Abstract
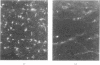
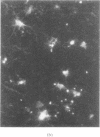
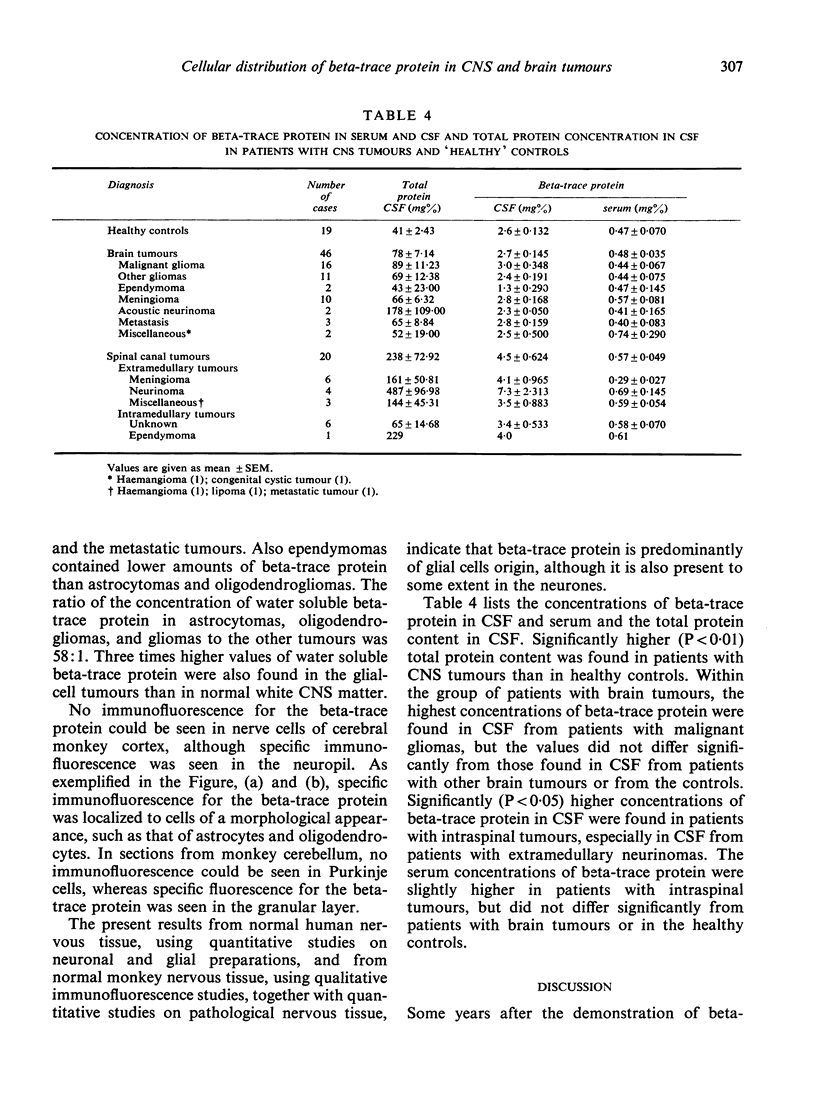
The low-molecular weight beta-trace protein constitutes about seven per cent of the total protein content in human cerebrospinal fluid. Within the central nervous system the protein is found predominantly in white matter and fractions enriched in glial cells. Immunofluorescence studies on sections of monkey brains show that beta-trace protein is particularly localized to cells such as astrocytes and oligodendrocytes. Significantly higher amounts of beta-trace protein are found in brain tumours derived from glial cells than in other tumours.
Full text
PDF

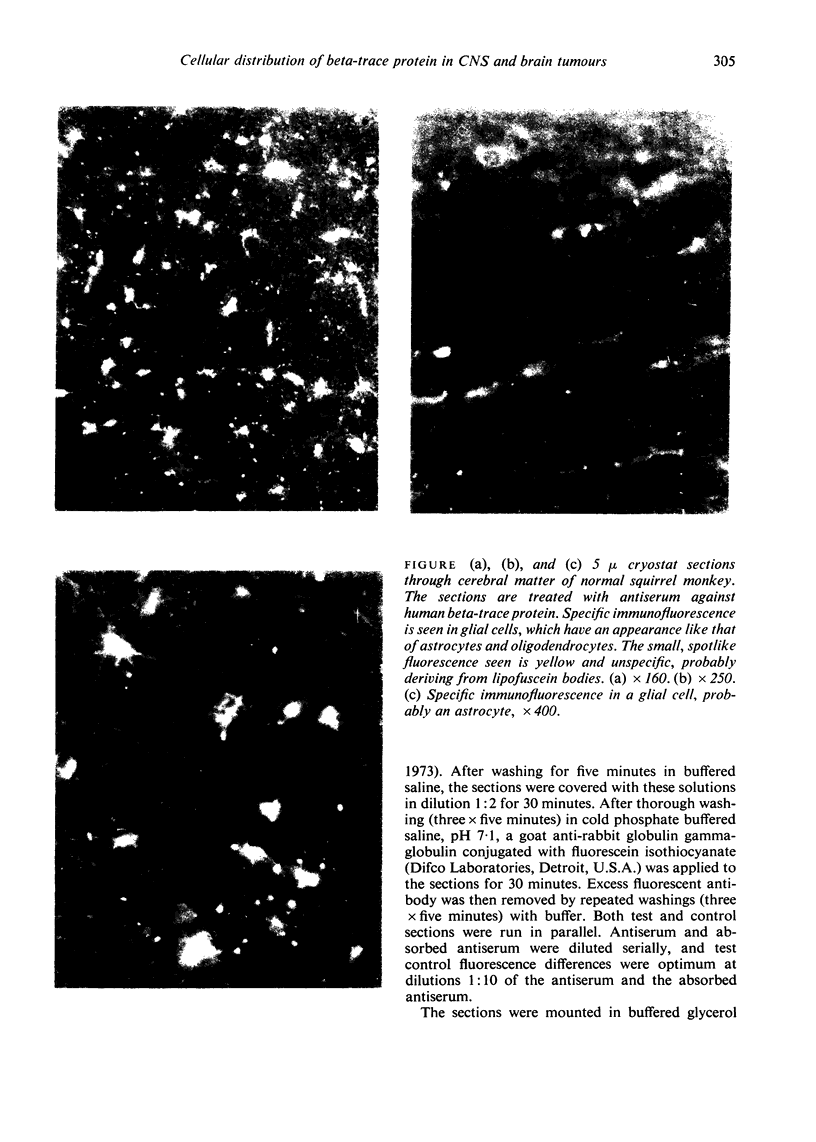





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benda P. Protéine S-100 et tumeurs cérébrales humaines. Rev Neurol (Paris) 1968 May;118(5):368–372. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blomstrand C., Hamberger A. Amino acid incorporation in vitro into protein of neuronal and glial cell-enriched fractions. J Neurochem. 1970 Aug;17(8):1187–1195. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1970.tb03367.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blomstrand C., Hamberger A. Protein turnover in cell-enriched fractions from rabbit brain. J Neurochem. 1969 Sep;16(9):1401–1407. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1969.tb05992.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COONS A. H. Fluorescent antibody methods. Gen Cytochem Methods. 1958;1:399–422. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COONS A. H. The application of fluorescent antibodies to the study of naturally occurring antibodies. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1957 Dec 16;69(4):658–662. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1957.tb49704.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cicero T. J., Cowan W. M., Moore B. W., Suntzeff V. The cellular localization of the two brain specific proteins, S-100 and 14-3-2. Brain Res. 1970 Feb 17;18(1):25–34. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(70)90454-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ericsson J., Link H., Zettervall O. Urinary excretion of a low molecular weight protein in cerebral damage. Neurology. 1969 Jun;19(6):606–610. doi: 10.1212/wnl.19.6.606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOCHWALD G. M., THORBECKE G. J. Use of an antiserum against cerebrospinal fluid in demonstration of trace proteins in biological fluids. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1962 Jan;109:91–95. doi: 10.3181/00379727-109-27113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haglid K. G., Carlsson C. A. An immunological study of some human brain tumours concerning the brain specific protein S100. Neurochirurgia (Stuttg) 1971 Jan;14(1):24–27. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1090551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haglid K. G., Stavrou D., Rönnbäck L., Carlsson C. A., Weidenbach W. The S-100 protein in water-soluble and pentanol-extractable form in normal human brain and tumours of the human nervous system. A quantitative study. J Neurol Sci. 1973 Sep;20(1):103–111. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(73)90122-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haglid K. G., Stavrou D. Water-soluble and pentanol-extractable proteins in human brain normal tissue and human brain tumours, with special reference to S-100 protein. J Neurochem. 1973 Jun;20(6):1523–1532. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1973.tb00270.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hydén H., McEwen B. A glial protein specific for the nervous system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Feb;55(2):354–358. doi: 10.1073/pnas.55.2.354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LATERRE E. C., HEREMANS J. F., CARBONARA A. IMMUNOLOGICAL COMPARISON OF SOME PROTEINS FOUND IN CEREBROSPINAL FLUID, URINE AND EXTRACTS FROM BRAIN AND KIDNEY. Clin Chim Acta. 1964 Sep;10:197–209. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(64)90136-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lightbody J., Pfeiffer S. E., Kornblith P. L., Herschman H. Biochemically differentiated clonal human glial cells in tissue culture. J Neurobiol. 1970;1(4):411–417. doi: 10.1002/neu.480010405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Link H., Müller R. Immunoglobulins in multiple sclerosis and infections of the nervous system. Arch Neurol. 1971 Oct;25(4):326–344. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1971.00490040052007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Link H., Olsson J. E. Beta-trace protein concentration in CSF in neurological disorders. Acta Neurol Scand. 1972;48(1):57–68. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.1972.tb07527.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore B. W. A soluble protein characteristic of the nervous system. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1965 Jun 9;19(6):739–744. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(65)90320-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore B. W., Perez V. J. Complement fixation for antigens on a picogram level. J Immunol. 1966 Jun;96(6):1000–1005. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsson J. E., Link H. Distribution of serum proteins and beta-trace protein within the nervous system. J Neurochem. 1973 Mar;20(3):837–846. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1973.tb00043.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsson J. E., Link H. Immunoglobulin abnormalities in multiple sclerosis. Relation to clinical parameters: exacerbations and remissions. Arch Neurol. 1973 Jun;28(6):392–399. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1973.00490240052009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsson J. E., Link H., Nosslin B. Metabolic studies on 125I-labelled beta-trace protein, with special reference to synthesis within the central nervous system. J Neurochem. 1973 Nov;21(5):1153–1159. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1973.tb07570.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsson J. E., Nord L. Immunochemical and immunofluorescence studies of beta-trace protein in different species and organs, with special reference to the central nervous system. J Neurochem. 1973 Sep;21(3):625–633. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1973.tb06007.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Packman P. M., Blomstrand C., Hamberger A. Disc electrophoretic separation of proteins in neuronal, glial and subcellular fractions from cerebral cortex. J Neurochem. 1971 Mar;18(3):479–487. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1971.tb11975.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penny R., Osserman E. F. Studies on beta-trace protein. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1971 Feb;49(1):111–120. doi: 10.1038/icb.1971.9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart J. A. Tissue specific brain S-100. A demonstration of multiple proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Mar 15;263(1):178–192. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(72)90171-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sviridov S. M., Korochkin L. I., Ivanov V. N., Maletskaya E. I., Bakhtina T. K. Immunohistochemical studies of S-100 protein during postnatal ontogenesis of the brain of two strains of rats. J Neurochem. 1972 Mar;19(3):713–718. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1972.tb01386.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WIEME R. J. An improved technique of agar-gel electrophoresis on microscope slides. Clin Chim Acta. 1959 May;4(3):317–321. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(59)90096-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]