Full text
PDF

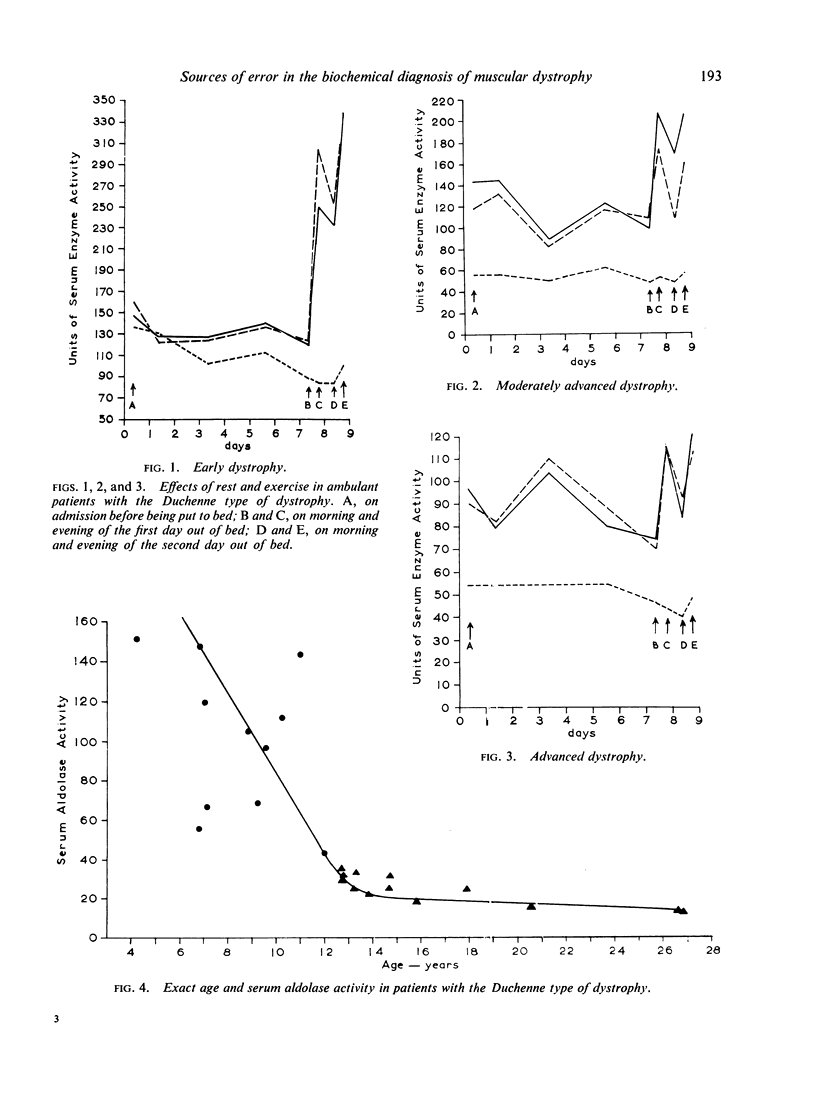
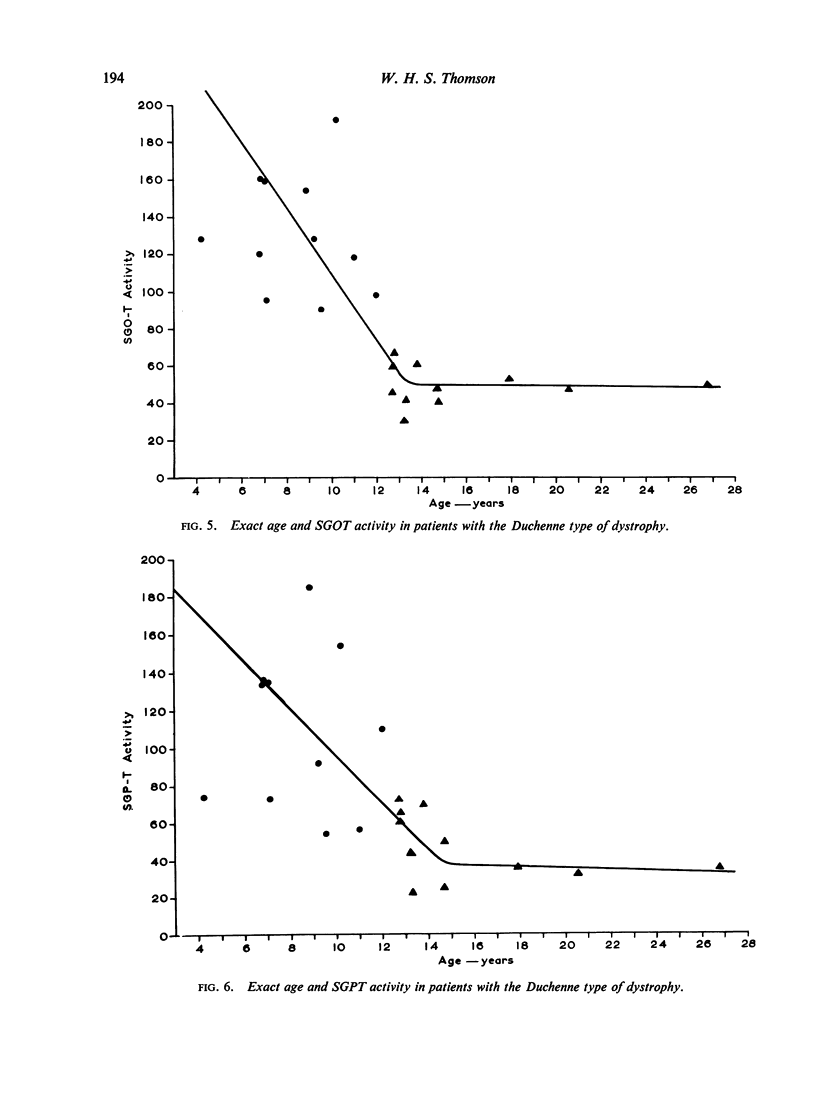
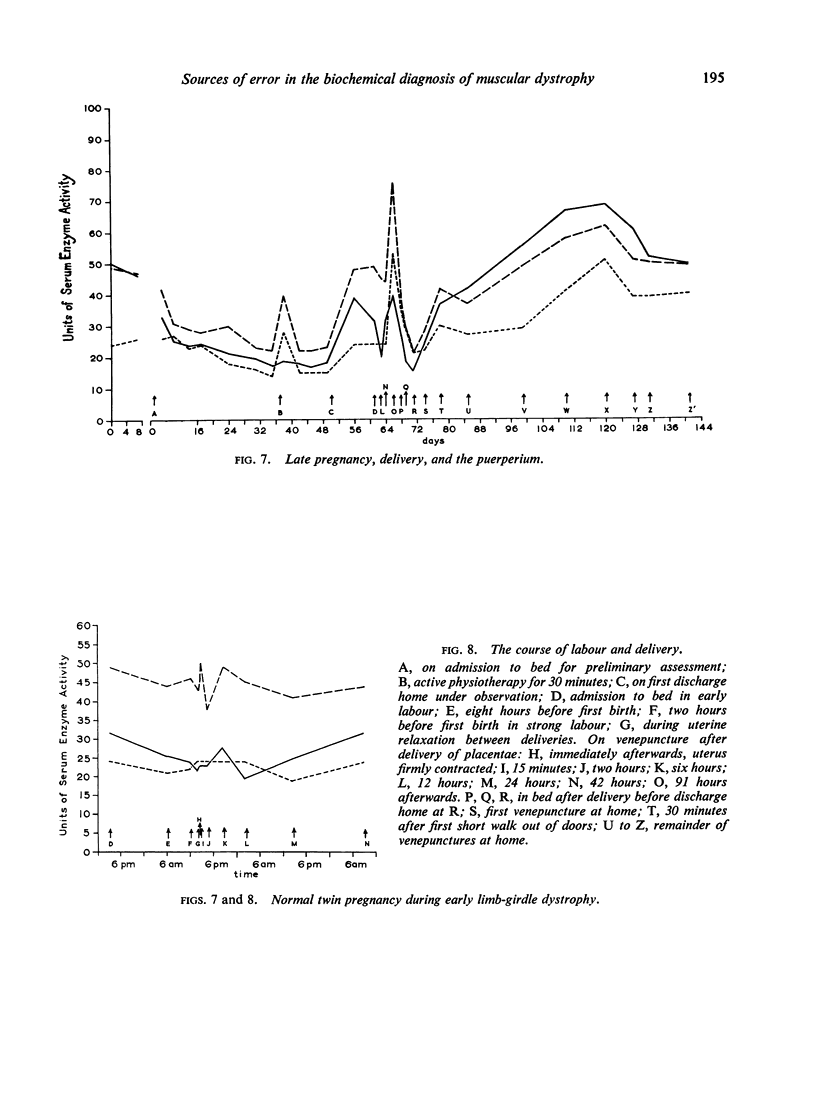
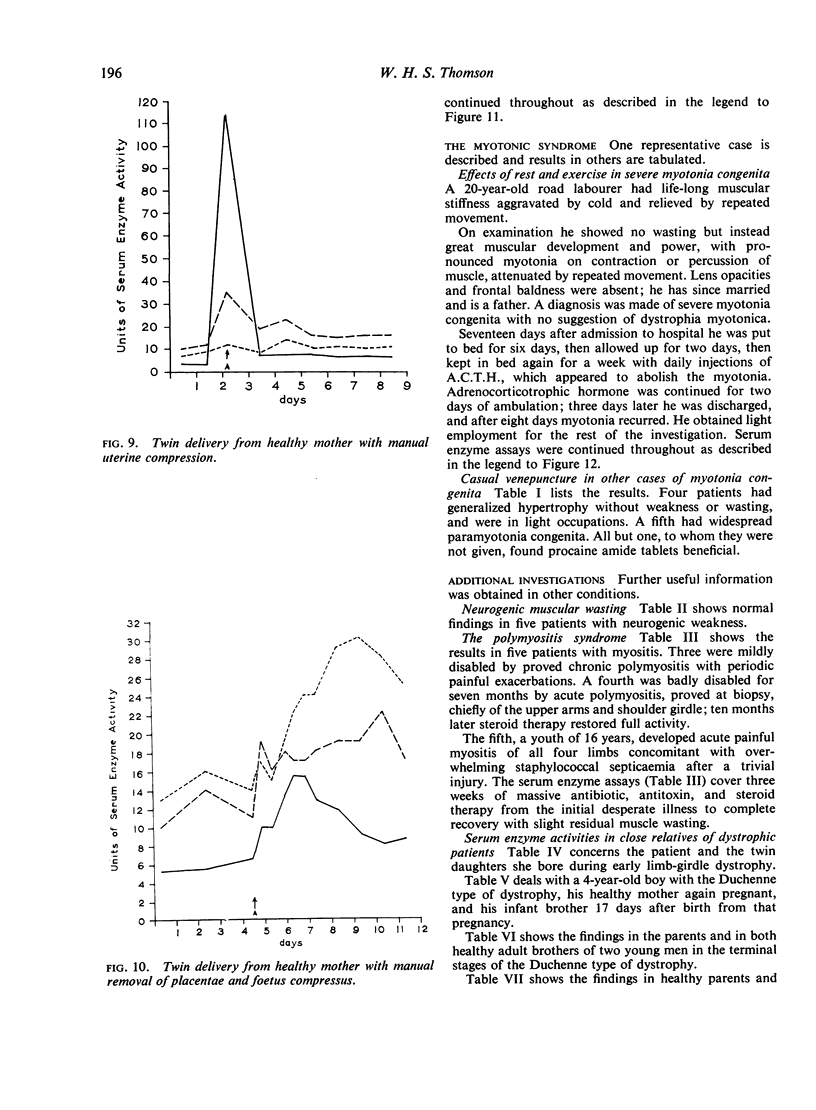




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BAKER R. W., EVANS J. H. Serum aldolase and the diagnosis of myopathy. Brain. 1957 Dec;80(4):557–570. doi: 10.1093/brain/80.4.557. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARRETT A. M., GRESHAM G. A. Acute streptococcal myositis. Lancet. 1958 Feb 15;1(7016):347–350. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(58)90971-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLYTH H., PUGH R. J. Muscular dystrophy in childhood; the genetic aspect; a field study in the Leeds region of clinical types and their inheritance. Ann Hum Genet. 1959 Apr;23(2):127–163. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1958.tb01457.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOMPIANI A. Attività glutamico-ossalacetico transaminasica del siero nella donna gravida, nella partoriente, nella puerpera. Ann Ostet Ginecol. 1956 Jun;78(6):705–717. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRETON A., GAUDIER B., TRAISNEL M., PONTE C. [Study of the level of serum transaminases and aldolase during myopathies]. Presse Med. 1959 Dec 26;67:2329–2331. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRUMLIK J., WACHS H., HUMMEL W., BOSHES B. Dermatomyositis; a discussion of the recent literature and report of two cases. Q Bull Northwest Univ Med Sch. 1959;33(1):22–28. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRUNS F. Bestimmung und Eigenschaften der Serumaldolase. Biochem Z. 1954;325(2):156–162. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CASULA D., CHERCHI P., SPINAZZOLA A. [Contribution to the blood enzyme picture during muscular work]. G Clin Med. 1961 May;42:499–513. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CERRETELLI P., CANTONE A., MORANDINI M. L., MAMMANO R. [Effect of fatigue on the efflux of aldolase from isolated muscle]. Boll Soc Ital Biol Sper. 1959 Dec 31;35:1935–1937. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHUNG C. S., MORTON N. E., PETERS H. A. Serum enzymes and genetic carriers in muscular dystrophy. Am J Hum Genet. 1960 Mar;12:52–66. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS H. A. Pregnancy in myotonica dystrophia; a case report. J Obstet Gynaecol Br Emp. 1958 Jun;65(3):479–480. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.1958.tb08542.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DREYFUS J. C., SCHAPIRA G., DEMOS J. Etude des différences artérioveineuses au cours des myopathies. 1. Oxygène, glucose et acide lactique. 2. Aldolase plasmatique. Clin Chim Acta. 1958 Nov;3(6):571–577. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(58)90010-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DREYFUS J. C., SCHAPIRA G. L'activité transaminasique du sérum au cours des myopathies. C R Seances Soc Biol Fil. 1955 Nov;149(21-22):1934–1935. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUBACH U. C., STAMM H. O. Transaminasebestimmungen in der Geburtshilfe. Arch Gynakol. 1958;190(4):394–403. doi: 10.1007/BF00672659. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRIEDMAN M. M., LAPAN B. Serum aldolase in the neonatal period: including a colorimetric determination of aldolase by standardization with dihydroxyacetone. J Lab Clin Med. 1958 May;51(5):745–752. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GASPARDY G., KOVACS L., SIMON M., VIDA M. [On the problem of the pathogenesis of muscular atrophy in chronic polyarthritis]. Z Rheumaforsch. 1959 Dec;18:455–459. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GENTILI C. [Significance of the increase of aldolase in blood in muscular dystrophy]. Clin Pediatr (Bologna) 1959 Sep;41:736–739. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JACOB W., NEUHAUS J. Die Aktivität der Serumaldolase bei der progressiven Muskeldystrophie (ERB). Klin Wochenschr. 1954 Oct 1;32(37-38):923–924. doi: 10.1007/BF01467153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAESER H. E. [The behavior of serum glutamic acid-oxalacetic acid transaminase in myopathies and neurogenic muscle atrophies]. Dtsch Z Nervenheilkd. 1959;179:353–362. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KARMEN A. A note on the spectrometric assay of glutamic-oxalacetic transaminase in human blood serum. J Clin Invest. 1955 Jan;34(1):131–133. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KARMEN A., WROBLEWSKI F., LADUE J. S. Transaminase activity in human blood. J Clin Invest. 1955 Jan;34(1):126–131. doi: 10.1172/JCI103055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRUH J., DREYFUS J. C., SCHAPIRA G., GEY G. O., Jr Abnormalities of muscle protein metabolism in mice with muscular dystrophy. J Clin Invest. 1960 Jul;39:1180–1184. doi: 10.1172/JCI104132. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAPAN B., FRIEDMAN M. M. A comparative study of fetal and maternal serum enzyme levels. J Lab Clin Med. 1959 Sep;54:417–426. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEYBURN P., THOMSON W. H., WALTON J. N. An investigation of the carrier state in the Duchenne type muscular dystrophy. Ann Hum Genet. 1961 May;25:41–49. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1961.tb01495.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAAS O., PATERSON A. S. Myotonia congenita, dystrophia myotonica and paramyotonia; reaffirmation of their identity. Brain. 1950;73(3):318–336. doi: 10.1093/brain/73.3.318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTONI L., MUSIANI S. Variazioni dell'attività aldolasica serica nell'età neonatale in condizioni fisiologiche, parafisiologiche e patologiche. Clin Pediatr (Bologna) 1958 May;40(5):397–409. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MASON J. H., WROBLEWSKI F. Serum glutamic oxalacetic transaminase activity in experimental and disease states; a review. AMA Arch Intern Med. 1957 Feb;99(2):245–252. doi: 10.1001/archinte.1957.00260020081012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MURPHY E. G., CHERNIAK M. M. Glutamic oxalacetic transaminase activity in the serum in muscular dystrophy and other neuromuscular disorders in childhood. Pediatrics. 1958 Dec;22(6):1110–1114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PEARSON C. M. Serum enzymes in muscular dystrophy and certain other muscular and neuromuscular diseases. I. Serum glutamic oxalacetic transaminase. N Engl J Med. 1957 Jun 6;256(23):1069–1075. doi: 10.1056/NEJM195706062562301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PRYSTOWSKY H., HELLEGERS A. E., RANKE E., RANKE B., CHOW B. F. Further observations on the metabolism of vitamin B12 in human pregnancy. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1959 Jan;77(1):1–5. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(59)90260-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REITMAN S., FRANKEL S. A colorimetric method for the determination of serum glutamic oxalacetic and glutamic pyruvic transaminases. Am J Clin Pathol. 1957 Jul;28(1):56–63. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/28.1.56. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RICHTER K., KONITZER K. [Changes in aldolase activity in the blood serum during muscular work]. Klin Wochenschr. 1960 Oct 1;38:998–999. doi: 10.1007/BF01484314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROWELL N. R., SMITH A. J. Multiple serial enzyme studies in acute myocardial infarction. Br Med J. 1959 Sep 19;2(5150):459–463. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5150.459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROWLAND L. P., ROSS G. Serum aldolase in muscular dystrophies, neuromuscular disorders, and wasting of skeletal muscle. AMA Arch Neurol Psychiatry. 1958 Aug;80(2):157–161. doi: 10.1001/archneurpsyc.1958.02340080027003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SALVI G., AMBANELLI U., ROSATI G., CARRERAS M., MIRONI F. [Changes in serum glutamic oxalacetic transaminases and aldolases in muscle diseases, with special reference to Steinert's myotonic dystrophy]. Riv Patol Nerv Ment. 1959;80:1–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SANTONI G. Sul diverso comportamento dell'attività glutammico-ossalacetico transaminasica sierica nel sangue materno, funicolo-placentare e del neonato. Ann Ostet Ginecol. 1956 Jun;78(6):718–724. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHAPIRA F., DEMOS J., SCHAPIRA G., DREYFUS J. C. Facteurs de l'hyperaldolasémie au cours des myopathies. Rev Fr Etud Clin Biol. 1957 Sep;2(7):728–734. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHAPIRA F., SCHAPIRA G., DREYFUS J. C. Hyperaldolasémie chez la souris myopathique. C R Hebd Seances Acad Sci. 1957 Aug 5;245(6):753–755. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHAPIRA G., DREYFUS J. C., SCHAPIRA F. L'élévation du taux de l'aldolase sérique; test biochimique des myopathies. Sem Hop. 1953 Jun 10;29(38):1917–1920. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHAPIRA G., KRUH J., DREYFUS J. C., SCHAPIRA F. The molecular turnover of muscle aldolase. J Biol Chem. 1960 Jun;235:1738–1741. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHLANG H. A. The effect of physical exercise on serum transaminase. Am J Med Sci. 1961 Sep;242:338–341. doi: 10.1097/00000441-196109000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SIBLEY J. A., FLEISHER G. A. The clinical significance of serum aldolase. Proc Staff Meet Mayo Clin. 1954 Nov 10;29(23):591–603. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SIBLEY J. A. Significance of serum aldolase levels. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1958 Oct 13;75(1):339–348. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1958.tb36881.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SIEKERT R. G., FLEISHER G. A. Serum glutamic oxalacetic transaminase in certain neurologic and neuromuscular diseases. Proc Staff Meet Mayo Clin. 1956 Aug 8;31(16):459–464. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SLATER E. C. Spectrophotometric determination of fructose-1:6-diphosphate, hexosemonophosphates, adenosinetriphosphate and adenosinediphosphate. Biochem J. 1953 Jan;53(1):157–167. doi: 10.1042/bj0530157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SOLTAN H. C. Muscular dystrophy in three pairs of twins. Acta Genet Med Gemellol (Roma) 1959 Oct;8:434–442. doi: 10.1017/s1120962300018618. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THOMPSON R. A., VIGNOS P. J., Jr Serum aldolase in muscle disease. AMA Arch Intern Med. 1959 Apr;103(4):551–564. doi: 10.1001/archinte.1959.00270040037004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THOMSON W. H., LEYBURN P., WALTON J. N. Serum enzyme activity in muscular dystrophy. Br Med J. 1960 Oct 29;2(5208):1276–1281. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5208.1276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WALTON J. N., NATTRASS F. J. On the classification, natural history and treatment of the myopathies. Brain. 1954;77(2):169–231. doi: 10.1093/brain/77.2.169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHITE A. A., HESS W. C. Some alterations in serum enzymes in progressive muscular dystrophy. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1957 Mar;94(3):541–544. doi: 10.3181/00379727-94-23006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHITE L. P. Some enigmas in the comparison of multiple serum enzyme levels. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1958 Oct 13;75(1):349–356. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1958.tb36882.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WROBLEWSKI F., LADUE J. S. Serum glutamic pyruvic transaminase in cardiac with hepatic disease. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1956 Apr;91(4):569–571. doi: 10.3181/00379727-91-22330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZIERLER K. L. Muscle membrane as a dynamic structure and its permeability to aldolase. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1958 Oct 13;75(1):227–234. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1958.tb36869.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


