Abstract
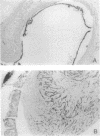
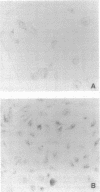
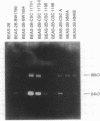
Using a xenotransplantation system in which immortalized nontumorigenic human bronchial epithelial cells (BEAS-2B cells) are grown in deepithelialized rat tracheas that are subcutaneously transplanted into athymic nude mice, we exposed BEAS-2B cells either to cigarette smoke condensate or to the tobacco-specific N-nitrosamine 4-(methylnitrosamine)-1-(3-pyridyl)-1- butanone. After 6 mo the carcinogen-exposed BEAS-2B cells were neoplastically transformed to invasive adenocarcinomas. Cell lines obtained from xenografts exposed in vivo to chemicals exhibited several features typical of malignant lung cancer cells, such as increased in vivo invasiveness that correlated well with enhanced type IV collagenolytic activity, resistance to serum-induced growth inhibition, and increased expression of transforming growth factor alpha and its cellular-membrane receptor. Invasiveness, similar to that seen after exposure to phorbol esters, was also detected after in vitro exposure of BEAS-2B cells to cigarette smoke condensate. Collectively, these data indicate that cigarette smoke condensate and N-nitrosamine 4-(methylnitrosamine)-1-(3-pyridyl)-1-butanone induce in vivo phenotypic changes in BEAS-2B cells similar to the progressive changes that occur during human lung carcinogenesis.
Full text
PDF
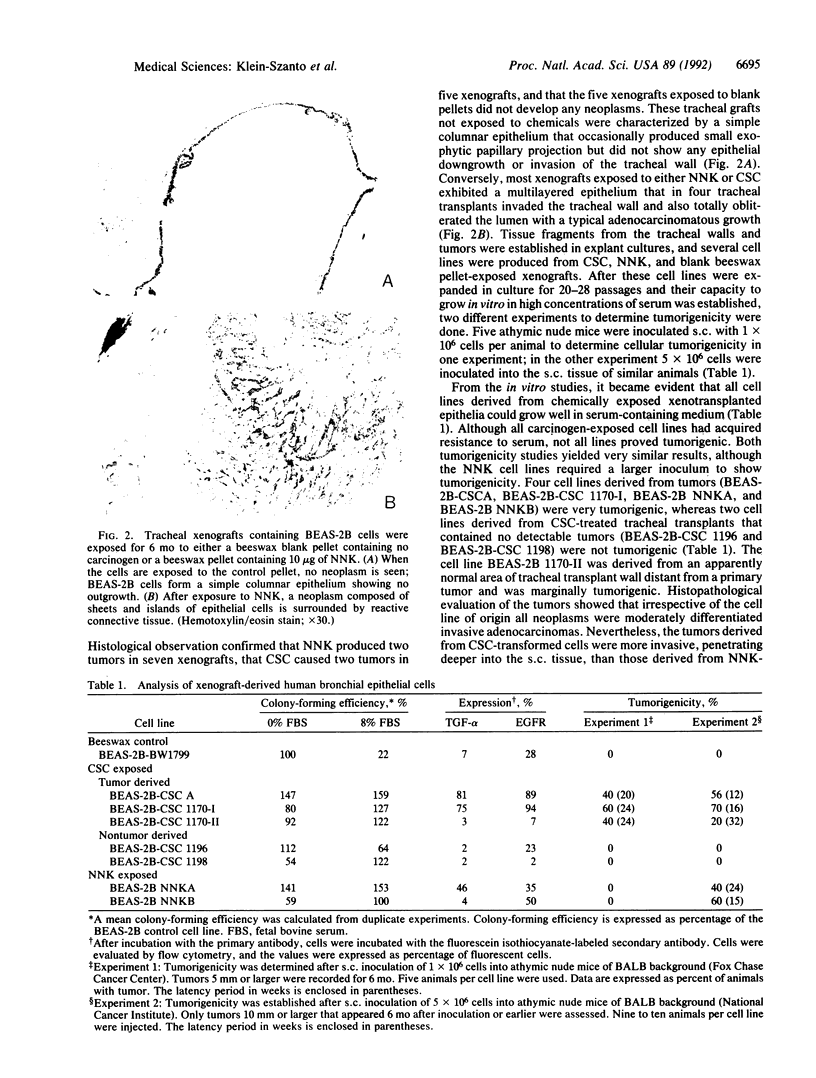


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albini A., Iwamoto Y., Kleinman H. K., Martin G. R., Aaronson S. A., Kozlowski J. M., McEwan R. N. A rapid in vitro assay for quantitating the invasive potential of tumor cells. Cancer Res. 1987 Jun 15;47(12):3239–3245. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ayesh R., Idle J. R., Ritchie J. C., Crothers M. J., Hetzel M. R. Metabolic oxidation phenotypes as markers for susceptibility to lung cancer. Nature. 1984 Nov 8;312(5990):169–170. doi: 10.1038/312169a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barton C. M., Hall P. A., Hughes C. M., Gullick W. J., Lemoine N. R. Transforming growth factor alpha and epidermal growth factor in human pancreatic cancer. J Pathol. 1991 Feb;163(2):111–116. doi: 10.1002/path.1711630206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bock F. G., Swain A. P., Stedman R. L. Composition studies on tobacco. XLI. Carcinogenesis assay of subfractions of the neutral fraction of cigarette smoke condensate. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1970 Jun;44(6):1305–1310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonfil R. D., Momiki S., Fridman R., Reich R., Reddel R., Harris C. C., Klein-Szanto A. Enhancement of the invasive ability of a transformed human bronchial epithelial cell line by 12-O-tetradecanoyl-phorbol-13-acetate and diacylglycerol. Carcinogenesis. 1989 Dec;10(12):2335–2338. doi: 10.1093/carcin/10.12.2335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caporaso N. E., Tucker M. A., Hoover R. N., Hayes R. B., Pickle L. W., Issaq H. J., Muschik G. M., Green-Gallo L., Buivys D., Aisner S. Lung cancer and the debrisoquine metabolic phenotype. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1990 Aug 1;82(15):1264–1272. doi: 10.1093/jnci/82.15.1264. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castonguay A., Stoner G. D., Schut H. A., Hecht S. S. Metabolism of tobacco-specific N-nitrosamines by cultured human tissues. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(21):6694–6697. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.21.6694. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crespi C. L., Penman B. W., Gelboin H. V., Gonzalez F. J. A tobacco smoke-derived nitrosamine, 4-(methylnitrosamino)-1-(3-pyridyl)-1-butanone, is activated by multiple human cytochrome P450s including the polymorphic human cytochrome P4502D6. Carcinogenesis. 1991 Jul;12(7):1197–1201. doi: 10.1093/carcin/12.7.1197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guo Z., Smith T. J., Ishizaki H., Yang C. S. Metabolism of 4-(methylnitrosamino)-1-(3-pyridyl)-1-butanone (NNK) by cytochrome P450IIB1 in a reconstituted system. Carcinogenesis. 1991 Dec;12(12):2277–2282. doi: 10.1093/carcin/12.12.2277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hecht S. S., Hoffmann D. The relevance of tobacco-specific nitrosamines to human cancer. Cancer Surv. 1989;8(2):273–294. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann D., Hecht S. S., Wynder E. L. Tumor promoters and cocarcinogens in tobacco carcinogenesis. Environ Health Perspect. 1983 Apr;50:247–257. doi: 10.1289/ehp.8350247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann D., Wynder E. L. A study of tobacco carcinogenesis. XI. Tumor initiators, tumor accelerators, and tumor promoting activity of condensate fractions. Cancer. 1971 Apr;27(4):848–864. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197104)27:4<848::aid-cncr2820270415>3.0.co;2-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollstein M., Sidransky D., Vogelstein B., Harris C. C. p53 mutations in human cancers. Science. 1991 Jul 5;253(5015):49–53. doi: 10.1126/science.1905840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaighn M. E., Gabrielson E. W., Iman D. S., Pauls E. A., Harris C. C. Suppression of tumorigenicity of a human lung carcinoma line by nontumorigenic bronchial epithelial cells in somatic cell hybrids. Cancer Res. 1990 Mar 15;50(6):1890–1896. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein-Szanto A. J., Pal B. C., Terzaghi M., Marchok A. C. Heterotopic tracheal transplants: techniques and applications. Environ Health Perspect. 1984 Jun;56:75–86. doi: 10.1289/ehp.845675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lechner J. F., McClendon I. A., LaVeck M. A., Shamsuddin A. M., Harris C. C. Differential control by platelet factors of squamous differentiation in normal and malignant human bronchial epithelial cells. Cancer Res. 1983 Dec;43(12 Pt 1):5915–5921. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehman T. A., Bennett W. P., Metcalf R. A., Welsh J. A., Ecker J., Modali R. V., Ullrich S., Romano J. W., Appella E., Testa J. R. p53 mutations, ras mutations, and p53-heat shock 70 protein complexes in human lung carcinoma cell lines. Cancer Res. 1991 Aug 1;51(15):4090–4096. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu C., Woo A., Tsao M. S. Expression of transforming growth factor-alpha in primary human colon and lung carcinomas. Br J Cancer. 1990 Sep;62(3):425–429. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1990.311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masui T., Wakefield L. M., Lechner J. F., LaVeck M. A., Sporn M. B., Harris C. C. Type beta transforming growth factor is the primary differentiation-inducing serum factor for normal human bronchial epithelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2438–2442. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyashita M., Smith M. W., Willey J. C., Lechner J. F., Trump B. F., Harris C. C. Effects of serum, transforming growth factor type beta, or 12-O-tetradecanoyl-phorbol-13-acetate on ionized cytosolic calcium concentration in normal and transformed human bronchial epithelial cells. Cancer Res. 1989 Jan 1;49(1):63–67. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyashita M., Willey J. C., Sasajima K., Lechner J. F., LaVoie E. J., Hoffmann D., Smith M., Trump B. F., Harris C. C. Differential effects of cigarette smoke condensate and its fractions on cultured normal and malignant human bronchial epithelial cells. Exp Pathol. 1990;38(1):19–29. doi: 10.1016/s0232-1513(11)80192-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima M., Lotan D., Baig M. M., Carralero R. M., Wood W. R., Hendrix M. J., Lotan R. Inhibition by retinoic acid of type IV collagenolysis and invasion through reconstituted basement membrane by metastatic rat mammary adenocarcinoma cells. Cancer Res. 1989 Apr 1;49(7):1698–1706. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddel R. R., Ke Y., Gerwin B. I., McMenamin M. G., Lechner J. F., Su R. T., Brash D. E., Park J. B., Rhim J. S., Harris C. C. Transformation of human bronchial epithelial cells by infection with SV40 or adenovirus-12 SV40 hybrid virus, or transfection via strontium phosphate coprecipitation with a plasmid containing SV40 early region genes. Cancer Res. 1988 Apr 1;48(7):1904–1909. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddel R. R., Ke Y., Gerwin B. I., McMenamin M. G., Lechner J. F., Su R. T., Brash D. E., Park J. B., Rhim J. S., Harris C. C. Transformation of human bronchial epithelial cells by infection with SV40 or adenovirus-12 SV40 hybrid virus, or transfection via strontium phosphate coprecipitation with a plasmid containing SV40 early region genes. Cancer Res. 1988 Apr 1;48(7):1904–1909. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivenson A., Hoffmann D., Prokopczyk B., Amin S., Hecht S. S. Induction of lung and exocrine pancreas tumors in F344 rats by tobacco-specific and Areca-derived N-nitrosamines. Cancer Res. 1988 Dec 1;48(23):6912–6917. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuller H. M. Cell type specific, receptor-mediated modulation of growth kinetics in human lung cancer cell lines by nicotine and tobacco-related nitrosamines. Biochem Pharmacol. 1989 Oct 15;38(20):3439–3442. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(89)90112-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swain A. P., Cooper J. E., Stedman R. L. Large-scale fractionation of cigarette smoke condensate for chemical and biologic investigations. Cancer Res. 1969 Mar;29(3):579–583. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tateishi M., Ishida T., Mitsudomi T., Kaneko S., Sugimachi K. Immunohistochemical evidence of autocrine growth factors in adenocarcinoma of the human lung. Cancer Res. 1990 Nov 1;50(21):7077–7080. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todd R., Donoff B. R., Gertz R., Chang A. L., Chow P., Matossian K., McBride J., Chiang T., Gallagher G. T., Wong D. T. TGF-alpha and EGF-receptor mRNAs in human oral cancers. Carcinogenesis. 1989 Aug;10(8):1553–1556. doi: 10.1093/carcin/10.8.1553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willey J. C., Grafstrom R. C., Moser C. E., Jr, Ozanne C., Sundquvist K., Harris C. C. Biochemical and morphological effects of cigarette smoke condensate and its fractions on normal human bronchial epithelial cells in vitro. Cancer Res. 1987 Apr 15;47(8):2045–2049. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]