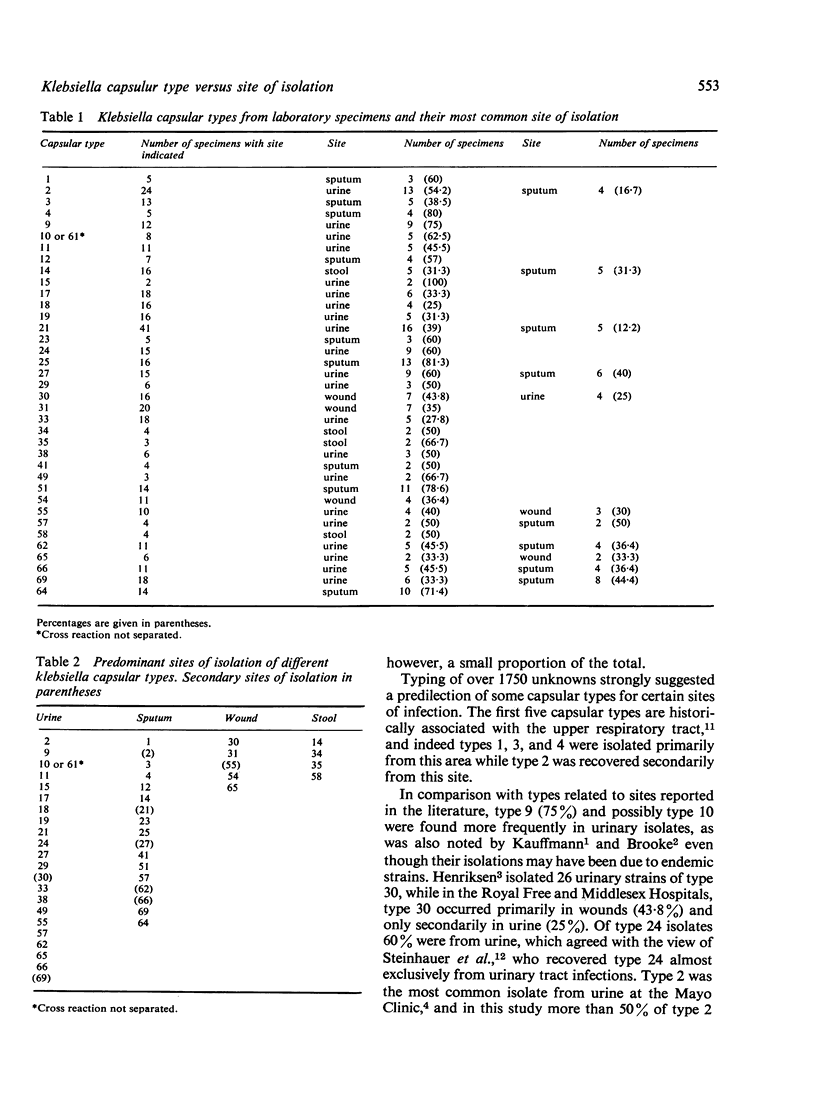
Abstract
More than 1750 clinical isolates of klebsiella were collected over a period of six years from two different hospitals and capsular typed by the fluorescent antibody technique. A correlation was made between type and site of isolation. Many types were found to be associated more frequently with one site, which suggested a predilection of some capsular types for certain sites of infection. The site may also be a factor contributing to the virulence of a particular type. A greater antibiotic resistance was often noted in types isolated from their predominant sites; however, antibiograms were not consistent for a type from a given site. The combination of site specificity, resistance, and another 'virulence factor' may all be involved in the determination of a pathogenic strain.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BROOKE M. S. Further capsular antigens of Klebsiella strains. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1951;28(4):313–327. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1951.tb03697.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EISENBERG G. M., FLIPPIN H. F., KAYSER H. L., NADEL J., SATHAVARA S., SPIVACK A., WEISS W. Klebsiella in respiratory disease. Ann Intern Med. 1956 Dec;45(6):1010–1026. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-45-6-1010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HENRIKSEN S. D. Studies on the Klebsiella group (Kauffmann). I. Sero-types of a collection of strains from human sources and from water. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1954;34(3):249–258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hable K. A., Matsen J. M., Wheeler D. J., Hunt C. E., Quie P. G. Klebsiella type 33 septicemia in an infant intensive care unit. J Pediatr. 1972 Jun;80(6):920–924. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(72)80002-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin W. J., Yu P. K., Washington J. A., 2nd Epidemiologic significance of Klebsiella pneumoniae. A 3-month study. Mayo Clin Proc. 1971 Dec;46(12):785–793. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierog S., Nigam S., Lala R. V., Crichlow D. K., Evans H. E. Neonatal septicemia due to Klebsiella pneumoniae type 60. Epidemic of unusually low virulence. N Y State J Med. 1977 Apr;77(5):737–741. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinarz J. A. Nosocomial infections. Clin Symp. 1978;30(6):1–35. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riser E., Noone P., Howard F. M. Epidemiological study of klebsiella infection in the special care baby unit of a London hospital. J Clin Pathol. 1980 Apr;33(4):400–407. doi: 10.1136/jcp.33.4.400. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riser E., Noone P., Poulton T. A. A new serotyping method for Klebsiella species: development of the technique. J Clin Pathol. 1976 Apr;29(4):296–304. doi: 10.1136/jcp.29.4.296. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riser E., Noone P., Thompson R. E. The use of a fluorescence typing method in an epidemiological study of Klebsiella infection in a London hospital. J Hyg (Lond) 1978 Feb;80(1):43–56. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400053389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinhauer B. W., Eickhoff T. C., Kislak J. W., Finland M. The Klebsiella-Enterobacter-Serratia division. Clinical and epidemiologic characteristics. Ann Intern Med. 1966 Dec;65(6):1180–1194. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-65-6-1180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


