Abstract
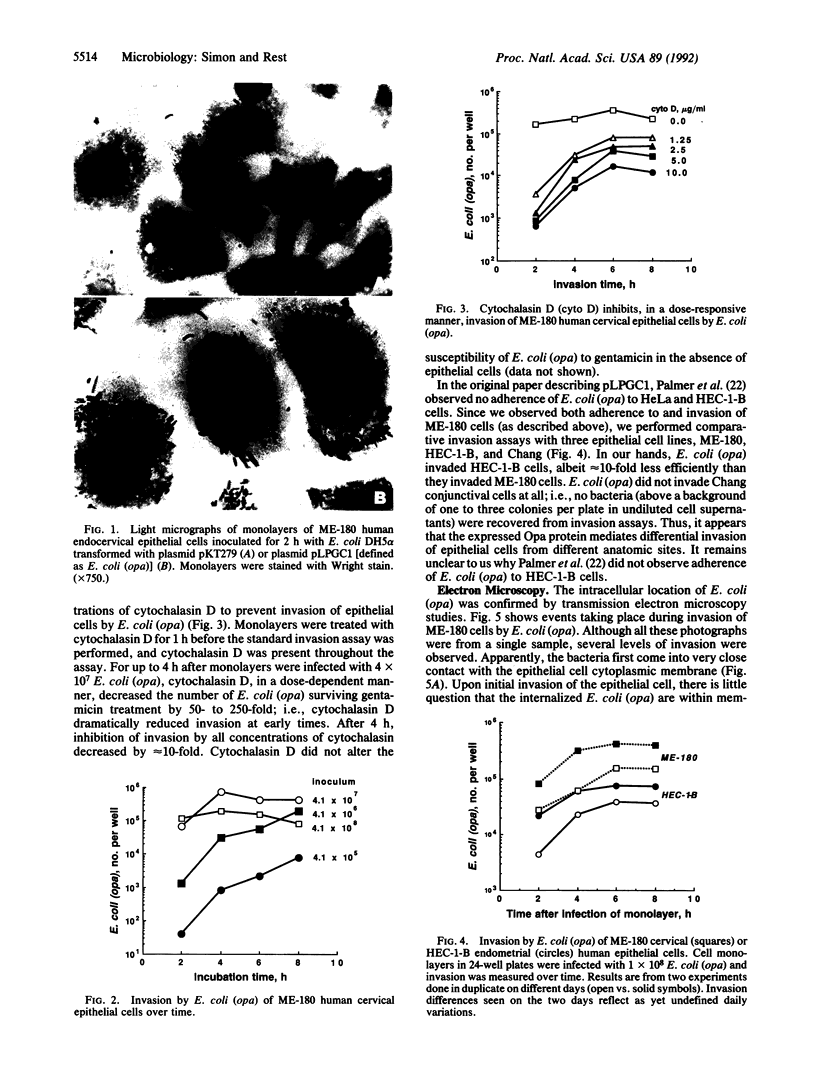
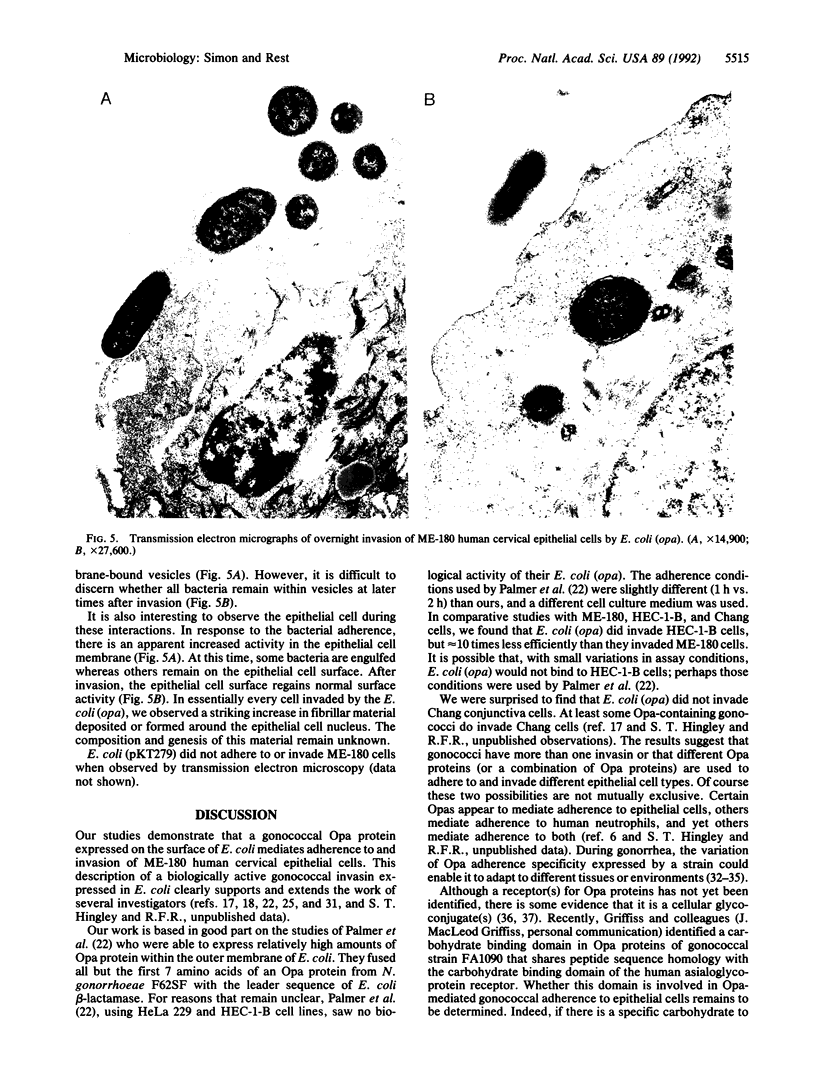
Members of the opacity-associated (Opa) outer membrane protein family of Neisseria gonorrhoeae have been proposed to mediate adherence to and invasion of cultured human epithelial cells. We transformed Escherichia coli with a plasmid containing a gonococcal opa gene fused in-frame to the leader sequence of the beta-lactamase gene as described by Palmer et al. [Palmer, L., Brooks, G. F. & Falkow, S. (1989) Mol. Microbiol. 3, 663-671]. These transformed E. coli [E. coli (opa)] expressed the heat-modifiable opa gene product (the Opa protein) in their outer membrane and adhered to and invaded ME-180 human endocervical epithelial cells. In a 2-h adherence assay, an average of 26.7 E. coli (opa) adhered per ME-180 cell, whereas the control E. coli carrying only the expression vector (pKT279) did not adhere at all (less than 0.15 bacterium per cell). We investigated the ability of the adherent E. coli (opa) to invade ME-180 epithelial cells by using a gentamicin selection assay. We recovered up to 1 x 10(6) gentamicin-resistant bacteria per monolayer when ME-180 cells were infected with E. coli (opa) compared to less than 10 bacteria when the epithelial cells were infected with the same number of control E. coli (pKT279). The kinetics and level of invasion by E. coli (opa) were similar to invasion by Opa+ N. gonorrhoeae. Maximum invasion occurred 4 h after infection with 4 x 10(7) bacteria. Transmission electron microscopy studies confirmed that E. coli (opa) invaded ME-180 cells. In comparative studies, the number of E. coli (opa) that invaded HEC-1-B human endometrial epithelial cells was about an order of magnitude less than the number that invaded ME-180 cells, and E. coli (opa) did not invade Chang human conjunctival epithelial cells at all. The observations that early (less than 4 h) invasion by E. coli (opa) was dramatically inhibited, in a dose-responsive manner, by the actin-disrupting reagent cytochalasin D but later invasion (8-24 h) was not suggest that invasion mediated by Opa proteins may occur by two mechanisms, only one of which is dependent upon microfilament function. Transmission electron microscopy also revealed that infected epithelial cells had a dramatically increased amount of cytoplasmic fibrillar material surrounding the nucleus. The function and genesis of this material remain unclear. These studies indicate that at least one gonococcal Opa protein is an invasin.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bessen D., Gotschlich E. C. Chemical characterization of binding properties of opacity-associated protein II from Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Infect Immun. 1987 Jan;55(1):141–147. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.1.141-147.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bessen D., Gotschlich E. C. Interactions of gonococci with HeLa cells: attachment, detachment, replication, penetration, and the role of protein II. Infect Immun. 1986 Oct;54(1):154–160. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.1.154-160.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhat K. S., Gibbs C. P., Barrera O., Morrison S. G., Jähnig F., Stern A., Kupsch E. M., Meyer T. F., Swanson J. The opacity proteins of Neisseria gonorrhoeae strain MS11 are encoded by a family of 11 complete genes. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Aug;5(8):1889–1901. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb00813.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchanan T. M., Pearce W. A. Pili as a mediator of the attachment of gonococci to human erythrocytes. Infect Immun. 1976 May;13(5):1483–1489. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.5.1483-1489.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen J. C., Bavoil P., Clark V. L. Enhancement of the invasive ability of Neisseria gonorrhoeae by contact with HecIB, an adenocarcinoma endometrial cell line. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Jun;5(6):1531–1538. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb00800.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connell T. D., Black W. J., Kawula T. H., Barritt D. S., Dempsey J. A., Kverneland K., Jr, Stephenson A., Schepart B. S., Murphy G. L., Cannon J. G. Recombination among protein II genes of Neisseria gonorrhoeae generates new coding sequences and increases structural variability in the protein II family. Mol Microbiol. 1988 Mar;2(2):227–236. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1988.tb00024.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Draper D. L., James J. F., Brooks G. F., Sweet R. L. Comparison of virulence markers of peritoneal and fallopian tube isolates with endocervical Neisseria gonorrhoeae isolates from women with acute salpingitis. Infect Immun. 1980 Mar;27(3):882–888. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.3.882-888.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heckels J. E. The sixth C. L. Oakley lecture. Molecular studies on the pathogenesis of gonorrhoea. J Med Microbiol. 1984 Dec;18(3):293–307. doi: 10.1099/00222615-18-3-293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isberg R. R. Discrimination between intracellular uptake and surface adhesion of bacterial pathogens. Science. 1991 May 17;252(5008):934–938. doi: 10.1126/science.1674624. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isberg R. R., Falkow S. A single genetic locus encoded by Yersinia pseudotuberculosis permits invasion of cultured animal cells by Escherichia coli K-12. Nature. 1985 Sep 19;317(6034):262–264. doi: 10.1038/317262a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isberg R. R., Voorhis D. L., Falkow S. Identification of invasin: a protein that allows enteric bacteria to penetrate cultured mammalian cells. Cell. 1987 Aug 28;50(5):769–778. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90335-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James J. F., Swanson J. Studies on gonococcus infection. XIII. Occurrence of color/opacity colonial variants in clinical cultures. Infect Immun. 1978 Jan;19(1):332–340. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.1.332-340.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King G. J., Swanson J. Studies on gonococcus infection. XV. Identification of surface proteins of Neisseria gonorrhoeae correlated with leukocyte association. Infect Immun. 1978 Aug;21(2):575–584. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.2.575-584.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambden P. R., Heckels J. E., James L. T., Watt P. J. Variations in surface protein composition associated with virulence properties in opacity types of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Gen Microbiol. 1979 Oct;114(2):305–312. doi: 10.1099/00221287-114-2-305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makino S., van Putten J. P., Meyer T. F. Phase variation of the opacity outer membrane protein controls invasion by Neisseria gonorrhoeae into human epithelial cells. EMBO J. 1991 Jun;10(6):1307–1315. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07649.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer L. W. Rates in vitro changes of gonococcal colony opacity phenotypes. Infect Immun. 1982 Aug;37(2):481–485. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.2.481-485.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGee Z. A., Stephens D. S., Hoffman L. H., Schlech W. F., 3rd, Horn R. G. Mechanisms of mucosal invasion by pathogenic Neisseria. Rev Infect Dis. 1983 Sep-Oct;5 (Suppl 4):S708–S714. doi: 10.1093/clinids/5.supplement_4.s708. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moulder J. W. Comparative biology of intracellular parasitism. Microbiol Rev. 1985 Sep;49(3):298–337. doi: 10.1128/mr.49.3.298-337.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer L., Brooks G. F., Falkow S. Expression of gonococcal protein II in Escherichia coli by translational fusion. Mol Microbiol. 1989 May;3(5):663–671. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00214.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paruchuri D. K., Seifert H. S., Ajioka R. S., Karlsson K. A., So M. Identification and characterization of a Neisseria gonorrhoeae gene encoding a glycolipid-binding adhesin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(1):333–337. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.1.333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rest R. F., Lee N., Bowden C. Stimulation of human leukocytes by protein II+ gonococci is mediated by lectin-like gonococcal components. Infect Immun. 1985 Oct;50(1):116–122. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.1.116-122.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rest R. F., Shafer W. M. Interactions of Neisseria gonorrhoeae with human neutrophils. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1989 Apr;2 (Suppl):S83–S91. doi: 10.1128/cmr.2.suppl.s83. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwalbe R. S., Sparling P. F., Cannon J. G. Variation of Neisseria gonorrhoeae protein II among isolates from an outbreak caused by a single gonococcal strain. Infect Immun. 1985 Jul;49(1):250–252. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.1.250-252.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw J. H., Falkow S. Model for invasion of human tissue culture cells by Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Infect Immun. 1988 Jun;56(6):1625–1632. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.6.1625-1632.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugasawara R. J., Cannon J. G., Black W. J., Nachamkin I., Sweet R. L., Brooks G. F. Inhibition of Neisseria gonorrhoeae attachment to HeLa cells with monoclonal antibody directed against a protein II. Infect Immun. 1983 Dec;42(3):980–985. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.3.980-985.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson J., Barrera O., Sola J., Boslego J. Expression of outer membrane protein II by gonococci in experimental gonorrhea. J Exp Med. 1988 Dec 1;168(6):2121–2129. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.6.2121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson J., Kraus S. J., Gotschlich E. C. Studies on gonococcus infection. I. Pili and zones of adhesion: their relation to gonococcal growth patterns. J Exp Med. 1971 Oct 1;134(4):886–906. doi: 10.1084/jem.134.4.886. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson J., Robbins K., Barrera O., Corwin D., Boslego J., Ciak J., Blake M., Koomey J. M. Gonococcal pilin variants in experimental gonorrhea. J Exp Med. 1987 May 1;165(5):1344–1357. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.5.1344. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson J., Sparks E., Young D., King G. Studies on Gonococcus infection. X. Pili and leukocyte association factor as mediators of interactions between gonococci and eukaryotic cells in vitro. Infect Immun. 1975 Jun;11(6):1352–1361. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.6.1352-1361.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson J. Studies on gonococcus infection. IV. Pili: their role in attachment of gonococci to tissue culture cells. J Exp Med. 1973 Mar 1;137(3):571–589. doi: 10.1084/jem.137.3.571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson J. Surface components affecting interactions between Neisserai gonorrhoeae and eucaryotic cells. J Infect Dis. 1977 Aug;136 (Suppl):S138–S143. doi: 10.1093/infdis/136.supplement.s138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talmadge K., Stahl S., Gilbert W. Eukaryotic signal sequence transports insulin antigen in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3369–3373. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tjia K. F., van Putten J. P., Pels E., Zanen H. C. The interaction between Neisseria gonorrhoeae and the human cornea in organ culture. An electron microscopic study. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 1988;226(4):341–345. doi: 10.1007/BF02172964. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Virji M., Heckels J. E. The effect of protein II and pili on the interaction of Neisseria gonorrhoeae with human polymorphonuclear leucocytes. J Gen Microbiol. 1986 Feb;132(2):503–512. doi: 10.1099/00221287-132-2-503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward M. E., Watt P. J., Robertson J. N. The human fallopian tube: a laboratory model for gonococcal infection. J Infect Dis. 1974 Jun;129(6):650–659. doi: 10.1093/infdis/129.6.650. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]