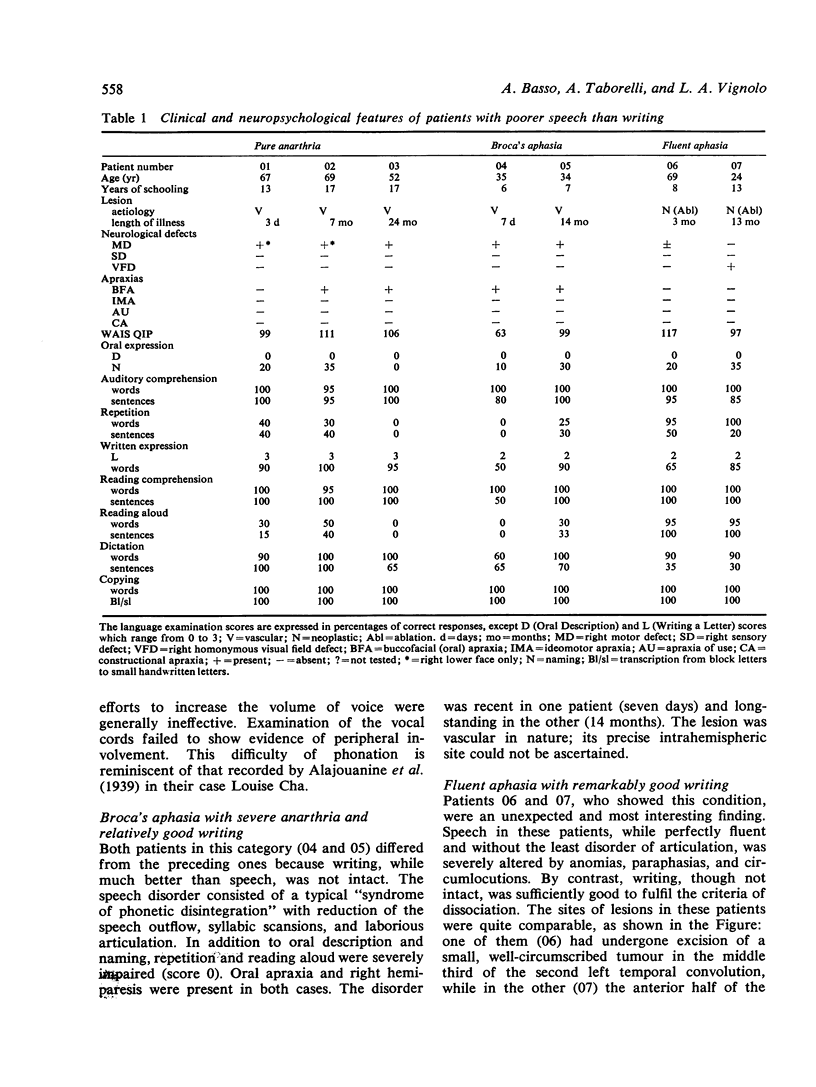
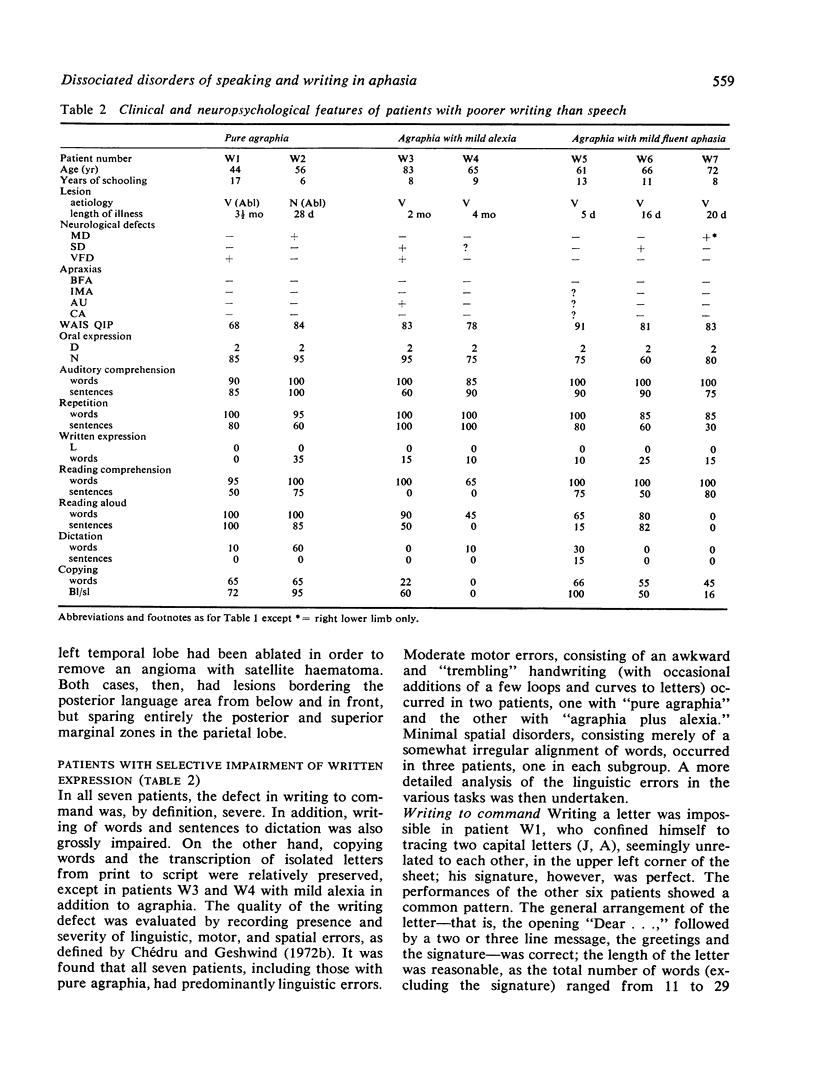
Of 500 left brain-damaged patients with educational level above elementary school investigated with a standard quantitative battery for dissociation between oral and written expression, speech was found to be selectively impaired in seven (three with "pure anarthria," two with anarthria in the context of Broca's aphasia, and two with fluent aphasia with remarkable sparing of writing), and writing in another seven (two with "pure" agraphia, two with "agraphia with mild alexia," and three with "agraphia with mild fluent aphasia.") The nature of three conditions (pure anarthria, fluent aphasia with sparing of writing, and pure agraphia) is discussed, with evidence of a selective association between pure agraphia and lesions of the upper left parietal lobule.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALAJOUANINE T., LHERMITTE F. [Disorders of language expressive activities in aphasia. Their relation to apraxia]. Rev Neurol (Paris) 1960 Jun;102:604–629. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chédru F., Geschwind N. Disorders of higher cortical functions in acute confusional states. Cortex. 1972 Dec;8(4):395–411. doi: 10.1016/s0010-9452(72)80004-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chédru F., Geschwind N. Writing disturbances in acute confusional states. Neuropsychologia. 1972 Sep;10(3):343–353. doi: 10.1016/0028-3932(72)90026-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Renzi E., Scotti G. Autotopagnosia: fiction or reality? Report of a case. Arch Neurol. 1970 Sep;23(3):221–227. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1970.00480270031005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heilman K. M., Coyle J. M., Gonyea E. F., Geschwind N. Apraxia and agraphia in a left-hander. Brain. 1973;96(1):21–28. doi: 10.1093/brain/96.1.21. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heilman K. M., Gonyea E. F., Geschwind N. Apraxia and agraphia in a right-hander. Cortex. 1974 Sep;10(3):284–288. doi: 10.1016/s0010-9452(74)80021-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hier D. B., Mohr J. P. Incongruous oral and written naming. Evidence for a subdivision of the syndrome of Wernicke's aphasia. Brain Lang. 1977 Jan;4(1):115–126. doi: 10.1016/0093-934x(77)90010-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lecours A. R. The "Pure Form" of the phonetic disintegration syndrome (pure anarthria); anatomo-clinical report of a historical case. Brain Lang. 1976 Jan;3(1):88–113. doi: 10.1016/0093-934x(76)90008-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lhermitte F., Derouesné J. Paraphasies et jargonaphasie dans le langage oral avec conservation du langage écrit. Genèse des néologismes. Rev Neurol (Paris) 1974 Jan-Feb;130(1-2):21–38. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


