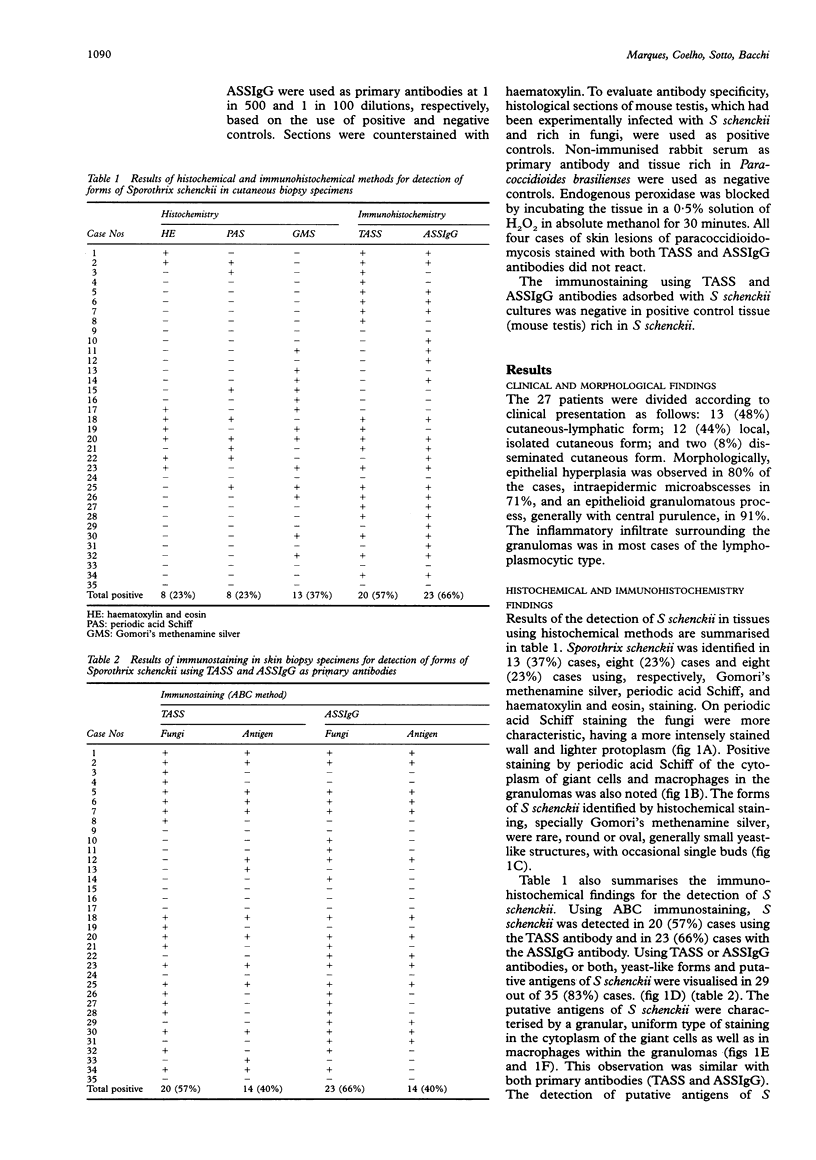
Abstract
AIMS: To compare the efficacy of histochemical and immunohistochemical methods in detecting forms of Sporothrix schenckii in tissue. METHODS: Thirty five cutaneous biopsy specimens from 27 patients with sporotrichosis were stained by histochemical haematoxylin and eosin, periodic acid Schiff, and Gomori's methenamine silver methods and an immunohistochemical (avidin-biotin complex immunoperoxidase) (ABC) technique associated with a newly produced rabbit polyclonal antibody anti-Sporothrix schenckii. RESULTS: A total of 29 (83%) cases were positive by the ABC method used in association with anti-Sporothrix schenckii rabbit polyclonal antibodies. Histochemical methods, using silver staining, periodic acid Schiff, and conventional haematoxylin and eosin detected 37%, 23%, and 23% of forms of S schenckii, respectively. The ABC technique was significantly more reliable than periodic acid Schiff and silver staining techniques. CONCLUSIONS: It is concluded that immunostaining is an easy and rapid method which can efficiently increase the accuracy of the diagnosis of sporotrichosis in human tissue.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ey P. L., Prowse S. J., Jenkin C. R. Isolation of pure IgG1, IgG2a and IgG2b immunoglobulins from mouse serum using protein A-sepharose. Immunochemistry. 1978 Jul;15(7):429–436. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(78)90070-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Findlay G. H., Vismer H. F., Dreyer L. Studies on sporotrichosis. Pathogenicity and morphogenesis in the Transvaal strains of Sporothrix schenckii. Mycopathologia. 1984 Aug 30;87(1-2):85–93. doi: 10.1007/BF00436634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hachisuka H., Sasai Y. A peculiar case of sporotrichosis. Dermatologica. 1980;160(1):37–40. doi: 10.1159/000250465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiruma M., Kagawa S. A case of sporotrichosis with numerous fungal elements phagocytized by polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Mykosen. 1986 Feb;29(2):59–63. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu S. M., Raine L., Fanger H. Use of avidin-biotin-peroxidase complex (ABC) in immunoperoxidase techniques: a comparison between ABC and unlabeled antibody (PAP) procedures. J Histochem Cytochem. 1981 Apr;29(4):577–580. doi: 10.1177/29.4.6166661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinbara T., Fukushiro R. Fungal elements in tissues of sporotrichosis. Mykosen. 1983 Jan;26(1):35–41. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0507.1983.tb03936.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi K., Hayama M., Hotchi M. The application of immunoperoxidase staining for the detection of causative fungi in tissue specimens of mycosis I. Mycopathologia. 1988 May;102(2):107–113. doi: 10.1007/BF00437447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Male O. Diagnostische und therapeutische Probleme bei der kutanen Sporotrichose. Z Hautkr. 1974 Jun 15;49(12):505–515. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moskowitz L. B., Ganjei P., Ziegels-Weissman J., Cleary T. J., Penneys N. S., Nadji M. Immunohistologic identification of fungi in systemic and cutaneous mycoses. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1986 May;110(5):433–436. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell B., Beckett J. H., Jacobs P. H. Immunoperoxidase localization of Sporothrix schenckii and Cryptococcus neoformans. Staining of tissue sections fixed in 4% formaldehyde solution and embedded in paraffin. Arch Dermatol. 1979 Apr;115(4):433–435. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz J. N. Specific fungal diagnosis. Help on the way. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1986 May;110(5):369–370. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal R. J., Jacobs P. H. Sporotrichosis. Int J Dermatol. 1979 Oct;18(8):639–644. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-4362.1979.tb04682.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]