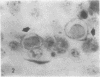
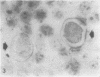
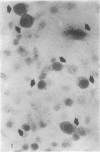
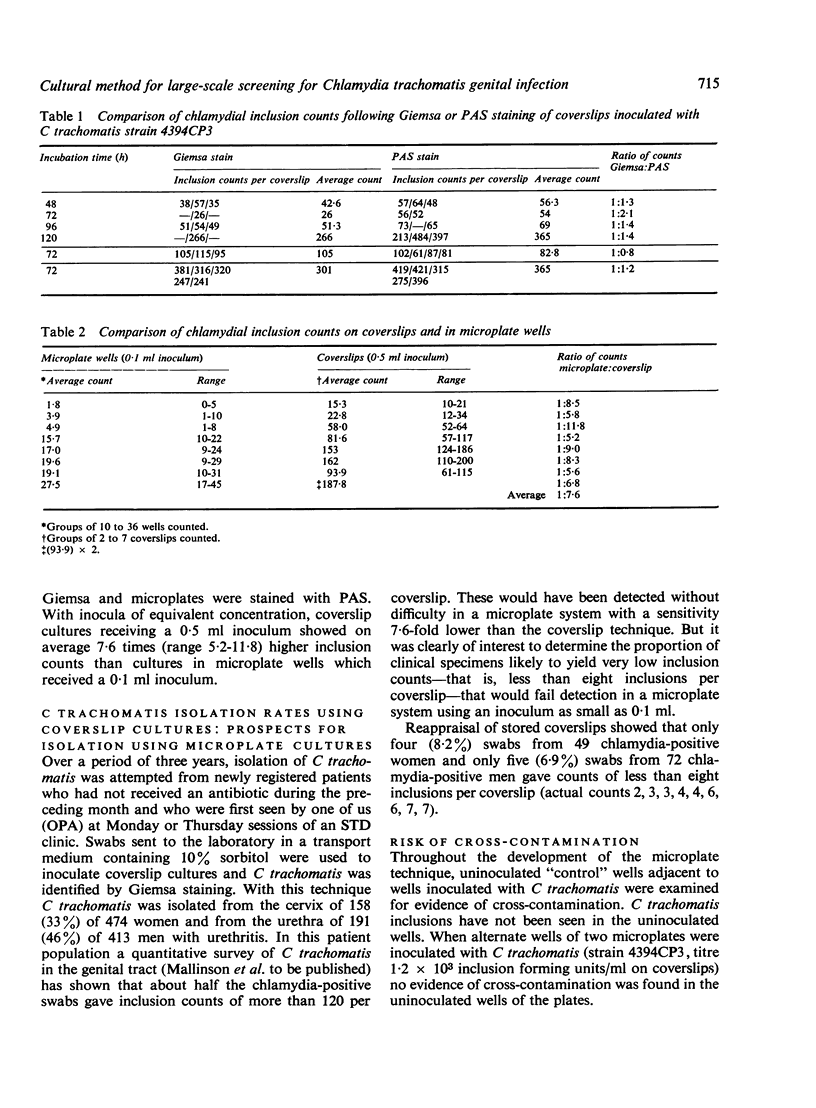
Abstract
Idoxuridine-treated McCoy cells grown as monolayers in 96 well microplates provide a convenient method for the isolation of Chlamydia trachomatis. Staining of infected monolayers with periodic acid-Schiff reagent (PAS) allows easy recognition of C trachomatis inclusions without the need for dark-ground microscopy. By this method 384 clinical specimens can be examined concurrently. It is sufficiently sensitive to form the basis of a chlamydial culture service for patients attending Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STD) Clinics.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Hammerschlag M. R., Anderka M., Semine D. Z., McComb D., McCormack W. M. Prospective study of maternal and infantile infection with Chlamydia trachomatis. Pediatrics. 1979 Aug;64(2):142–148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson F. W. A comparison of staining techniques for demonstrating group A chlamydia in tissue culture. Med Lab Technol. 1975 Jul;32(3):233–238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson F. W., Hobson D. Factors affecting the sensitivity of replicating McCoy cells in the isolation and growth of chlamydia A (TRIC agents). J Hyg (Lond) 1976 Jun;76(3):441–451. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400055376. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McComb D. E., Puzniak C. I. Micro cell culture method for isolation of Chlamydia trachomatis. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Oct;28(4):727–729. doi: 10.1128/am.28.4.727-729.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormack W. M., Alpert S., McComb D. E., Nichols R. L., Semine D. Z., Zinner S. H. Fifteen-month follow-up study of women infected with Chlamydia trachomatis. N Engl J Med. 1979 Jan 18;300(3):123–125. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197901183000305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeve P., Owen J., Oriel J. D. Laboratory procedures for the isolation of chlamydia trachomatis from the human genital tract. J Clin Pathol. 1975 Nov;28(11):910–914. doi: 10.1136/jcp.28.11.910. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richmond S. J., Paul I. D., Taylor P. K. Value and feasibility of screening women attending STD clinics for cervical chlamydial infections. Br J Vener Dis. 1980 Apr;56(2):92–95. doi: 10.1136/sti.56.2.92. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richmond S. J. The isolation of Chlamydia subgroup A (Chlamydia trachomatis) in irradiated McCoy cells. Med Lab Technol. 1974 Jan;31(1):7–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rota T. R. Techniques for culturing and determining antimicrobial susceptibility of Chlamydia trachomatis. Arch Androl. 1980 Feb;4(1):63–69. doi: 10.3109/01485018008988281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor-Robinson D., Thomas B. J. The rôle of Chlamydia trachomatis in genital-tract and associated diseases. J Clin Pathol. 1980 Mar;33(3):205–233. doi: 10.1136/jcp.33.3.205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willcox J. R., Fisk P. G., Barrow J., Barlow D. The need for a chlamydial culture service. Br J Vener Dis. 1979 Aug;55(4):281–283. doi: 10.1136/sti.55.4.281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]