Abstract
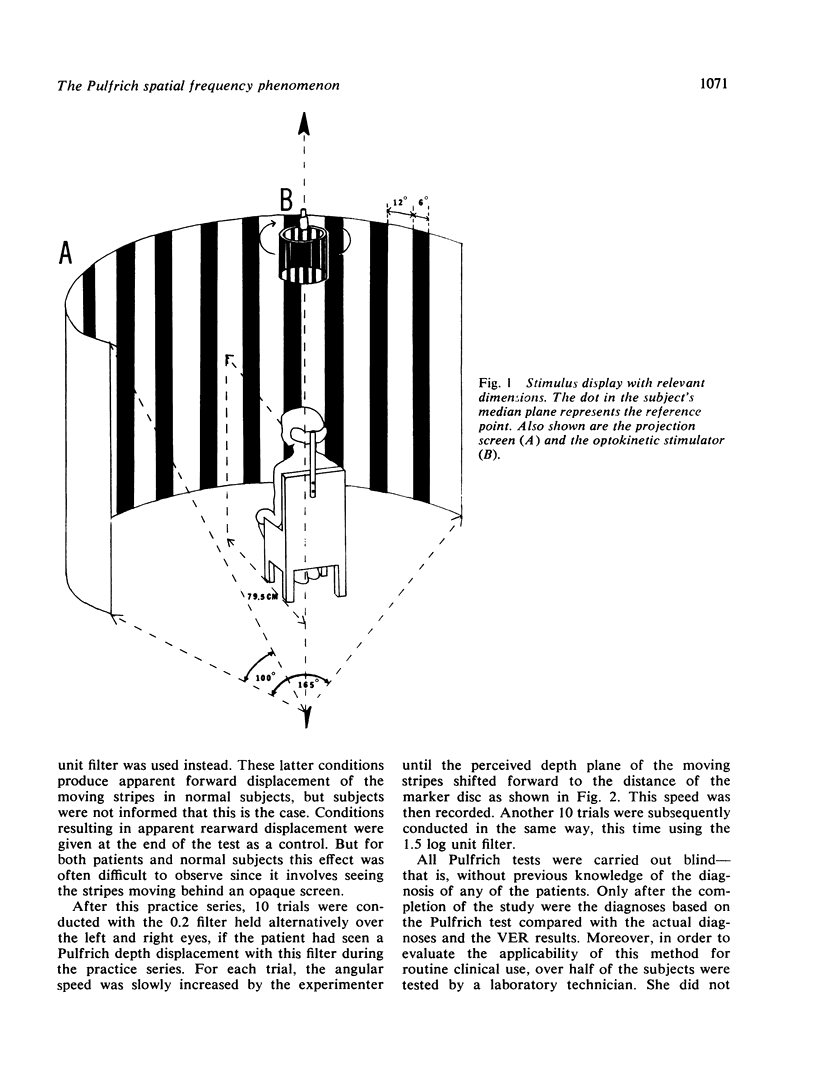
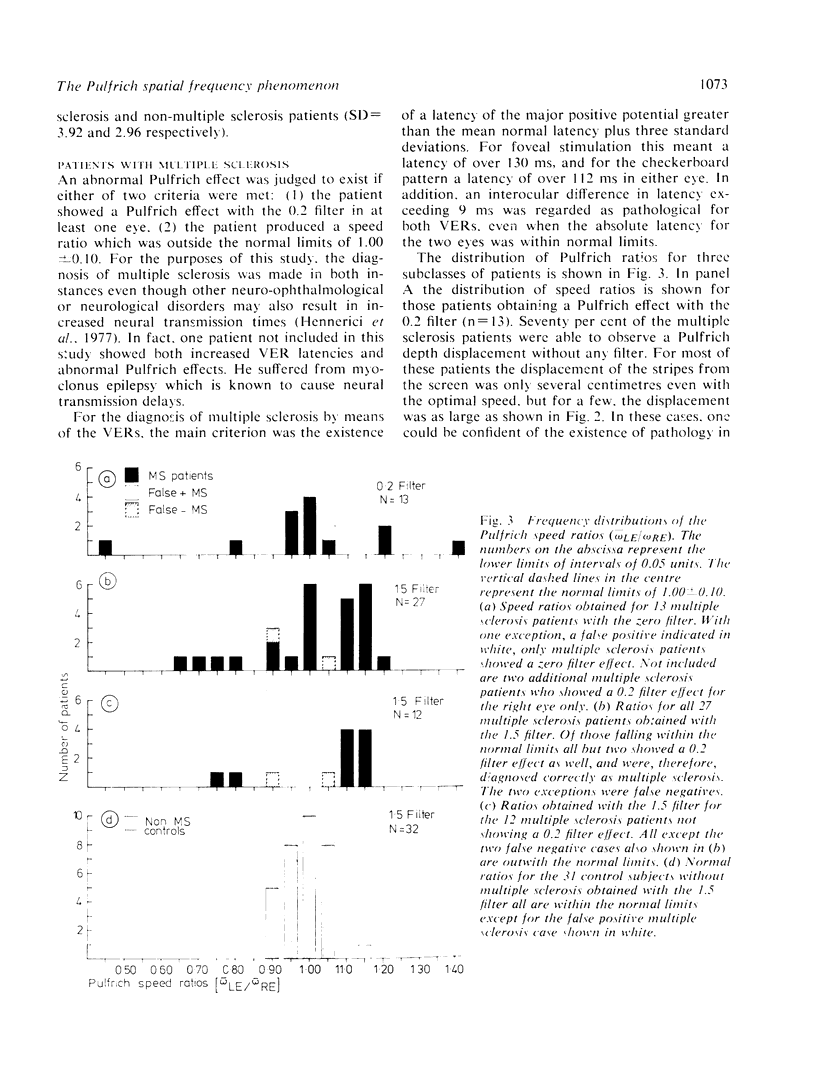
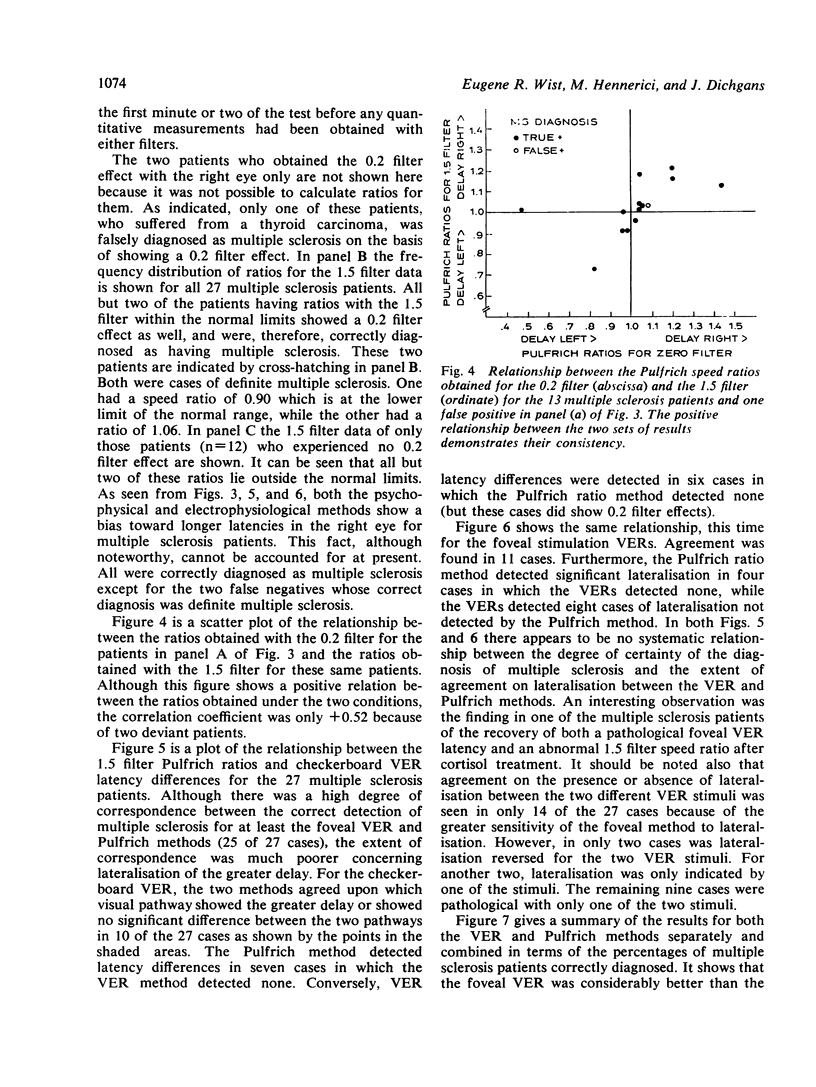
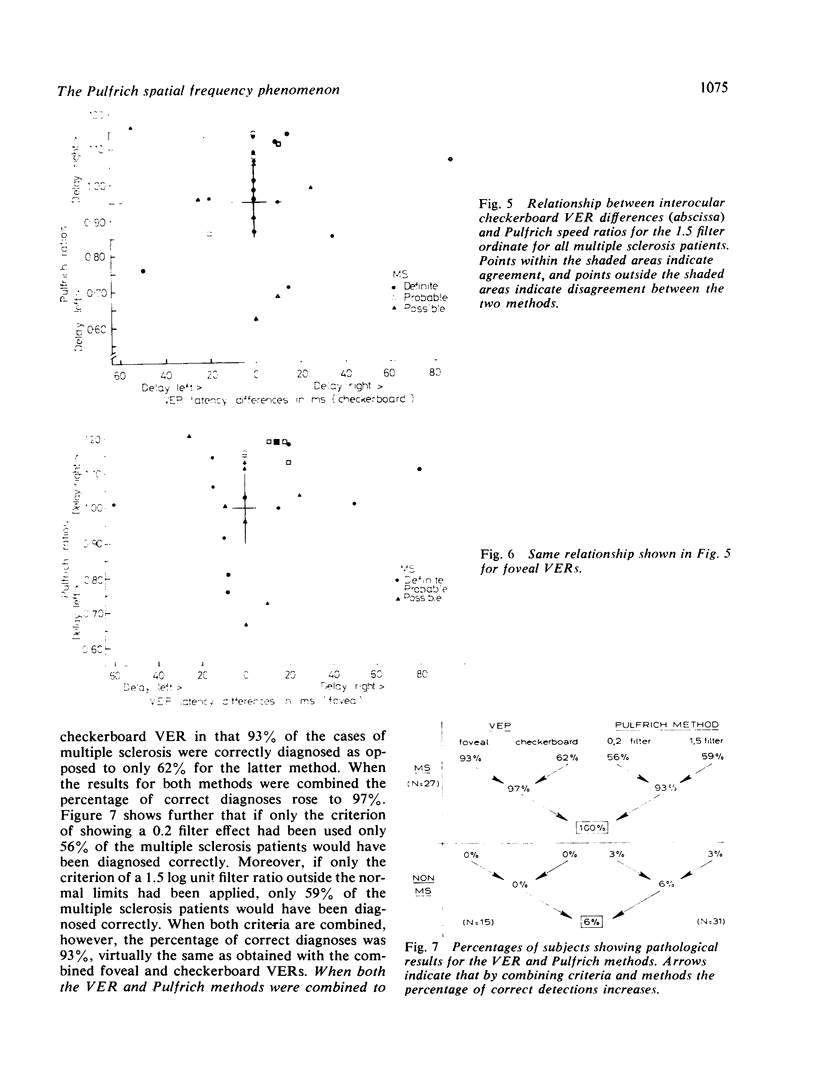
The results of a study in which visual evoked responses (VERs) and a modified Pulfrich method were compared showed that both methods are very effective for the diagnosis of multiple sclerosis. With VERs, 97% of the multiple sclerosis cases were diagnosed correctly, while the corresponding value for the Pulfrich method was 93%. In contrast to VERs, the Pulfrich method allows only measurement of latency differences between the two visual pathways. This method involves measuring the speed required to cause a shift in the apparent depth location of a large, moving, striped pattern observed with a neutral density filter over one eye. A pathological transmission time was inferred when the patients observed a shift in the depth of the moving pattern either without any filter at all or with a filter whose attentuation was no more than 0.2 log units. A further criterion for pathology was a difference of more than 10% between the two eyes in the retinal speed required for a depth displacement using a 1.5 log unit filter. This test requires about 15 minutes, and can be carried out by a technical assistant.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Asselman P., Chadwick D. W., Marsden D. C. Visual evoked responses in the diagnosis and management of patients suspected of multiple sclerosis. Brain. 1975 Jun;98(2):261–282. doi: 10.1093/brain/98.2.261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frisen L., Hoyt W. F., Bird A. C., Weale R. A. Diagnostic uses of the Pulfrich phenomenon. Lancet. 1973 Aug 18;2(7825):385–386. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)93238-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halliday A. M., McDonald W. I., Mushin J. Delayed visual evoked response in optic neuritis. Lancet. 1972 May 6;1(7758):982–985. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)91155-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hennerici M., Wenzel D., Freund H. J. The comparison of small-size rectangle and checkerboard stimulation for the evaluation of delayed visual evoked responses in patients suspected of multiple sclerosis. Brain. 1977 Mar;100(Pt 1):119–136. doi: 10.1093/brain/100.1.119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heron J. R., Regan D., Milner B. A. Delay in visual perception in unilateral optic atrophy after retrobulbar neuritis. Brain. 1974 Mar;97(1):69–78. doi: 10.1093/brain/97.1.69. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald W. I., Halliday A. M. Diagnosis and classification of multiple sclerosis. Br Med Bull. 1977 Jan;33(1):4–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rushton D. Use of the Pulfrich pendulum for detecting abnormal delay in the visual pathway in multiple sclerosis. Brain. 1975 Jun;98(2):283–296. doi: 10.1093/brain/98.2.283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wist E. R., Brandt T., Diener H. C., Dichgans J. Spatial frequency effect on the Pulfrich stereophenomenon. Vision Res. 1977;17(3):391–397. doi: 10.1016/0042-6989(77)90029-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]