Abstract
Aminoguanidine decreases the formation of advanced glycosylation end products that occurs during chronic hyperglycemia. Presumably this occurs because early glycosylation products preferentially bind to aminoguanidine rather than to lysine groups of adjacent proteins. Because oxidative modification of low density lipoprotein (LDL) also involves derivatization of lysine residues of apolipoprotein (apo) B by reactive aldehydes formed during the decomposition of oxidized fatty acids, we postulated that aminoguanidine might also inhibit the oxidatively induced modification of LDL protein. To test this hypothesis we oxidized LDL by incubation with Cu2+ or with endothelial cells in the absence or presence of aminoguanidine. Aminoguanidine prevented apo B lysine modification, as measured by fluorescence spectroscopy, and inhibited in a dose-dependent manner the oxidatively induced increase in subsequent macrophage uptake. At concentrations that inhibited apo B modification (5-10 mM), aminoguanidine increased the lag time in diene conjugation but did not affect the plateau value reached. These data indicate that aminoguanidine inhibits oxidative modification of LDL protein in large part by binding reactive aldehydes formed during lipid peroxidation and preventing their subsequent conjugation to apo B. Thus, aminoguanidine (and related compounds) may be of dual benefit in inhibiting atherosclerosis, both by inhibiting formation of advanced glycosylation end products and by inhibiting the modification of LDL apo B that makes it a ligand for scavenger receptors.
Full text
PDF
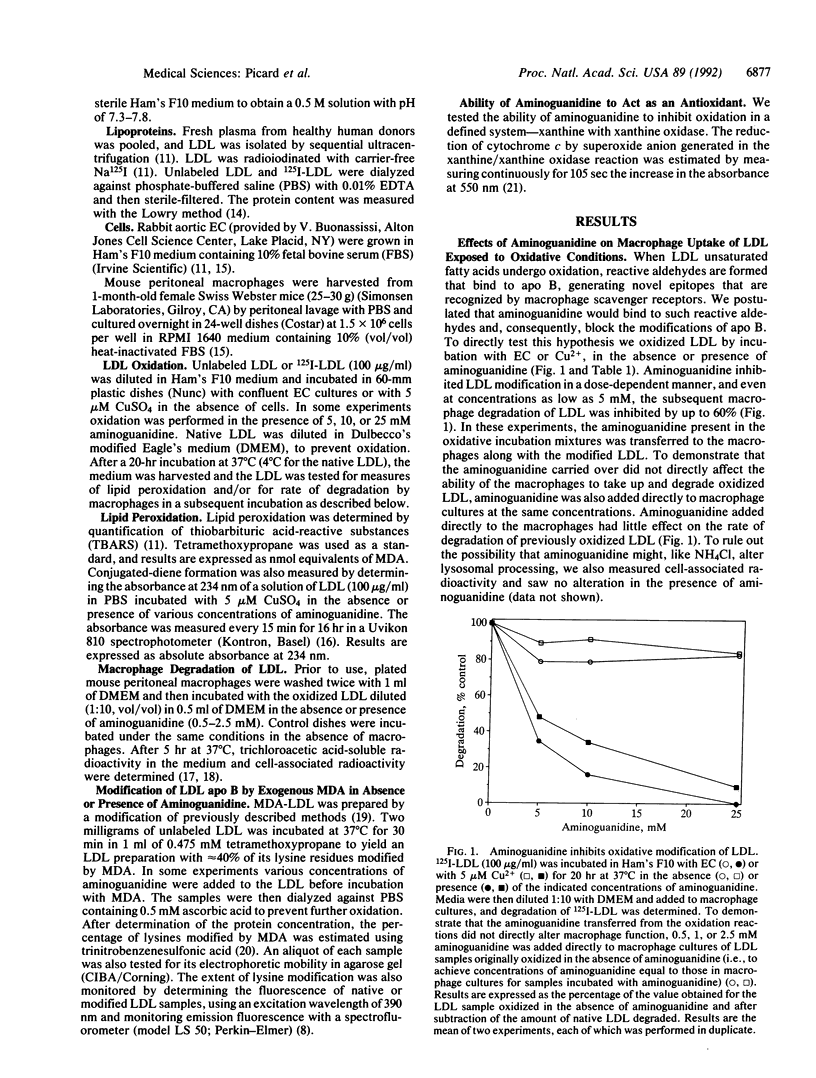
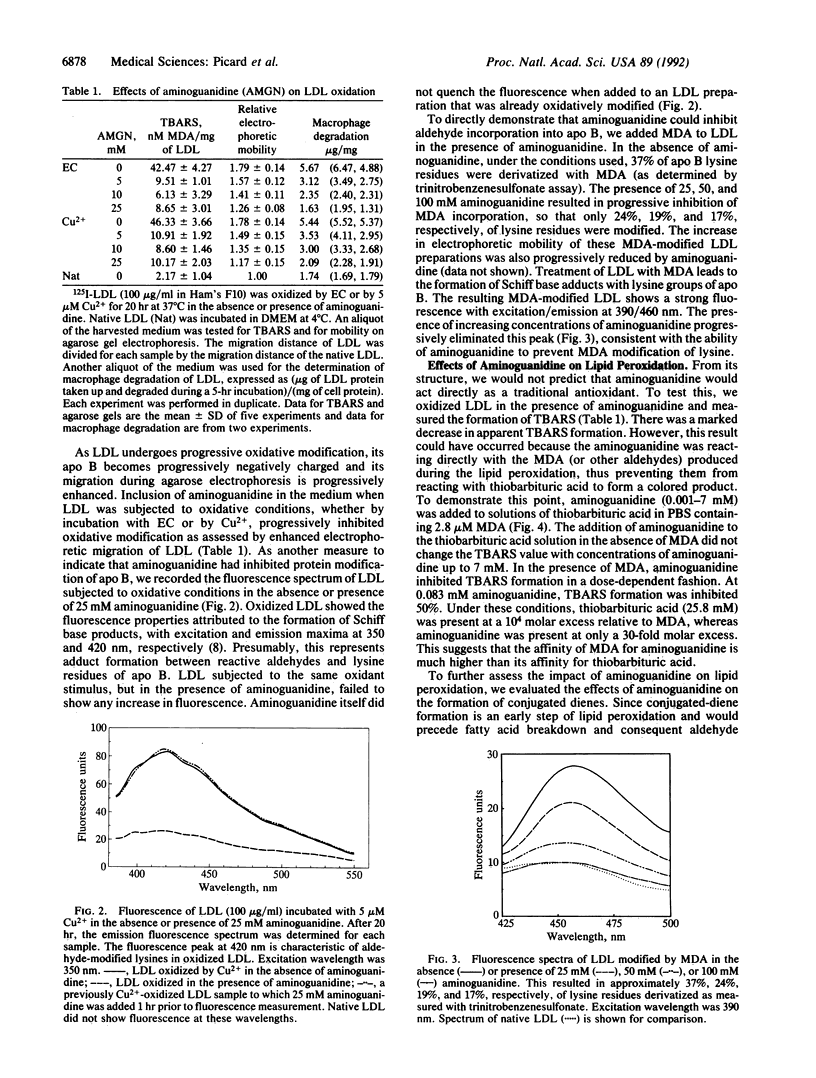
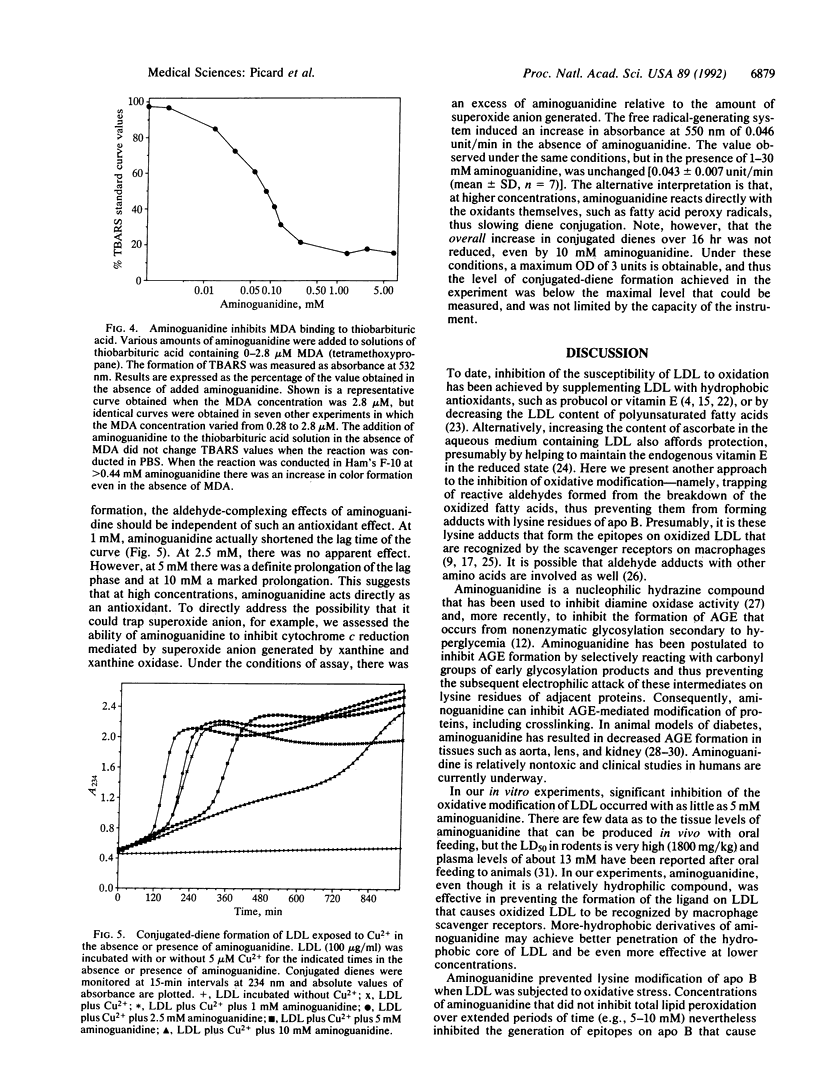

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akeson A. L., Woods C. W., Mosher L. B., Thomas C. E., Jackson R. L. Inhibition of IL-1 beta expression in THP-1 cells by probucol and tocopherol. Atherosclerosis. 1991 Feb;86(2-3):261–270. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(91)90222-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baylin S., Horakova Z., Beaven M. A. Increase in food consumption and growth after treatment with aminoguanidine. Experientia. 1975 May 15;31(5):562–564. doi: 10.1007/BF01932459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baynes J. W. Role of oxidative stress in development of complications in diabetes. Diabetes. 1991 Apr;40(4):405–412. doi: 10.2337/diab.40.4.405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brownlee M., Cerami A., Vlassara H. Advanced glycosylation end products in tissue and the biochemical basis of diabetic complications. N Engl J Med. 1988 May 19;318(20):1315–1321. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198805193182007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brownlee M., Vlassara H., Cerami A. Nonenzymatic glycosylation products on collagen covalently trap low-density lipoprotein. Diabetes. 1985 Sep;34(9):938–941. doi: 10.2337/diab.34.9.938. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brownlee M., Vlassara H., Kooney A., Ulrich P., Cerami A. Aminoguanidine prevents diabetes-induced arterial wall protein cross-linking. Science. 1986 Jun 27;232(4758):1629–1632. doi: 10.1126/science.3487117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carew T. E., Schwenke D. C., Steinberg D. Antiatherogenic effect of probucol unrelated to its hypocholesterolemic effect: evidence that antioxidants in vivo can selectively inhibit low density lipoprotein degradation in macrophage-rich fatty streaks and slow the progression of atherosclerosis in the Watanabe heritable hyperlipidemic rabbit. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(21):7725–7729. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.21.7725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esterbauer H., Dieber-Rotheneder M., Striegl G., Waeg G. Role of vitamin E in preventing the oxidation of low-density lipoprotein. Am J Clin Nutr. 1991 Jan;53(1 Suppl):314S–321S. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/53.1.314S. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esterbauer H., Schaur R. J., Zollner H. Chemistry and biochemistry of 4-hydroxynonenal, malonaldehyde and related aldehydes. Free Radic Biol Med. 1991;11(1):81–128. doi: 10.1016/0891-5849(91)90192-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esterbauer H., Striegl G., Puhl H., Rotheneder M. Continuous monitoring of in vitro oxidation of human low density lipoprotein. Free Radic Res Commun. 1989;6(1):67–75. doi: 10.3109/10715768909073429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henriksen T., Mahoney E. M., Steinberg D. Enhanced macrophage degradation of low density lipoprotein previously incubated with cultured endothelial cells: recognition by receptors for acetylated low density lipoproteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6499–6503. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hessler J. R., Morel D. W., Lewis L. J., Chisolm G. M. Lipoprotein oxidation and lipoprotein-induced cytotoxicity. Arteriosclerosis. 1983 May-Jun;3(3):215–222. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.3.3.215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hicks M., Delbridge L., Yue D. K., Reeve T. S. Increase in crosslinking of nonenzymatically glycosylated collagen induced by products of lipid peroxidation. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1989 Jan;268(1):249–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(89)90586-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt J. V., Smith C. C., Wolff S. P. Autoxidative glycosylation and possible involvement of peroxides and free radicals in LDL modification by glucose. Diabetes. 1990 Nov;39(11):1420–1424. doi: 10.2337/diab.39.11.1420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jialal I., Grundy S. M. Preservation of the endogenous antioxidants in low density lipoprotein by ascorbate but not probucol during oxidative modification. J Clin Invest. 1991 Feb;87(2):597–601. doi: 10.1172/JCI115035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jürgens G., Lang J., Esterbauer H. Modification of human low-density lipoprotein by the lipid peroxidation product 4-hydroxynonenal. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Jan 3;875(1):103–114. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(86)90016-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kita T., Nagano Y., Yokode M., Ishii K., Kume N., Ooshima A., Yoshida H., Kawai C. Probucol prevents the progression of atherosclerosis in Watanabe heritable hyperlipidemic rabbit, an animal model for familial hypercholesterolemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(16):5928–5931. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.16.5928. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kodama T., Freeman M., Rohrer L., Zabrecky J., Matsudaira P., Krieger M. Type I macrophage scavenger receptor contains alpha-helical and collagen-like coiled coils. Nature. 1990 Feb 8;343(6258):531–535. doi: 10.1038/343531a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis B. S., Harding J. J. The effects of aminoguanidine on the glycation (non-enzymic glycosylation) of lens proteins. Exp Eye Res. 1990 May;50(5):463–467. doi: 10.1016/0014-4835(90)90033-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liao F., Berliner J. A., Mehrabian M., Navab M., Demer L. L., Lusis A. J., Fogelman A. M. Minimally modified low density lipoprotein is biologically active in vivo in mice. J Clin Invest. 1991 Jun;87(6):2253–2257. doi: 10.1172/JCI115261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPherson R., Hogue M., Milne R. W., Tall A. R., Marcel Y. L. Increase in plasma cholesteryl ester transfer protein during probucol treatment. Relation to changes in high density lipoprotein composition. Arterioscler Thromb. 1991 May-Jun;11(3):476–481. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.11.3.476. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullarkey C. J., Edelstein D., Brownlee M. Free radical generation by early glycation products: a mechanism for accelerated atherogenesis in diabetes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Dec 31;173(3):932–939. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)80875-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palinski W., Rosenfeld M. E., Ylä-Herttuala S., Gurtner G. C., Socher S. S., Butler S. W., Parthasarathy S., Carew T. E., Steinberg D., Witztum J. L. Low density lipoprotein undergoes oxidative modification in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(4):1372–1376. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.4.1372. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parthasarathy S., Fong L. G., Otero D., Steinberg D. Recognition of solubilized apoproteins from delipidated, oxidized low density lipoprotein (LDL) by the acetyl-LDL receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jan;84(2):537–540. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.2.537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reaven P., Parthasarathy S., Grasse B. J., Miller E., Almazan F., Mattson F. H., Khoo J. C., Steinberg D., Witztum J. L. Feasibility of using an oleate-rich diet to reduce the susceptibility of low-density lipoprotein to oxidative modification in humans. Am J Clin Nutr. 1991 Oct;54(4):701–706. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/54.4.701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rokkas T., Vaja S., Murphy G. M., Dowling R. H. Aminoguanidine blocks intestinal diamine oxidase (DAO) activity and enhances the intestinal adaptive response to resection in the rat. Digestion. 1990;46 (Suppl 2):447–457. doi: 10.1159/000200420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfeld M. E. Oxidized LDL affects multiple atherogenic cellular responses. Circulation. 1991 Jun;83(6):2137–2140. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.83.6.2137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soulis-Liparota T., Cooper M., Papazoglou D., Clarke B., Jerums G. Retardation by aminoguanidine of development of albuminuria, mesangial expansion, and tissue fluorescence in streptozocin-induced diabetic rat. Diabetes. 1991 Oct;40(10):1328–1334. doi: 10.2337/diab.40.10.1328. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sparrow C. P., Parthasarathy S., Steinberg D. A macrophage receptor that recognizes oxidized low density lipoprotein but not acetylated low density lipoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 15;264(5):2599–2604. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg D., Parthasarathy S., Carew T. E., Khoo J. C., Witztum J. L. Beyond cholesterol. Modifications of low-density lipoprotein that increase its atherogenicity. N Engl J Med. 1989 Apr 6;320(14):915–924. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198904063201407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg D., Witztum J. L. Lipoproteins and atherogenesis. Current concepts. JAMA. 1990 Dec 19;264(23):3047–3052. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinbrecher U. P. Oxidation of human low density lipoprotein results in derivatization of lysine residues of apolipoprotein B by lipid peroxide decomposition products. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 15;262(8):3603–3608. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinbrecher U. P., Parthasarathy S., Leake D. S., Witztum J. L., Steinberg D. Modification of low density lipoprotein by endothelial cells involves lipid peroxidation and degradation of low density lipoprotein phospholipids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(12):3883–3887. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.12.3883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinbrecher U. P., Witztum J. L., Parthasarathy S., Steinberg D. Decrease in reactive amino groups during oxidation or endothelial cell modification of LDL. Correlation with changes in receptor-mediated catabolism. Arteriosclerosis. 1987 Mar-Apr;7(2):135–143. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.7.2.135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinbrecher U. P., Witztum J. L., Parthasarathy S., Steinberg D. Decrease in reactive amino groups during oxidation or endothelial cell modification of LDL. Correlation with changes in receptor-mediated catabolism. Arteriosclerosis. 1987 Mar-Apr;7(2):135–143. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.7.2.135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witztum J. L., Steinberg D. Role of oxidized low density lipoprotein in atherogenesis. J Clin Invest. 1991 Dec;88(6):1785–1792. doi: 10.1172/JCI115499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


