Abstract
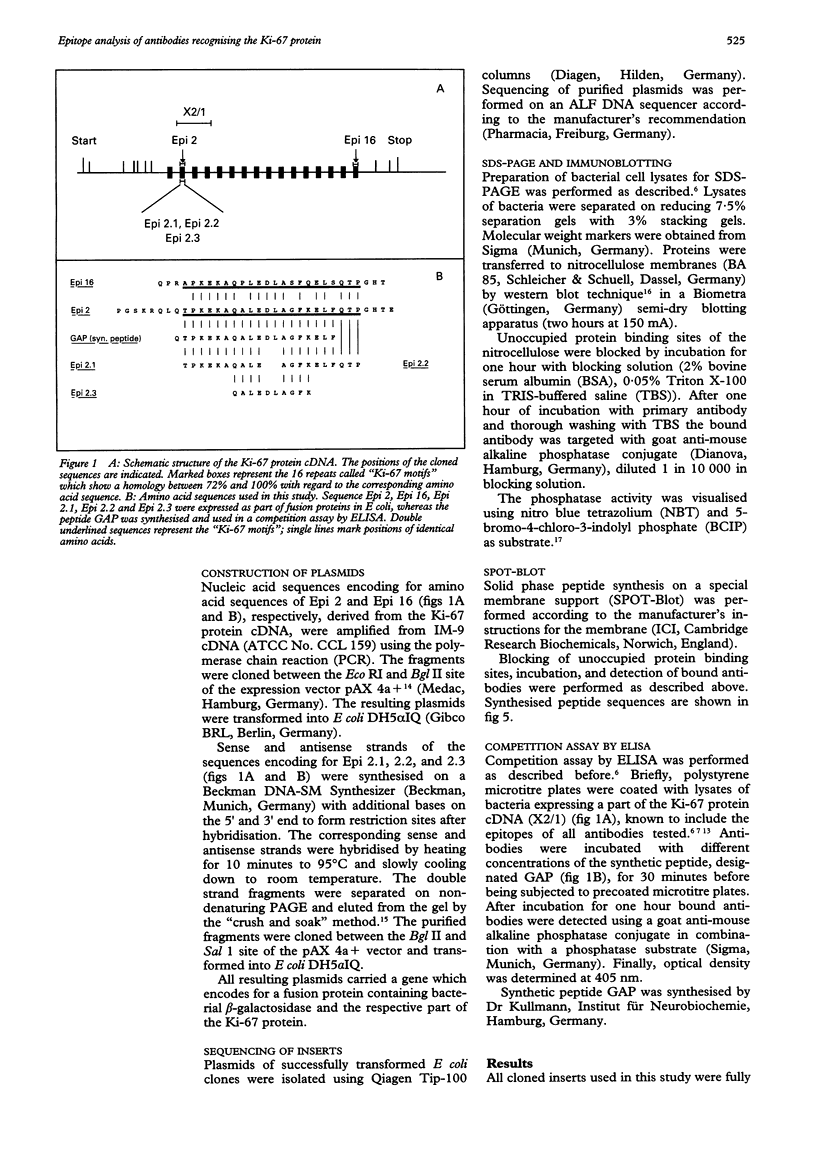
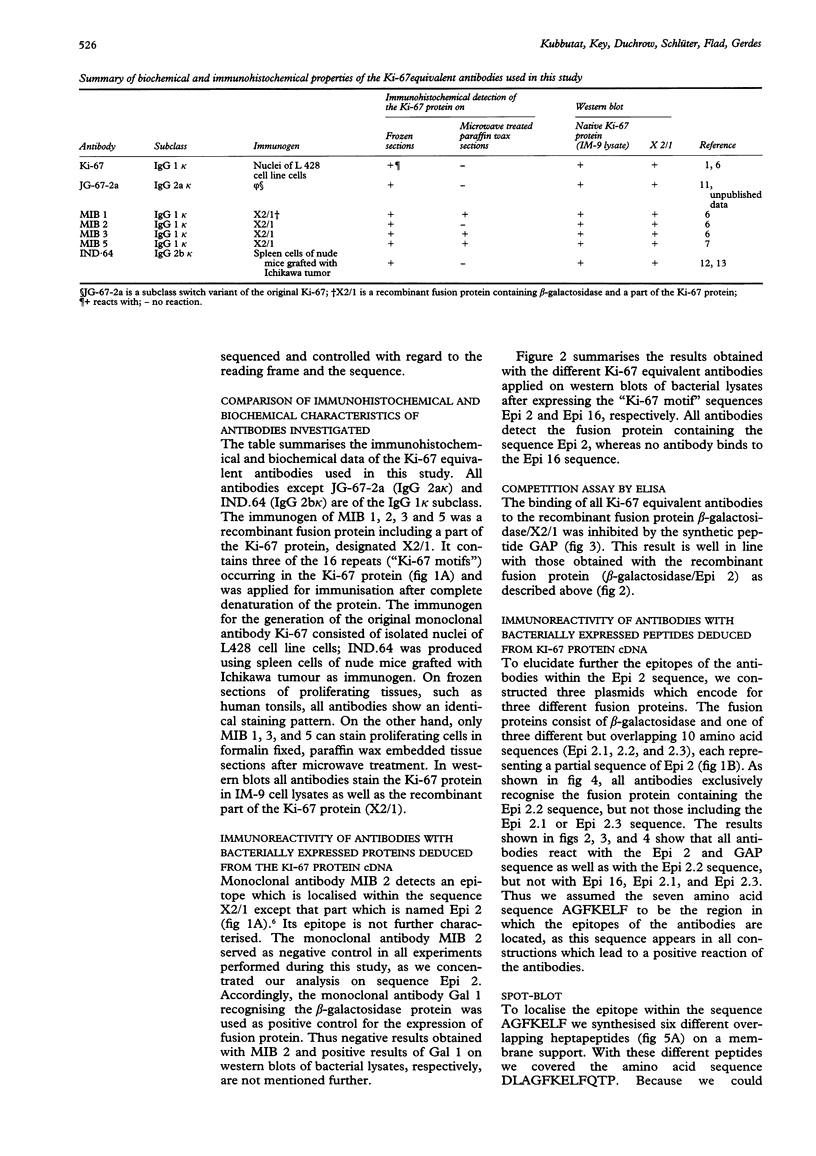
AIMS--To elucidate the fine specificities of the antibodies MIB 1 and MIB 3 and of additional monoclonal antibodies which also recognise the Ki-67 protein (MIB 5, IND.64, JG-67-2a). METHODS--Different parts of the Ki-67 protein cDNA were expressed in Escherichia coli. Bacterial lysates were separated by sodium dodecyl sulphate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) and blotted on to nitrocellulose. Additionally different peptides were synthesised on a membrane support (SPOT-Blot). The immunoreactivity of the antibodies with the recombinant proteins and the immobilised synthetic peptides, respectively, was analysed. A competition enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) using a soluble synthetic peptide was also performed. RESULTS--The epitopes of all antibodies tested were contained within the same region of seven amino acids. The antibodies MIB 1 and MIB 3 required the five amino acid sequence FKELF for binding, whereas Ki-67, JG-67-2a, MIB 5 and IND.64 detected the sequence FKEL. CONCLUSIONS--It is concluded that the amino acid sequence FKELF represents an immunodominant area of the Ki-67 protein and that there is no correlation between the ability to detect the Ki-67 protein in paraffin wax sections irradiated with microwaves and the epitopes recognised by the antibodies.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brown D. C., Gatter K. C. Monoclonal antibody Ki-67: its use in histopathology. Histopathology. 1990 Dec;17(6):489–503. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.1990.tb00788.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cattoretti G., Becker M. H., Key G., Duchrow M., Schlüter C., Galle J., Gerdes J. Monoclonal antibodies against recombinant parts of the Ki-67 antigen (MIB 1 and MIB 3) detect proliferating cells in microwave-processed formalin-fixed paraffin sections. J Pathol. 1992 Dec;168(4):357–363. doi: 10.1002/path.1711680404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerdes J., Becker M. H., Key G., Cattoretti G. Immunohistological detection of tumour growth fraction (Ki-67 antigen) in formalin-fixed and routinely processed tissues. J Pathol. 1992 Sep;168(1):85–86. doi: 10.1002/path.1711680114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerdes J. Ki-67 and other proliferation markers useful for immunohistological diagnostic and prognostic evaluations in human malignancies. Semin Cancer Biol. 1990 Jun;1(3):199–206. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerdes J., Lemke H., Baisch H., Wacker H. H., Schwab U., Stein H. Cell cycle analysis of a cell proliferation-associated human nuclear antigen defined by the monoclonal antibody Ki-67. J Immunol. 1984 Oct;133(4):1710–1715. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerdes J., Schwab U., Lemke H., Stein H. Production of a mouse monoclonal antibody reactive with a human nuclear antigen associated with cell proliferation. Int J Cancer. 1983 Jan 15;31(1):13–20. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910310104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall P. A., Woods A. L. Immunohistochemical markers of cellular proliferation: achievements, problems and prospects. Cell Tissue Kinet. 1990 Nov;23(6):505–522. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2184.1990.tb01343.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Key G., Becker M. H., Baron B., Duchrow M., Schlüter C., Flad H. D., Gerdes J. New Ki-67-equivalent murine monoclonal antibodies (MIB 1-3) generated against bacterially expressed parts of the Ki-67 cDNA containing three 62 base pair repetitive elements encoding for the Ki-67 epitope. Lab Invest. 1993 Jun;68(6):629–636. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Key G., Meggetto F., Becker M. H., al Saati T., Schlüter C., Duchrow M., Delsol G., Gerdes J. Immunobiochemical characterization of the antigen detected by monoclonal antibody IND.64. Evidence that IND.64 reacts with the cell proliferation associated nuclear antigen previously defined by Ki-67. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol Incl Mol Pathol. 1992;62(4):259–262. doi: 10.1007/BF02899690. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markmeyer P., Rühlmann A., Englisch U., Cramer F. The pAX plasmids: new gene-fusion vectors for sequencing, mutagenesis and expression of proteins in Escherichia coli. Gene. 1990 Sep 1;93(1):129–134. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90146-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meggetto F., al Saati T., Cohen-Knafo E., Roubinet F., Selves J., Bouche G., Key G., Gerdes J., Delsol G. Production of a monoclonal antibody (IND.64) identifying a cell cycle-associated antigen using spleen cells from nude mice bearing Ichikawa tumour. J Pathol. 1992 Oct;168(2):187–196. doi: 10.1002/path.1711680206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlüter C., Duchrow M., Wohlenberg C., Becker M. H., Key G., Flad H. D., Gerdes J. The cell proliferation-associated antigen of antibody Ki-67: a very large, ubiquitous nuclear protein with numerous repeated elements, representing a new kind of cell cycle-maintaining proteins. J Cell Biol. 1993 Nov;123(3):513–522. doi: 10.1083/jcb.123.3.513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]