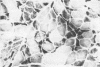
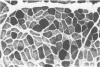
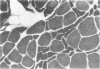
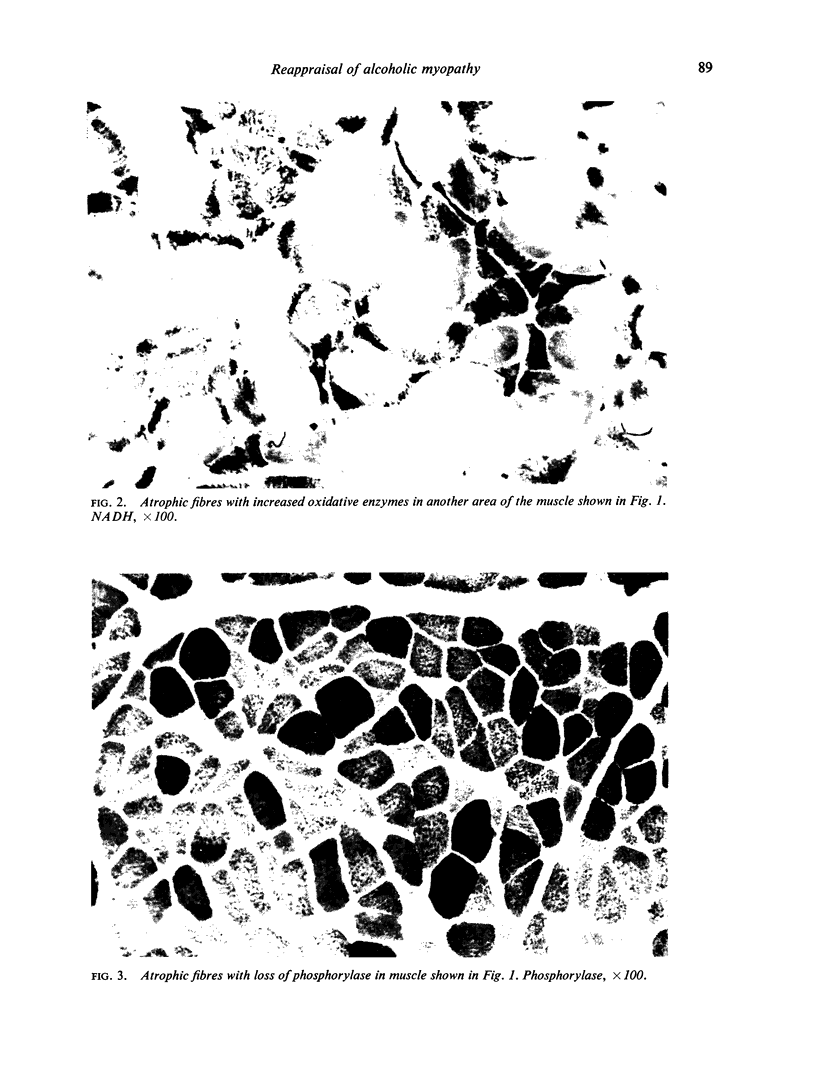
Abstract
To determine if alcoholic neuropathy which causes denervation of the distal muscles of chronic alcoholics also produces a subclinical myopathy of their proximal muscles, we studied 11 chronic alcoholics who had no muscular weakness or wasting. Six patients demonstrated distal hyporeflexic (ankle jerks) sensory neuropathy on clinical examination. Four patients, one of whom was asymptomatic, had slow peroneal motor nerve conduction velocities. Patterns of neuropathy were present in the electromyograms of the proximal muscles of two patients. Muscle biopsy studies with enzyme histochemistry indicated denervation atrophy and myopathic changes in the contralateral quadriceps muscles of eight patients. As denervation atrophy was present, we concluded that these myopathic changes represented the effects of denervation of these muscles. We conclude, therefore, that the proximal subclinical alcoholic myopathy, previously described as primary by ourselves and others, is the result of denervation due to the well-known alcoholic neuropathy.
Full text
PDF


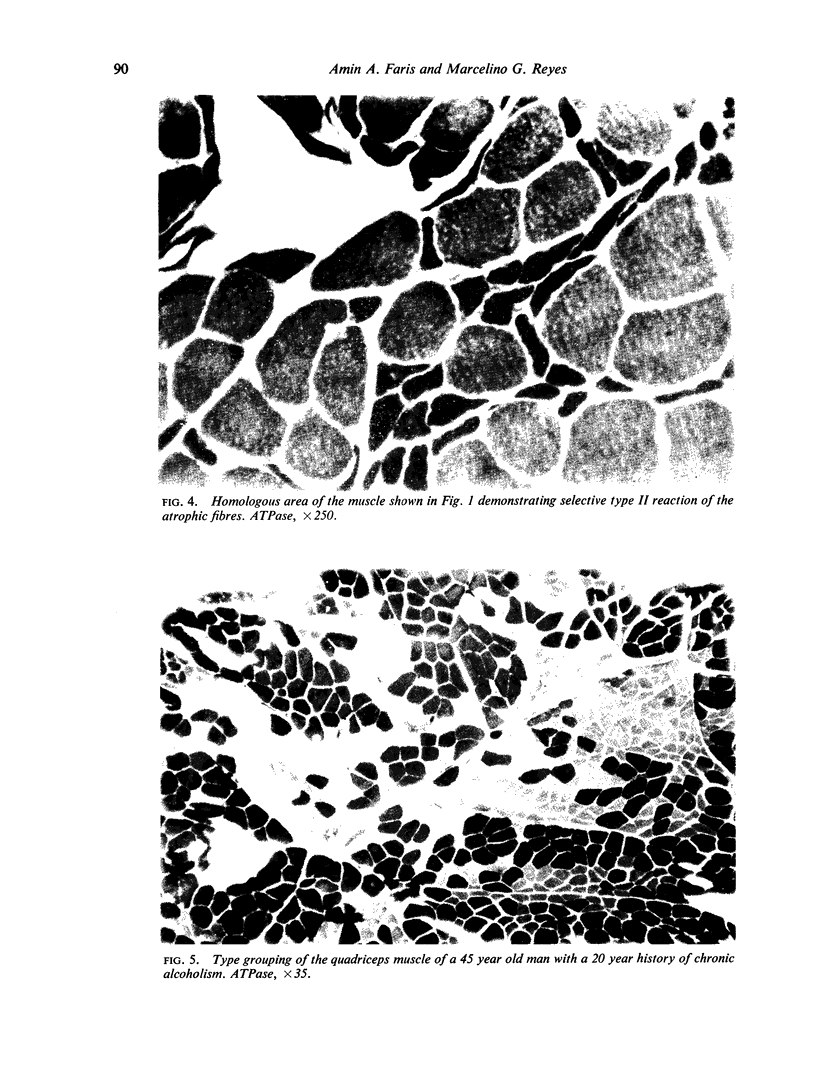
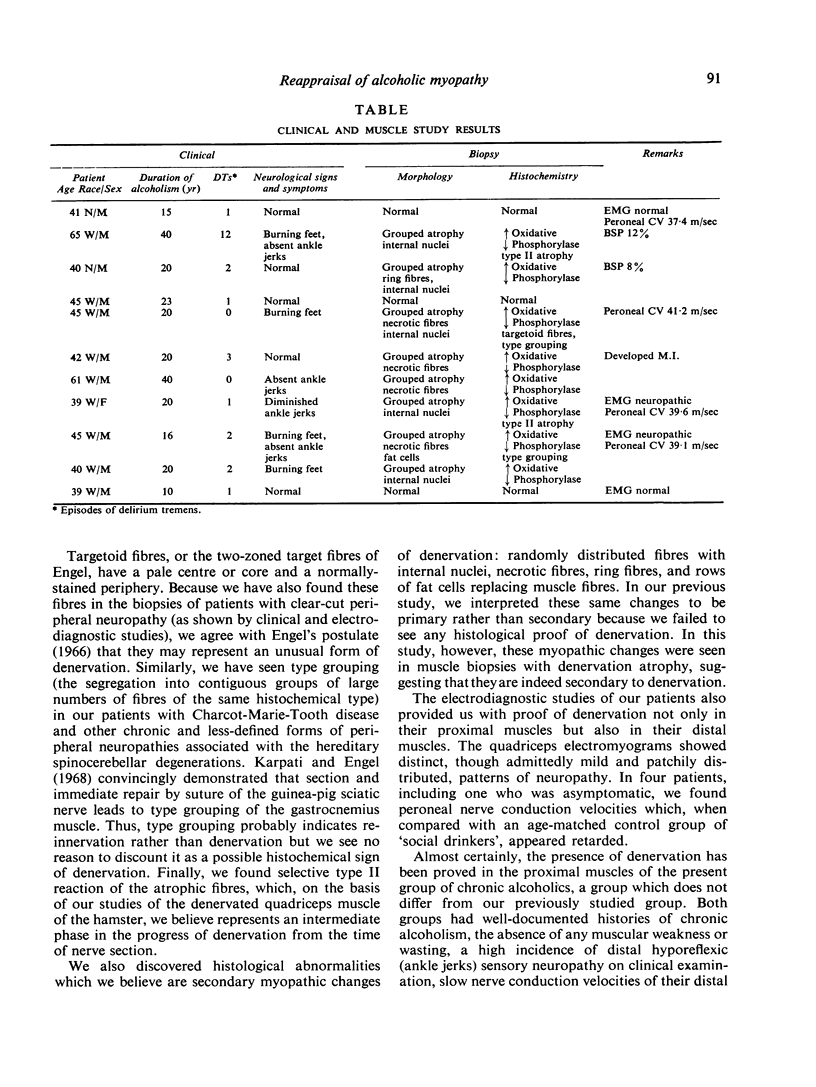

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Drachman D. B., Murphy S. R., Nigam M. P., Hills J. R. "Myopathic" changes in chronically denervated muscle. Arch Neurol. 1967 Jan;16(1):14–24. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1967.00470190018002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EKBOM K., HED R., KIRSTEIN L., ASTROM K. E. MUSCULAR AFFECTIONS IN CHRONIC ALCOHOLISM. Arch Neurol. 1964 May;10:449–458. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1964.00460170019003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ENGEL W. K., CUNNINGHAM G. G. RAPID EXAMINATION OF MUSCLE TISSUE. AN IMPROVED TRICHROME METHOD FOR FRESH-FROZEN BIOPSY SECTIONS. Neurology. 1963 Nov;13:919–923. doi: 10.1212/wnl.13.11.919. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engel W. K., Brooke M. H., Nelson P. G. Histochemical studies of denervated or tenotomized cat muscle: illustrating difficulties in relating experimental animal conditions to human neuromuscular diseases. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1966 Sep 9;138(1):160–185. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1966.tb41164.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faris A. A., Reyes M. G., Abrams B. M. Subclinical alcoholic myopathy: electromyographic and biopsy study. Trans Am Neurol Assoc. 1967;92:102–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HED C., LUNDMARK C., FAHLGREN H., ORELL S. Acute muscular syndrome in chronic alcoholism. Acta Med Scand. 1962 May;171:585–599. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1962.tb04224.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karpati G., Engel W. K. "Type grouping" in skeletal muscles after experimental reinnervation. Neurology. 1968 May;18(5):447–455. doi: 10.1212/wnl.18.5.447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NOVIKOFF A. B., SHIN W. Y., DRUCKER J. Mitochondrial localization of oxidative enzymes: staining results with two tetrazolium salts. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1961 Jan;9:47–61. doi: 10.1083/jcb.9.1.47. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PADYKULA H. A., HERMAN E. The specificity of the histochemical method for adenosine triphosphatase. J Histochem Cytochem. 1955 May;3(3):170–195. doi: 10.1177/3.3.170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkoff G. T., Hardy P., Velez-Garcia E. Reversible acute muscular syndrome in chronic alcoholism. N Engl J Med. 1966 Jun 9;274(23):1277–1285. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196606092742301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WATTENBERG L. W., LEONG J. L. Effects of coenzyme Q10 and menadione on succinic dehydrogenase activity as measured by tetrazolium salt reduction. J Histochem Cytochem. 1960 Jul;8:296–303. doi: 10.1177/8.4.296. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]