Abstract
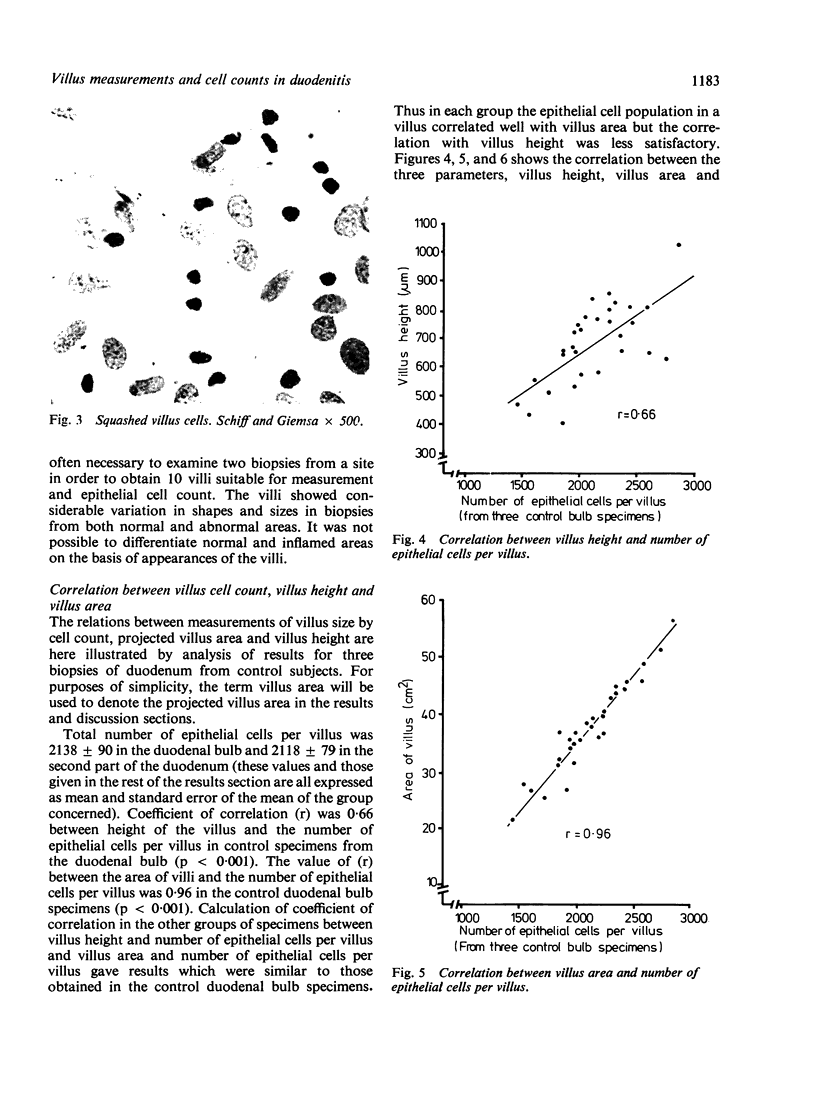
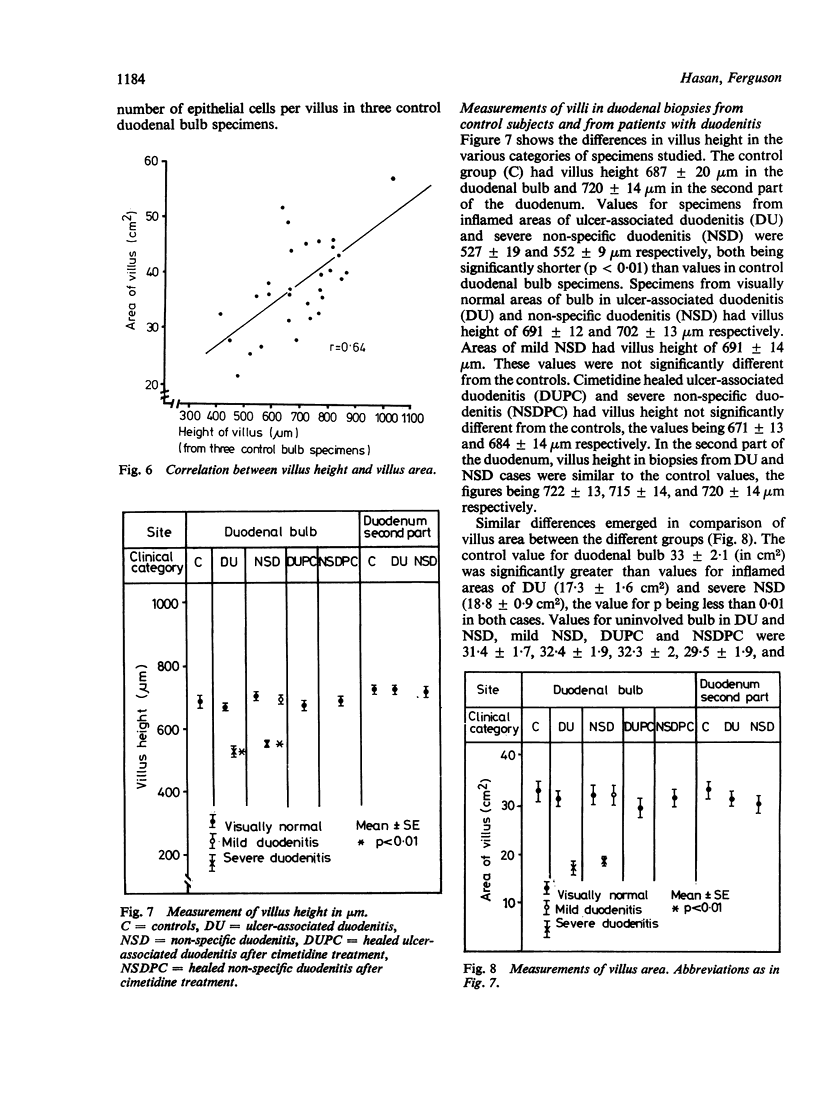
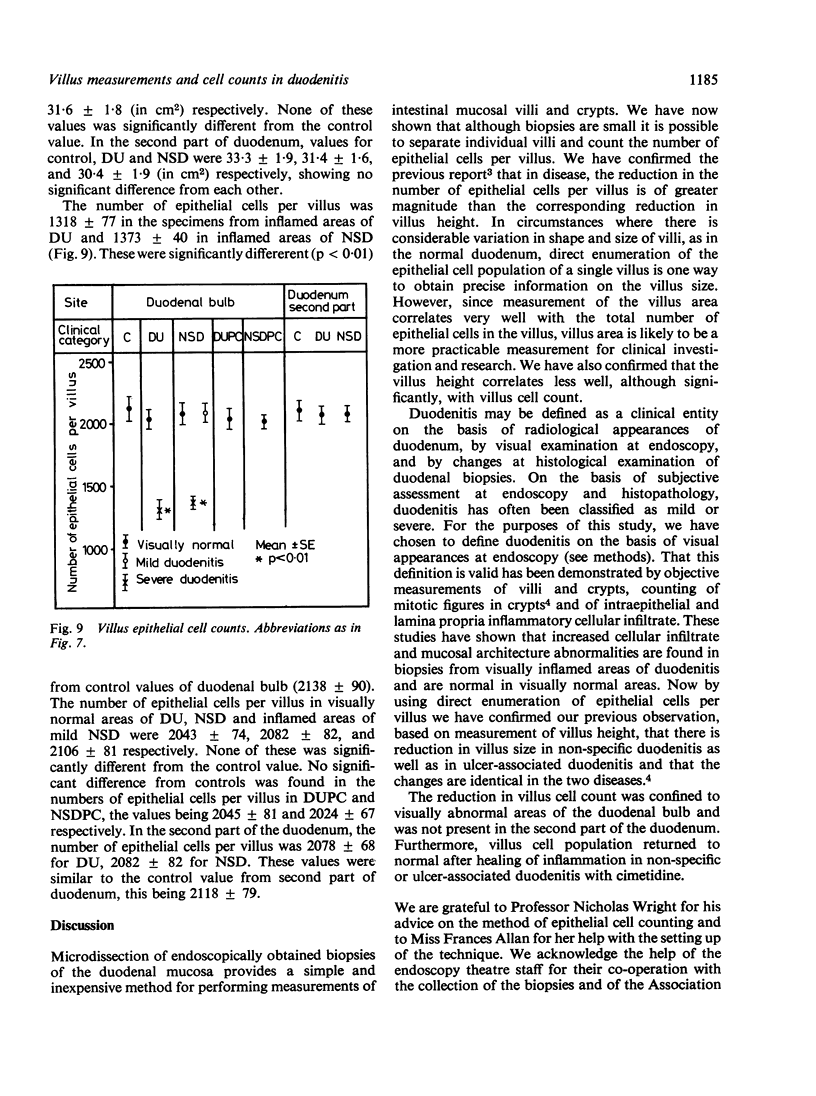
Measurements of villus height, villus area, together with counts of epithelial cells in individual villi, were performed on endoscopic duodenal biopsies from five groups of patients: controls, ulcer-associated duodenitis, mild and severe non-specific (non-ulcerative) duodenitis, cimetidine healed ulcer-associated duodenitis and cimetidine healed non-specific duodenitis. The objectives of the study were two-fold: to establish if epithelial cell count correlated with simpler measurements of villus height or area; and to compare the findings in ulcer-associated and in non-specific duodenitis. Villus area correlated well with epithelial cell count per villus (r = 0.96); villus height correlated less well (r = 0.66). When compared with controls, there was a significant decrease in the epithelial cell count per villus in ulcer-associated and severe non-specific duodenitis, but this was confined to the visually inflamed area of the duodenal bulb. After healing of inflammation with cimetidine villus height, area, and epithelial cell count returned to values similar to those in controls. This study confirms that the effects of ulcer-associated and severe non-specific duodenitis on duodenal villi are identical.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Clarke R. M. Control of intestinal epithelial replacement: lack of evidence for a tissue-specific blood-borne factor. Cell Tissue Kinet. 1974 May;7(3):241–250. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2184.1974.tb00904.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke R. M. Control of intestinal epithelial replacement: lack of evidence for a tissue-specific blood-borne factor. Cell Tissue Kinet. 1974 May;7(3):241–250. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2184.1974.tb00904.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]