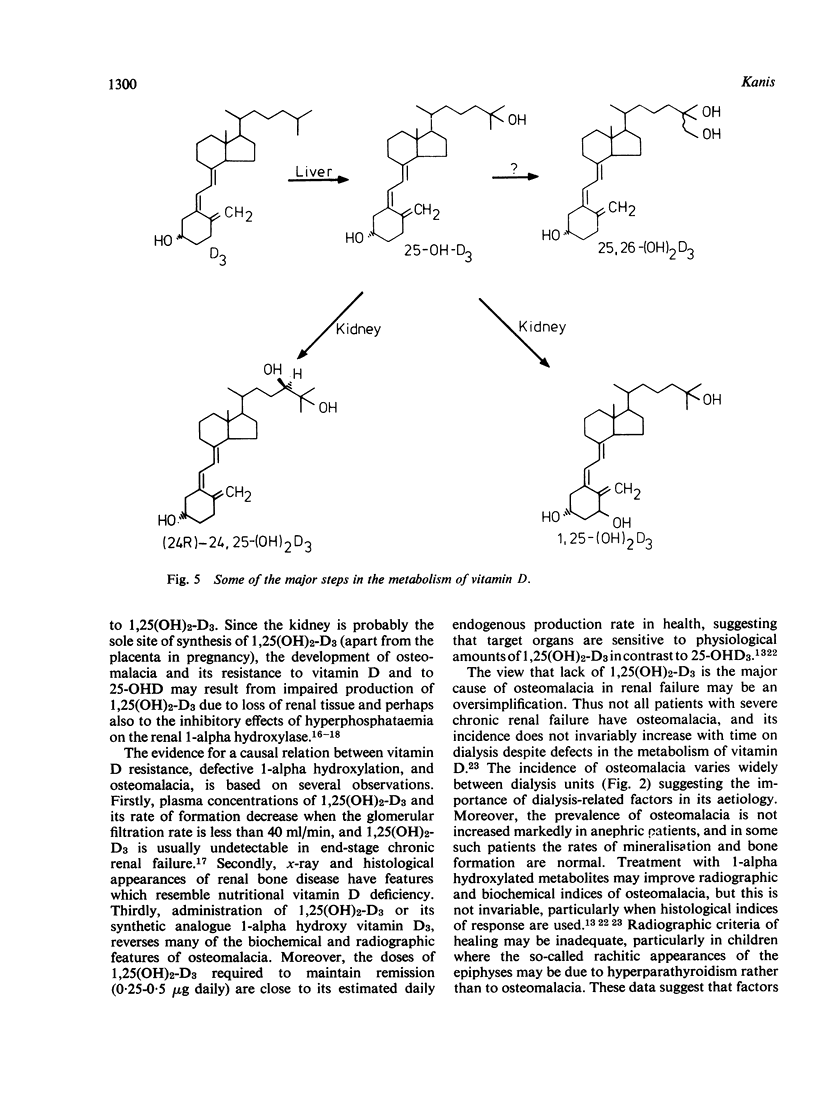
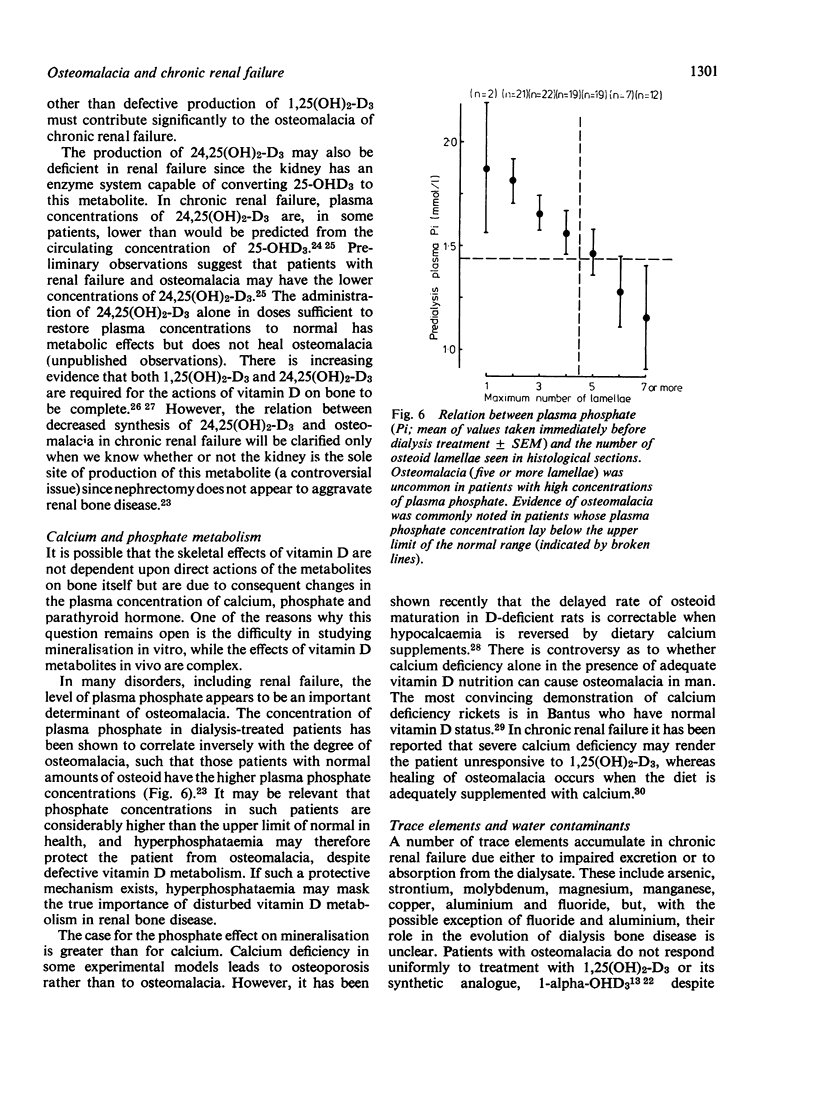
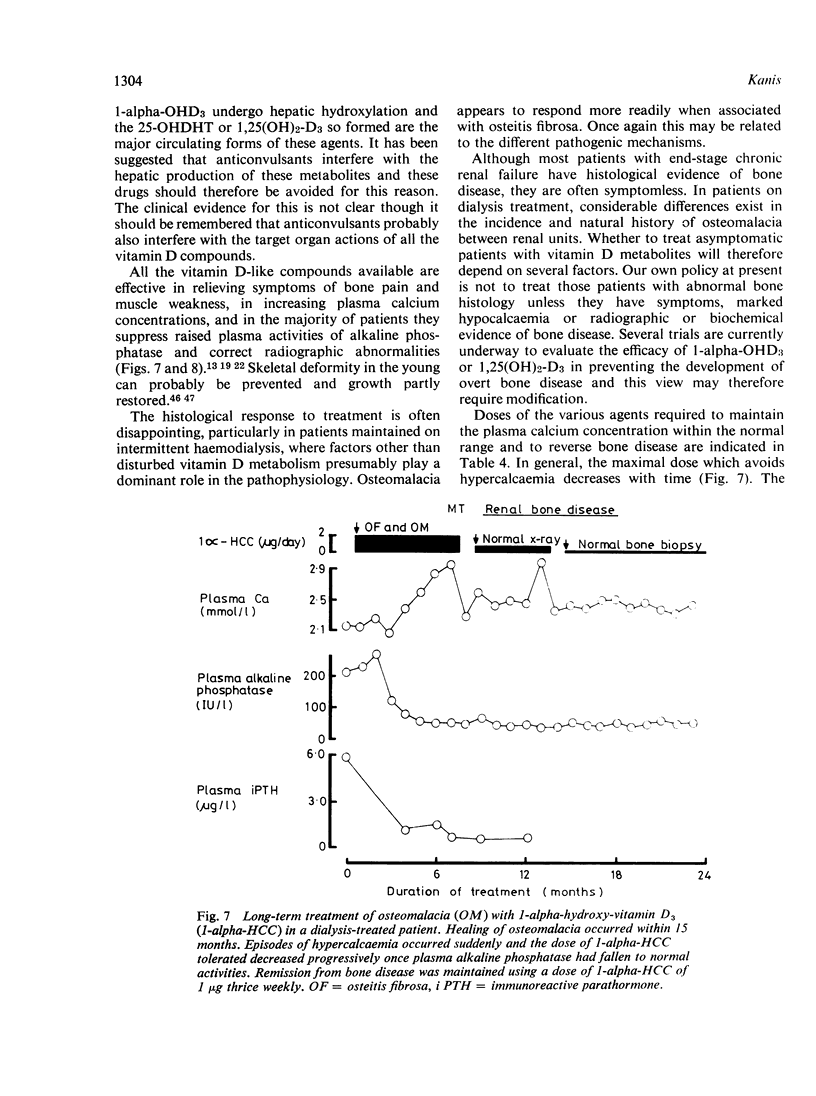
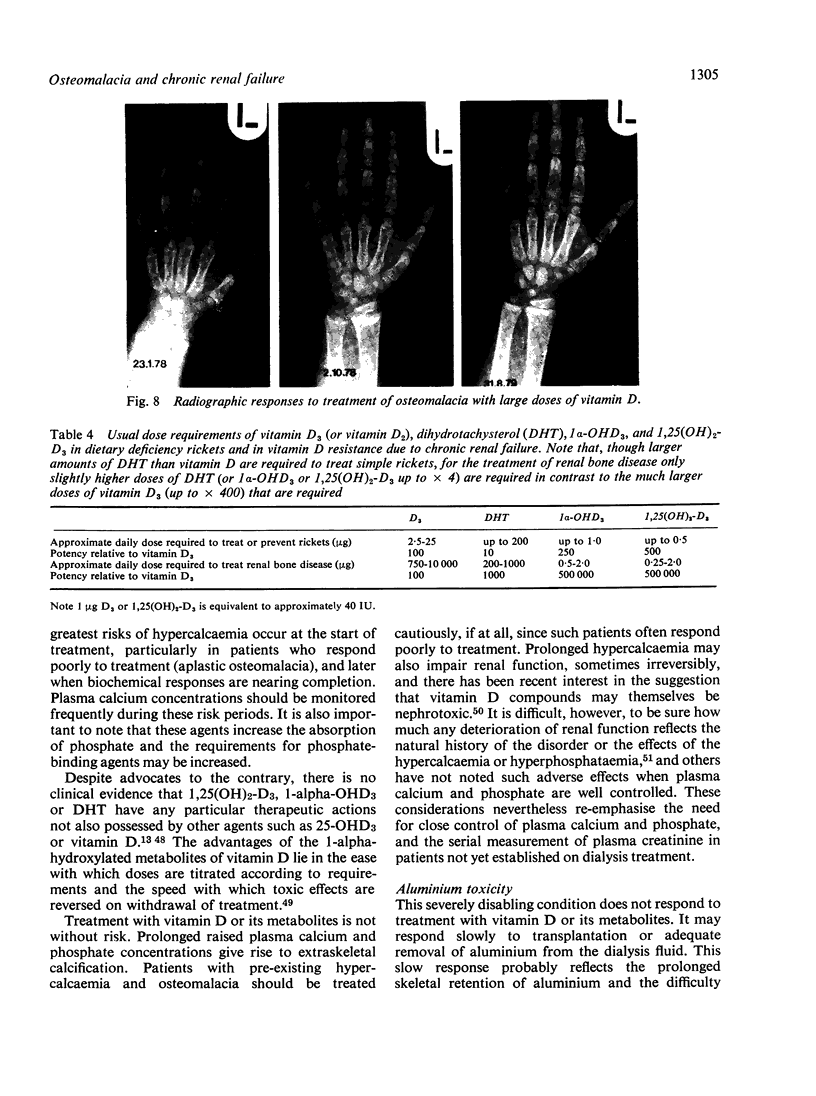
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahmed K. Y., Varghese Z., Wills M. R., Meinhard E., Skinner R. K., Baillod R. A., Moorhead J. F. Persistent hypophosphataemia and osteomalacia in dialysis patients not on oral phosphate-binders: Response to dihydrotachysterol therapy. Lancet. 1976 Aug 28;2(7983):439–442. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)92526-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bordier P., Rasmussen H., Marie P., Miravet L., Gueris J., Ryckwaert A. Vitamin D metabolites and bone mineralization in man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1978 Feb;46(2):284–294. doi: 10.1210/jcem-46-2-284. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chesney R. W., Moorthy A. V., Eisman J. A., Jax D. K., Mazess R. B., DeLuca H. F. Increased growth after long-term oral 1alpha,25-vitamin D3 in childhood renal osteodystrophy. N Engl J Med. 1978 Feb 2;298(5):238–242. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197802022980503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christiansen C., Rødbro P., Christensen M. S., Hartnack B., Transbøl I. Deterioration of renal function during treatment of chronic renal failure with 1,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol. Lancet. 1978 Sep 30;2(8092 Pt 1):700–703. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)92702-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarkson E. M., Luck V. A., Hynson W. V., Bailey R. R., Eastwood J. B., Woodhead J. S., Clements V. R., O'Riordan J. L., De Wardener H. E. The effect of aluminium hydroxide on calcium, phosphorus and aluminium balances, the serum parathyroid hormone concentration and the aluminium content of bone in patients with chronic renal failure. Clin Sci. 1972 Oct;43(4):519–531. doi: 10.1042/cs0430519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochran M., Wilkinson R. Effect of correction of metabolic acidosis on bone mineralisation rates in patients with renal osteomalacia. Nephron. 1975;15(2):98–110. doi: 10.1159/000180501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Luca H. F. Recent advances in our understanding of the vitamin D endocrine system. J Lab Clin Med. 1976 Jan;87(1):7–26. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FLETCHER R. F., JONES J. H., MORGAN D. B. BONE DISEASE IN CHRONIC RENAL FAILURE. Q J Med. 1963 Oct;32:321–329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feest T. G., Ward M. K., Ellis H. A., Aljama P., Kerr D. N. Osteomalacic dialysis osteodystrophy: a trial of phosphate-enriched dialysis fluid. Br Med J. 1978 Jan 7;1(6104):18–20. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.6104.18. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flendrig J. A., Kruis H., Das H. A. Letter: Aluminum and dialysis dementia. Lancet. 1976 Jun 5;1(7971):1235–1235. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)92177-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frost H. M. Relation between bone tissue and cell population dynamics, histology and tetracycline labeling. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1966 Nov-Dec;49:65–75. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haussler M. R., McCain T. A. Basic and clinical concepts related to vitamin D metabolism and action (first of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1977 Nov 3;297(18):974–983. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197711032971804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins M. V., Harris M., Wills M. R. The effect of phenytoin on parathyroid extract and 25-hydroxycholecalciferol-induced bone resorption: adenosine 3, 5 cyclic monophosphate production. Calcif Tissue Res. 1974;16(2):163–167. doi: 10.1007/BF02008223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanis J. A., Cundy T., Earnshaw M., Henderson R. G., Heynen G., Naik R., Russell R. G., Smith R., Woods C. G. Treatment of renal bone disease with 1 alpha-hydroxylated derivatives of vitamin D3. Clinical, biochemical, radiographic and histological responses. Q J Med. 1979 Apr;48(190):289–322. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanis J. A., Henderson R. G., Heynen G., Ledingham J. G., Russell R. G., Smith R., Walton R. J. Renal osteodystrophy in nondialysed adolescents. Long-term treatment with 1alpha-hydroxycholecalciferol. Arch Dis Child. 1977 Jun;52(6):473–481. doi: 10.1136/adc.52.6.473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanis J. A., Russell R. G. Rate of reversal of hypercalcaemia and hypercalciuria induced by vitamin D and its 1alpha-hydroxylated derivatives. Br Med J. 1977 Jan 8;1(6053):78–81. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.6053.78. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanis J. A., Russell R. G., Taylor C. M., Cundy T., Andrade A., Heynen G. The relationship between disturbed metabolism of vitamin D and bone disease in chronic renal failure. Proc Eur Dial Transplant Assoc. 1979;16:630–636. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krempien B., Mehls O., Ritz E. Morphological studies on pathogenesis of epiphyseal slipping in uremic children. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histol. 1974 Jan 30;362(2):129–143. doi: 10.1007/BF00432391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemann J., Jr, Litzow J. R., Lennon E. J. The effects of chronic acid loads in normal man: further evidence for the participation of bone mineral in the defense against chronic metabolic acidosis. J Clin Invest. 1966 Oct;45(10):1608–1614. doi: 10.1172/JCI105467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malluche H. H., Goldstein D. A., Massry S. G. Osteomalacia and hyperparathyroid bone disease in patients with nephrotic syndrome. J Clin Invest. 1979 Mar;63(3):494–500. doi: 10.1172/JCI109327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyrier A., Marsac J., Richet G. The influence of a high calcium carbonate intake on bone disease in patients undergoing hemodialysis. Kidney Int. 1973 Aug;4(2):146–153. doi: 10.1038/ki.1973.93. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moorhead J. F., Wills M. R., Ahmed K. Y., Baillod R. A., Varghese Z., Tatler G. L. Hypophosphataemic osteomalacia after cadaveric renal transplantation. Lancet. 1974 Apr 20;1(7860):694–697. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)92902-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naik R. B., Cundy T., Robinson B. H., Russell R. G., Kanis J. A. Effects of vitamin D metabolites and analogues on renal function. Nephron. 1981;28(1):17–25. doi: 10.1159/000182088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parfitt A. M. Soft-tissue calcification in uremia. Arch Intern Med. 1969 Nov;124(5):544–556. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkinson I. S., Ward M. K., Feest T. G., Fawcett R. W., Kerr D. N. Fracturing dialysis osteodystrophy and dialysis encephalopathy. An epidemiological survey. Lancet. 1979 Feb 24;1(8113):406–409. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)90883-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pellegrino E. D., Biltz R. M. The composition of human bone in uremia. Observations on the reservoir functions of bone and demonstration of a labile fraction of bone carbonate. Medicine (Baltimore) 1965 Sep;44(5):397–418. doi: 10.1097/00005792-196509000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Platts M. M., Goode G. C., Hislop J. S. Composition of the domestic water supply and the incidence of fractures and encephalopathy in patients on home dialysis. Br Med J. 1977 Sep 10;2(6088):657–660. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6088.657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prior J. C., Cameron E. C., Ballon H. S., Lirenman D. S., Moriarty M. V., Price J. D. Experience with 1,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol therapy in undergoing hemodialysis patients with progressive vitamin D2-treated osteodystrophy. Am J Med. 1979 Oct;67(4):583–589. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(79)90238-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao T. K., Friedman E. A. Editorial: Fluoride and bone disease in uremia. Kidney Int. 1975 Mar;7(3):125–129. doi: 10.1038/ki.1975.19. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritz E., Krempien B., Mehls O., Malluche H. Skeletal abnormalities in chronic renal insufficiency before and during maintenance hemodialysis. Kidney Int. 1973 Aug;4(2):116–127. doi: 10.1038/ki.1973.90. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STANBURY S. W., LUMB G. A. Metabolic studies of renal osteodystrophy. I. Calcium, phosphorus and nitrogen metabolism in rickets, osteomalacia and hyperparathyroidism complicating chronic uremia and in the osteomalacia of the adult Fanconi syndrome. Medicine (Baltimore) 1962 Feb;41:1–34. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanbury S. W., Lumb G. A., Mawer E. B. Osteodystrophy developing spontaneously in the course of chronic renal failure. Arch Intern Med. 1969 Sep;124(3):274–281. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisman Y., Eisenberg Z., Leib L., Harell A., Shasha S. M., Edelstein S. Serum concentrations of 24,25-dihydroxy vitamin D in different degrees of chronic renal failure. Br Med J. 1980 Sep 13;281(6242):712–713. doi: 10.1136/bmj.281.6242.712. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods C. G., Morgan D. B., Paterson C. R., Gossmann H. H. Measurement of osteoid in bone biopsy. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1968 Apr;95(2):441–447. doi: 10.1002/path.1700950214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YENDT E. R., CONNOR T. B., HOWARD J. E. In vitro calcification of rachitic rat cartilage in normal and pathological human sera with some observations on the pathogenesis of renal rickets. Bull Johns Hopkins Hosp. 1955 Jan;96(1):1–19. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]