Abstract
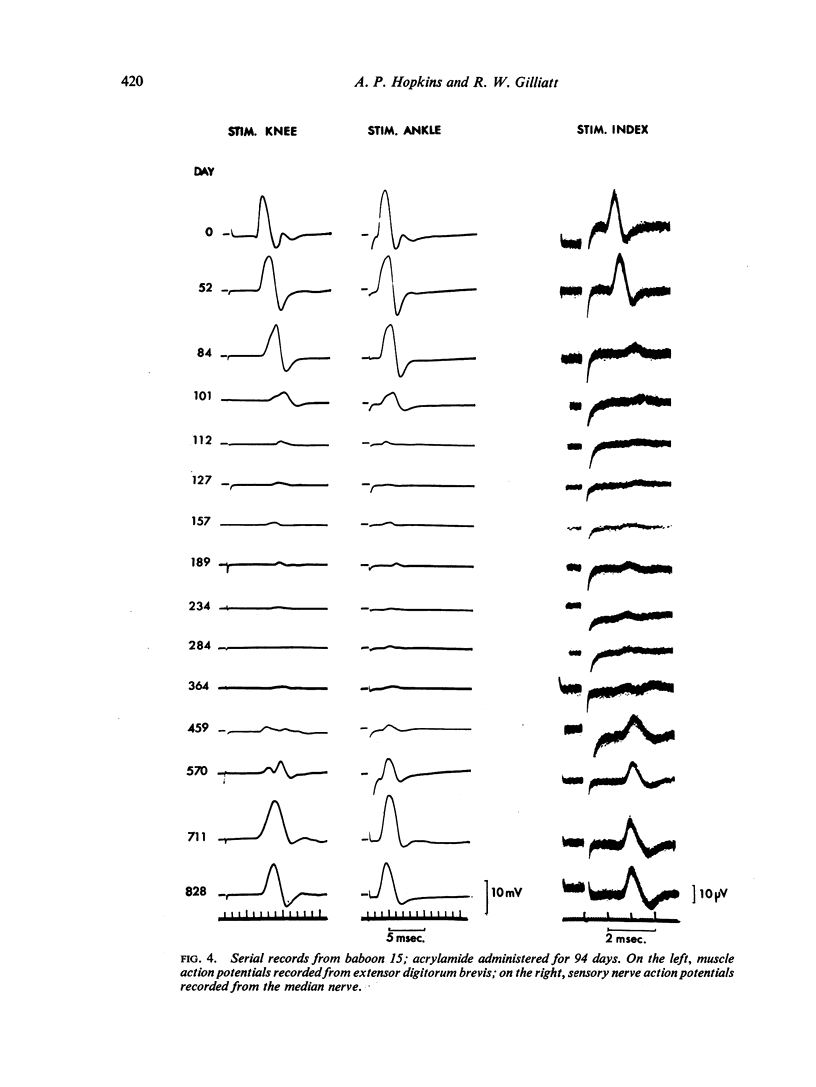
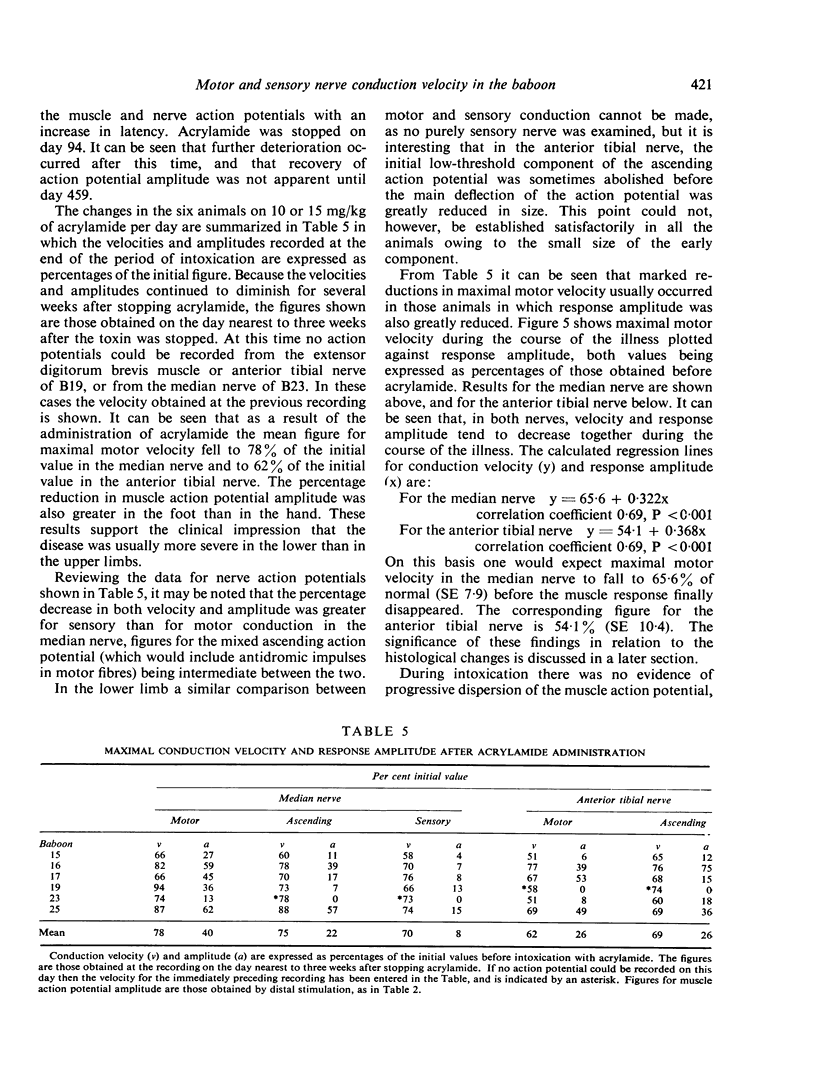
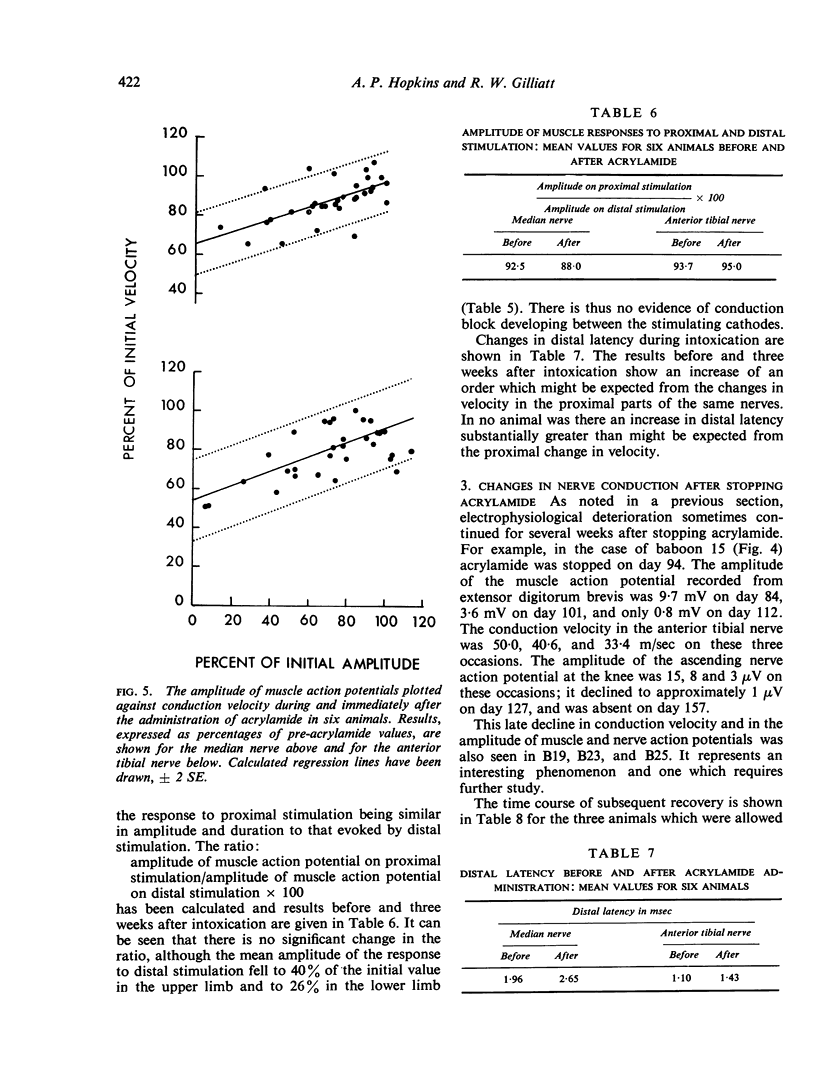
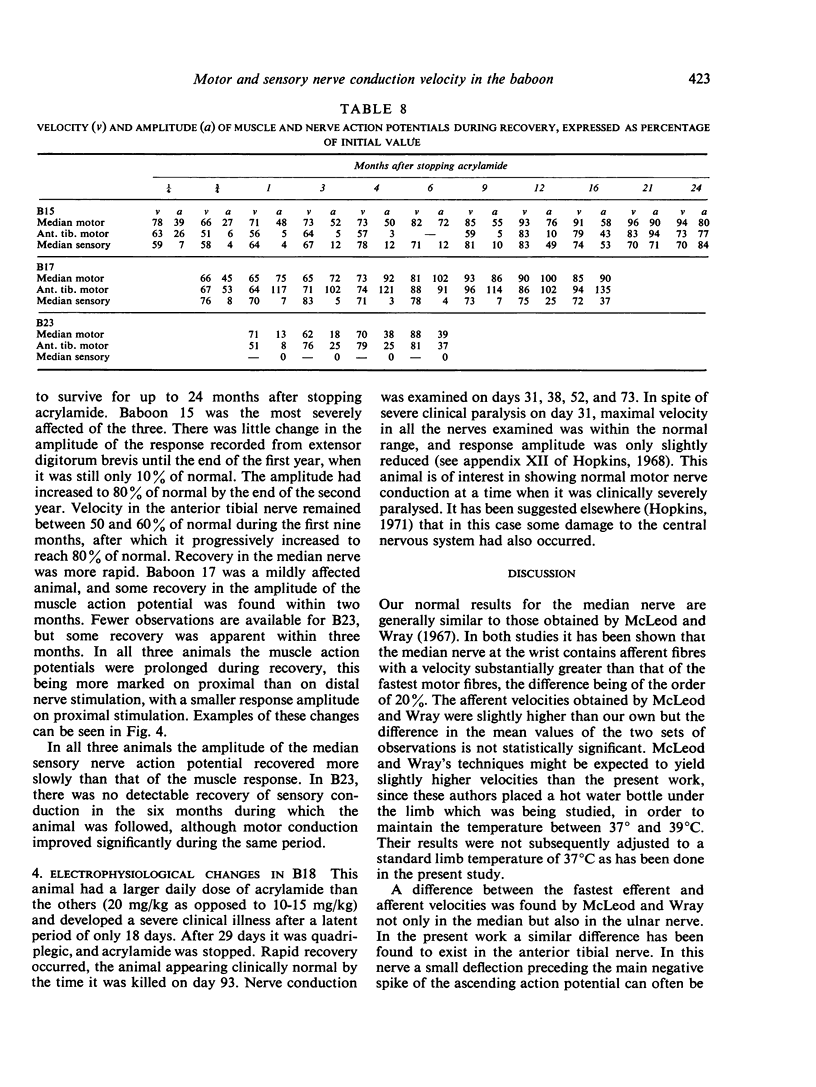
Nerve conduction velocity and the amplitude of nerve and muscle action potentials have been measured in the median and anterior tibial nerves of normal adult and infant baboons. The effect of altered temperature on velocity has also been investigated. Seven adult baboons were intoxicated with acrylamide. In animals given 10-15 mg/kg/day, the gradual development of a peripheral neuropathy was accompanied by a decline in the amplitude of both muscle and nerve action potentials. There was also a gradual fall in conduction velocity. In some cases maximal motor velocity in the median nerve fell by as much as 34%, and in the anterior tibial nerve by as much as 49%, the largest falls being seen in animals showing the greatest reductions in response amplitude. Histological studies, reported elsewhere, have shown that the main pathological change in our animals was a degeneration of the peripheral nerves, with little demyelination. Fibre diameter histograms indicated that large fibres were particularly severely affected, and it seems likely that the reduced maximal conduction velocities were due to this selective loss of large-diameter fibres.
Full text
PDF
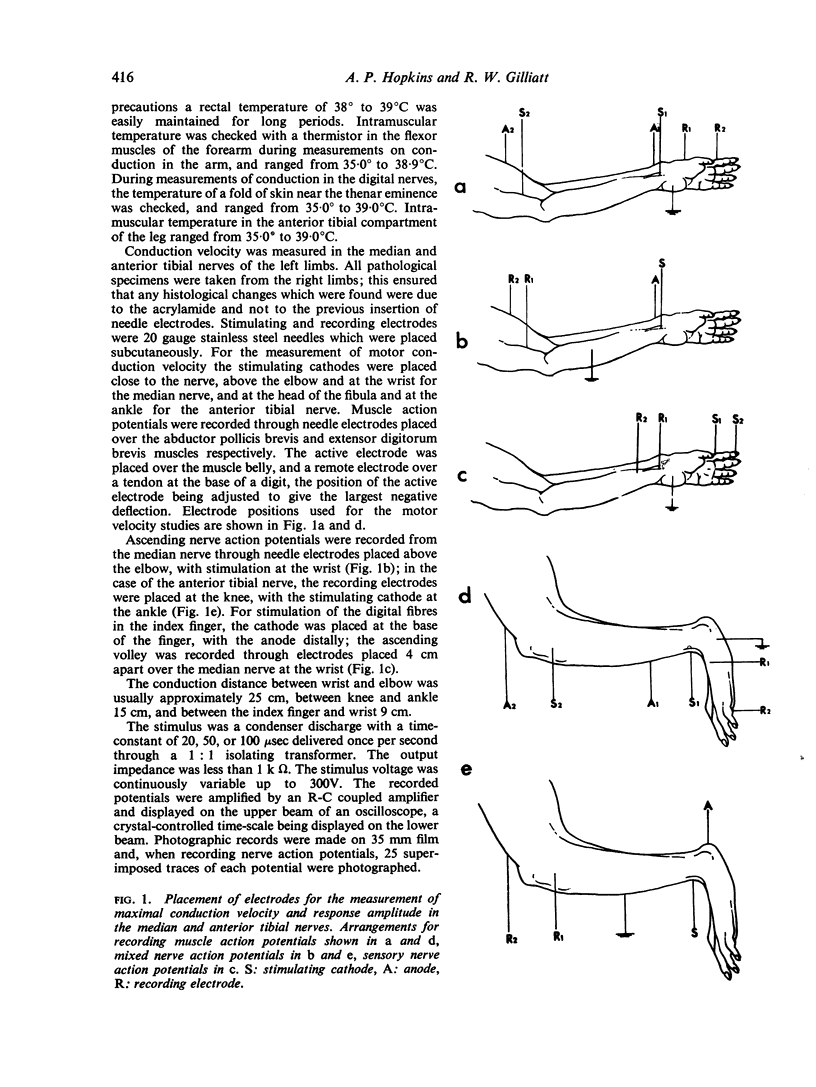
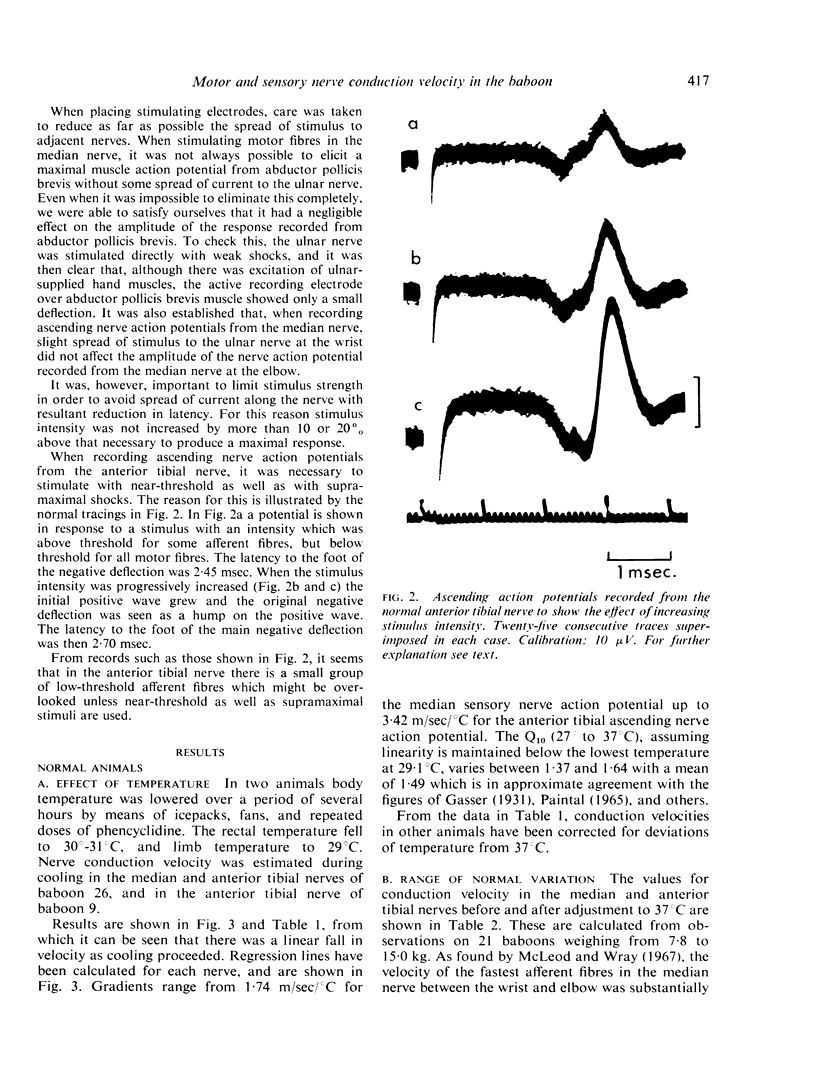
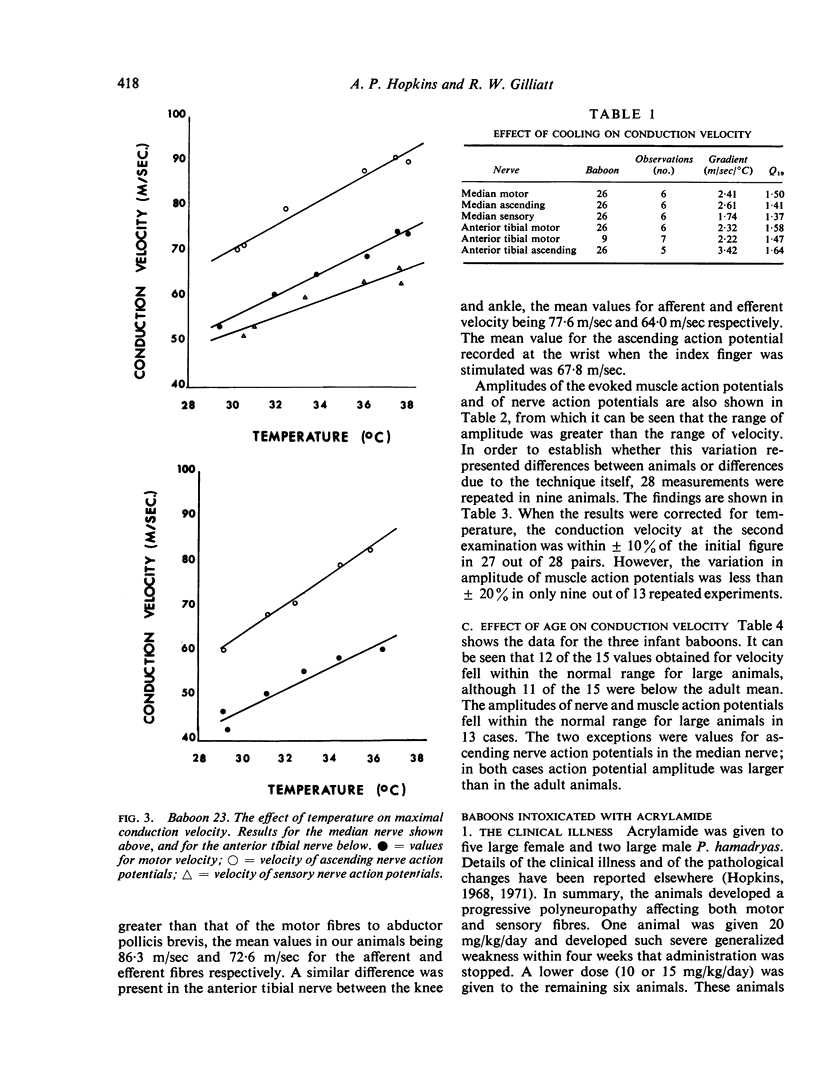
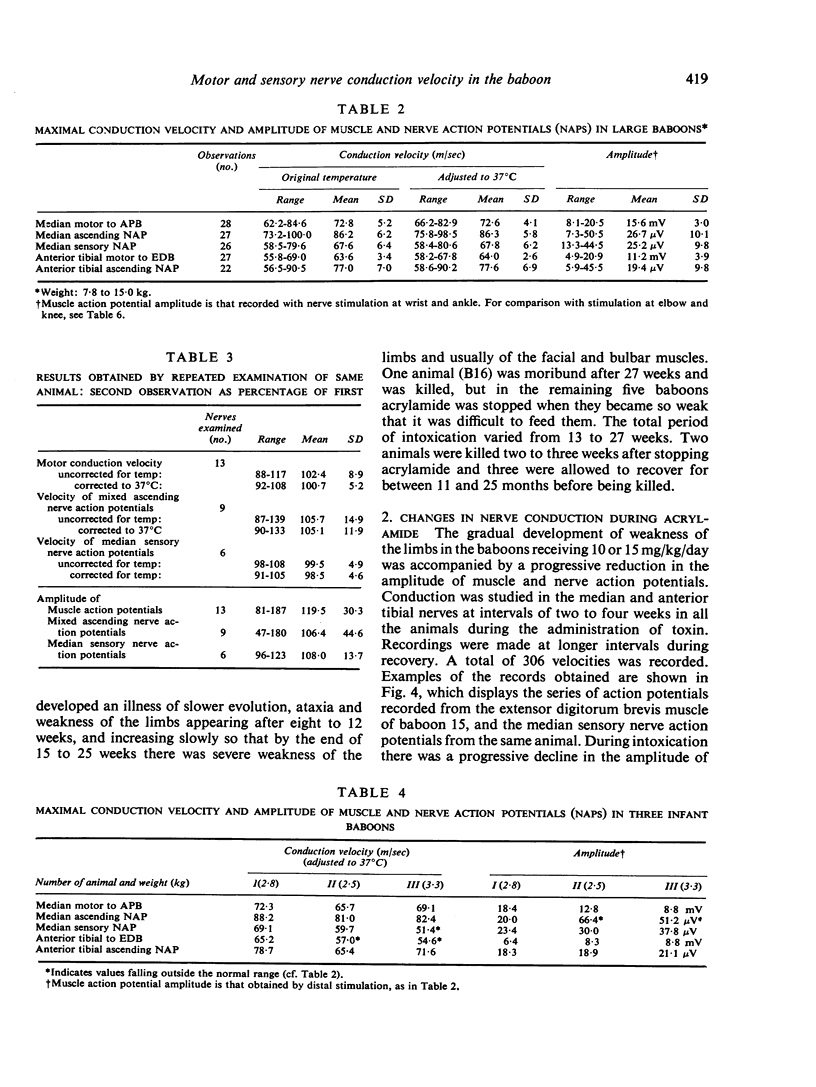


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CRAGG B. G., THOMAS P. K. Changes in conduction velocity and fibre size proximal to peripheral nerve lesions. J Physiol. 1961 Jul;157:315–327. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1961.sp006724. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catton M. J., Harrison M. J., Fullerton P. M., Kazantzis G. Subclinical neuropathy in lead workers. Br Med J. 1970 Apr 11;2(5701):80–82. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5701.80. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eccles R. M., Phillips C. G., Chien-Ping W. Motor innervation, motor unit organization and afferent innervation of m. extensor digitorum communis of the baboon's forearm. J Physiol. 1968 Sep;198(1):179–192. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008600. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fullerton P. M., Barnes J. M. Peripheral neuropathy in rats produced by acrylamide. Br J Ind Med. 1966 Jul;23(3):210–221. doi: 10.1136/oem.23.3.210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fullerton P. M. Electrophysiological and histological observations on peripheral nerves in acrylamide poisoning in man. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1969 Jun;32(3):186–192. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.32.3.186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garland T. O., Patterson M. W. Six cases of acrylamide poisoning. Br Med J. 1967 Oct 28;4(5572):134–138. doi: 10.1136/bmj.4.5572.134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopkins A. The effect of acrylamide on the peripheral nervous system of the baboon. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1970 Dec;33(6):805–816. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.33.6.805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLeod J. G., Wray S. H. Conduction velocity and fibre diameter of the median and ulnar nerves of the baboon. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1967 Jun;30(3):240–247. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.30.3.240. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oxnard C. E., Smith W. T. Neurological degeneration and reduced serum vitamin B12-levels in captive monkeys. Nature. 1966 Apr 30;210(5035):507–509. doi: 10.1038/210507a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paintal A. S. Effects of temperature on conduction in single vagal and saphenous myelinated nerve fibres of the cat. J Physiol. 1965 Sep;180(1):20–49. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THOMAS J. E., LAMBERT E. H. Ulnar nerve conduction velocity and H-reflex in infants and children. J Appl Physiol. 1960 Jan;15:1–9. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1960.15.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wray S. H. Innervation ratios for large and small limb muscles in the baboon. J Comp Neurol. 1969 Oct;137(2):227–250. doi: 10.1002/cne.901370207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


