Abstract
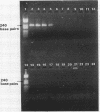
AIMS: To develop a readily applicable polymerase chain reaction (PCR) based technique which would permit the identification of Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex isolates from Bactec phials at an earlier stage than currently available methods. METHODS: Mycobacterial cells cultured in Bactec 12B medium were harvested by centrifugation. The cells were lysed by heating in distilled water. Oligonucleotide primers based on the sequence of the gene coding for the immunogenic protein MPB64 were then used to amplify a 240 base pair fragment of DNA directly from the crude cell lysate. The PCR product was visualised under ultraviolet light following electrophoresis of an aliquot in an agarose gel containing ethidium bromide. The sensitivity of the PCR was adjusted so that about 600 cfu of M tuberculosis gave a positive result. The lowest growth index at which this method of identification might be applied to Bactec phials was determined and a number of routine cultures giving a positive growth index examined. RESULTS: M tuberculosis was positively identified at the lowest growth index, as determined by the Bactec system. Of 45 routine cultures examined, with growth indexes ranging from 6 to 999, the 15 confirmed by conventional means to contain M tuberculosis were correctly identified from 1 ml of culture medium. CONCLUSIONS: The method described can be used to identify M tuberculosis isolates cultured in the Bactec system at the earliest detectable rise in growth index. It may therefore allow cultured mycobacteria to be identified at an earlier stage than conventional methods or the commercially available DNA probes adapted for use with the Bactec system.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anargyros P., Astill D. S., Lim I. S. Comparison of improved BACTEC and Lowenstein-Jensen media for culture of mycobacteria from clinical specimens. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Jun;28(6):1288–1291. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.6.1288-1291.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barry T., Powell R., Gannon F. A general method to generate DNA probes for microorganisms. Biotechnology (N Y) 1990 Mar;8(3):233–236. doi: 10.1038/nbt0390-233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bates J. H. Diagnosis of tuberculosis. Chest. 1979 Dec;76(6 Suppl):757–763. doi: 10.1378/chest.76.6_supplement.757. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brisson-Noël A., Gicquel B., Lecossier D., Lévy-Frébault V., Nassif X., Hance A. J. Rapid diagnosis of tuberculosis by amplification of mycobacterial DNA in clinical samples. Lancet. 1989 Nov 4;2(8671):1069–1071. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)91082-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böddinghaus B., Rogall T., Flohr T., Blöcker H., Böttger E. C. Detection and identification of mycobacteria by amplification of rRNA. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Aug;28(8):1751–1759. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.8.1751-1759.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Wit D., Steyn L., Shoemaker S., Sogin M. Direct detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in clinical specimens by DNA amplification. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Nov;28(11):2437–2441. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.11.2437-2441.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermans P. W., Schuitema A. R., Van Soolingen D., Verstynen C. P., Bik E. M., Thole J. E., Kolk A. H., van Embden J. D. Specific detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex strains by polymerase chain reaction. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Jun;28(6):1204–1213. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.6.1204-1213.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermans P. W., van Soolingen D., Dale J. W., Schuitema A. R., McAdam R. A., Catty D., van Embden J. D. Insertion element IS986 from Mycobacterium tuberculosis: a useful tool for diagnosis and epidemiology of tuberculosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Sep;28(9):2051–2058. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.9.2051-2058.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pao C. C., Yen T. S., You J. B., Maa J. S., Fiss E. H., Chang C. H. Detection and identification of Mycobacterium tuberculosis by DNA amplification. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Sep;28(9):1877–1880. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.9.1877-1880.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson E. M., Lu R., Floyd C., Nakasone A., Friedly G., de la Maza L. M. Direct identification of Mycobacterium tuberculosis, Mycobacterium avium, and Mycobacterium intracellulare from amplified primary cultures in BACTEC media using DNA probes. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Jul;27(7):1543–1547. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.7.1543-1547.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shankar P., Manjunath N., Lakshmi R., Aditi B., Seth P., Shriniwas Identification of Mycobacterium tuberculosis by polymerase chain reaction. Lancet. 1990 Feb 17;335(8686):423–423. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)90268-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shankar P., Manjunath N., Mohan K. K., Prasad K., Behari M., Shriniwas, Ahuja G. K. Rapid diagnosis of tuberculous meningitis by polymerase chain reaction. Lancet. 1991 Jan 5;337(8732):5–7. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)93328-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siddiqi S. H., Hwangbo C. C., Silcox V., Good R. C., Snider D. E., Jr, Middlebrook G. Rapid radiometric methods to detect and differentiate Mycobacterium tuberculosis/M. bovis from other mycobacterial species. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1984 Oct;130(4):634–640. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1984.130.4.634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi R., Matsuo K., Yamazaki A., Abe C., Nagai S., Terasaka K., Yamada T. Cloning and characterization of the gene for immunogenic protein MPB64 of Mycobacterium bovis BCG. Infect Immun. 1989 Jan;57(1):283–288. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.1.283-288.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]