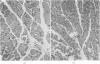
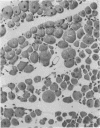
Full text
PDF











Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ambache N. The peripheral action of Cl. botulinum toxin. J Physiol. 1949 Mar 15;108(2):127–141. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BULLER A. J., ECCLES J. C., ECCLES R. M. Interactions between motoneurones and muscles in respect of the characteristic speeds of their responses. J Physiol. 1960 Feb;150:417–439. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1960.sp006395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURGEN A. S. V., DICKENS F., ZATMAN L. J. The action of botulinum toxin on the neuro-muscular junction. J Physiol. 1949 Aug;109(1-2):10–24. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1949.sp004364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COUTEAUX R. Morphological and cytochemical observations on the post-synaptic membrane at motor end-plates and ganglionic synapses. Exp Cell Res. 1958;14(Suppl 5):294–322. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DENZ F. A. On the histochemistry of the myoneural junction. Br J Exp Pathol. 1953 Jun;34(3):329–339. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R., Koelle G. B. Electron microscopic localization of acetylcholinesterase and nonspecific cholinesterase at the neuromuscular junction by the gold-thiocholine and gold-thiolacetic acid methods. J Cell Biol. 1967 Jul;34(1):157–171. doi: 10.1083/jcb.34.1.157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elul R., Miledi R., Stefani E. Neurotrophic control of contracture in slow muscle fibres. Nature. 1968 Mar 30;217(5135):1274–1275. doi: 10.1038/2171274a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GORDON G., HOLBOURN A. H. S. The mechanical activity of single motor units in reflex contractions of skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1949 Dec 15;110(1-2):26–35. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1949.sp004418. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutmann E., Young J. Z. The re-innervation of muscle after various periods of atrophy. J Anat. 1944 Jan;78(Pt 1-2):15–43. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOFFMAN H. Local re-innervation in partially denervated muscle; a histophysiological study. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1950 Jul;28(4):383–397. doi: 10.1038/icb.1950.39. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson J. R. The use of silver for intensifying sulfide deposits in the cholinesterase technique. Stain Technol. 1967 Mar;42(2):101–102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JIRMANOVA I., SOBOTKOVA M., THESLEFF S., ZELENA J. ATROPHY IN SKELETAL MUSCLES POISONED WITH BOTULINUM TOXIN. Physiol Bohemoslov. 1964;13:467–472. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEHMANN H., SILK E., LIDDELL J. Pseudo-cholinesterase. Br Med Bull. 1961 Sep;17:230–233. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a069914. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Namba T., Nakamura T., Grob D. Staining for nerve fiber and cholinesterase activity in fresh frozen sections. Am J Clin Pathol. 1967 Jan;47(1):74–77. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/47.1.74. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZACKS S. I., METZGER J., SMITH C. W., BLUMBERG J. M. Localization of ferritin-labelled botulinus toxin in the neuromuscular junction of the mouse. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1962 Oct;21:610–633. doi: 10.1097/00005072-196210000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]