Abstract
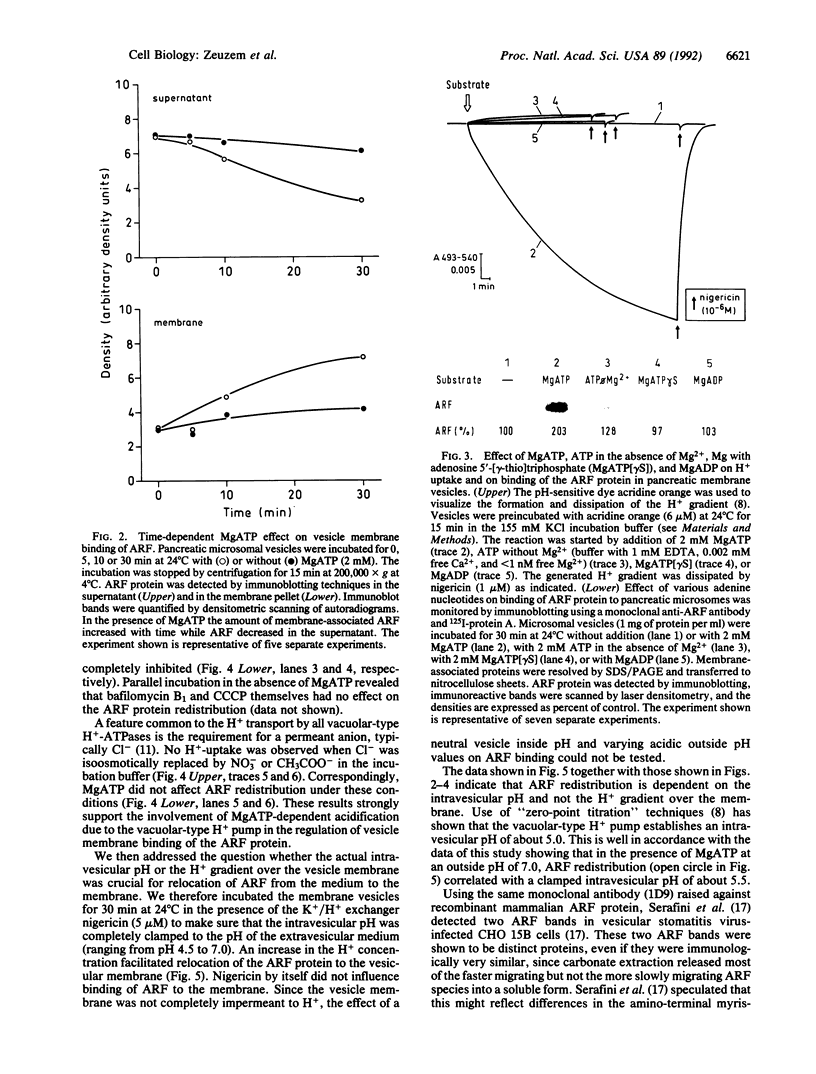
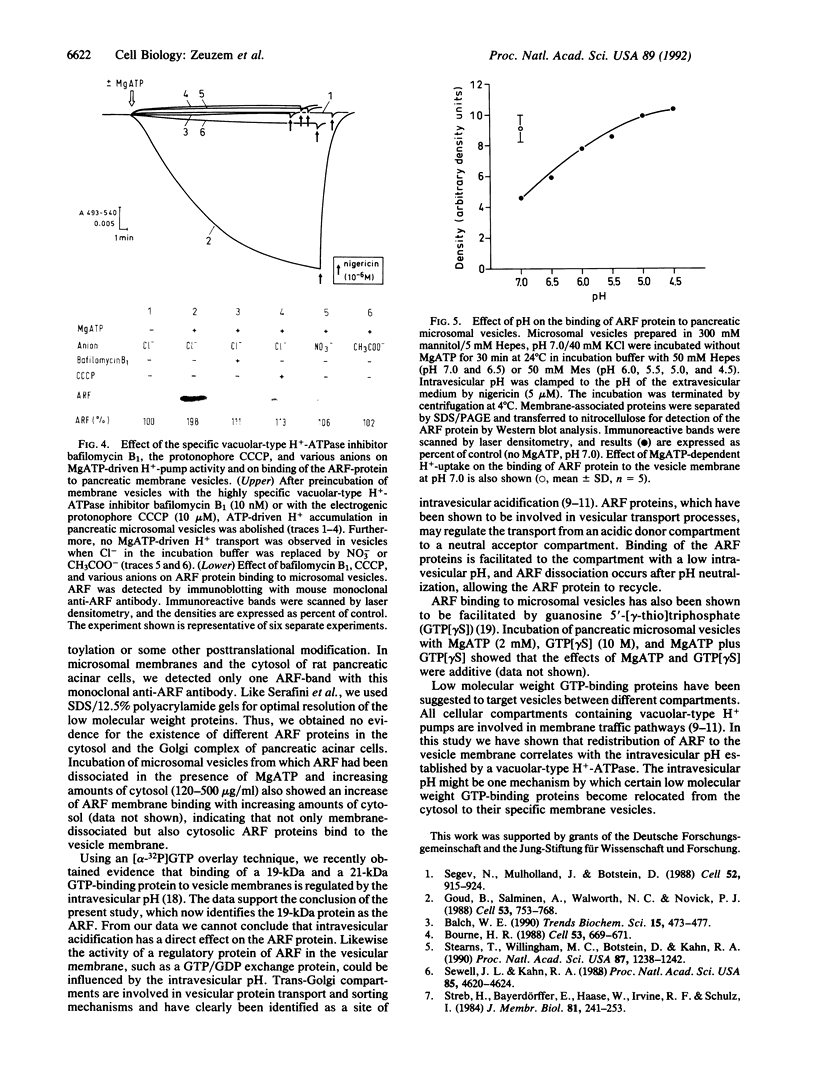
The ADP-ribosylation factor (ARF), a highly conserved low molecular weight GTP-binding protein, has been implicated to function in intracellular protein transport to and within the Golgi complex. In pancreatic acinar cells the ARF is confined to the cytoplasmic faces of trans-Golgi stack membranes, a compartment known to maintain a low intravesicular pH, which is established by a chloride-dependent MgATP-driven proton pump. The present study shows that MgATP (2mM), but neither adenosine 5'-[gamma-thio]triphosphate in the presence of Mg2+ nor ATP in the absence of Mg2+, increases transfer of ARF from the surrounding medium into the vesicle membranes. The specific vacuolar-type proton pump inhibitor bafilomycin B1 (10 nM), the protonophore carbonylcyanide m-chlorophenylhydrazone (10 microM), and replacement of chloride in the incubation buffer by acetate or nitrate resulted in an almost complete inhibition of the MgATP-dependent association of ARF to the vesicle membranes. The results demonstrate that redistribution of ARF to the vesicle membrane correlates with the intravesicular pH established by a vacuolar-type H(+)-ATPase. The intravesicular pH appears to be one mechanism by which certain low molecular weight GTP-binding proteins become relocated from the cytosol to their specific membrane vesicles.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Al-Awqati Q. Proton-translocating ATPases. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1986;2:179–199. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.02.110186.001143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balch W. E. Small GTP-binding proteins in vesicular transport. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Dec;15(12):473–477. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90301-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourne H. R. Do GTPases direct membrane traffic in secretion? Cell. 1988 Jun 3;53(5):669–671. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90081-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowman E. J., Siebers A., Altendorf K. Bafilomycins: a class of inhibitors of membrane ATPases from microorganisms, animal cells, and plant cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(21):7972–7976. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.21.7972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forgac M. Structure and function of vacuolar class of ATP-driven proton pumps. Physiol Rev. 1989 Jul;69(3):765–796. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1989.69.3.765. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goud B., Salminen A., Walworth N. C., Novick P. J. A GTP-binding protein required for secretion rapidly associates with secretory vesicles and the plasma membrane in yeast. Cell. 1988 Jun 3;53(5):753–768. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90093-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hampe W., Zimmermann P., Schulz I. GTP-induced fusion of isolated pancreatic microsomal vesicles is increased by acidification of the vesicle lumen. FEBS Lett. 1990 Oct 1;271(1-2):62–66. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80372-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellman I., Fuchs R., Helenius A. Acidification of the endocytic and exocytic pathways. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:663–700. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.003311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regazzi R., Ullrich S., Kahn R. A., Wollheim C. B. Redistribution of ADP-ribosylation factor during stimulation of permeabilized cells with GTP analogues. Biochem J. 1991 May 1;275(Pt 3):639–644. doi: 10.1042/bj2750639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnefel S., Pröfrock A., Hinsch K. D., Schulz I. Cholecystokinin activates Gi1-, Gi2-, Gi3- and several Gs-proteins in rat pancreatic acinar cells. Biochem J. 1990 Jul 15;269(2):483–488. doi: 10.1042/bj2690483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segev N., Mulholland J., Botstein D. The yeast GTP-binding YPT1 protein and a mammalian counterpart are associated with the secretion machinery. Cell. 1988 Mar 25;52(6):915–924. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90433-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serafini T., Orci L., Amherdt M., Brunner M., Kahn R. A., Rothman J. E. ADP-ribosylation factor is a subunit of the coat of Golgi-derived COP-coated vesicles: a novel role for a GTP-binding protein. Cell. 1991 Oct 18;67(2):239–253. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90176-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sewell J. L., Kahn R. A. Sequences of the bovine and yeast ADP-ribosylation factor and comparison to other GTP-binding proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(13):4620–4624. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.13.4620. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stearns T., Willingham M. C., Botstein D., Kahn R. A. ADP-ribosylation factor is functionally and physically associated with the Golgi complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(3):1238–1242. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.3.1238. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streb H., Bayerdörffer E., Haase W., Irvine R. F., Schulz I. Effect of inositol-1,4,5-trisphosphate on isolated subcellular fractions of rat pancreas. J Membr Biol. 1984;81(3):241–253. doi: 10.1007/BF01868717. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thévenod F., Kemmer T. P., Christian A. L., Schulz I. Characterization of MgATP-driven H+ uptake into a microsomal vesicle fraction from rat pancreatic acinar cells. J Membr Biol. 1989 Mar;107(3):263–275. doi: 10.1007/BF01871941. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeuzem S., Zimmermann P., Schulz I. Association of a 19- and a 21-kDa GTP-binding protein to pancreatic microsomal vesicles is regulated by the intravesicular pH established by a vacuolar-type H(+)-ATPase. J Membr Biol. 1992 Feb;125(3):231–241. doi: 10.1007/BF00236436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]