Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ADRIAN R. H. The effect of internal and external potassium concentration on the membrane potential of frog muscle. J Physiol. 1956 Sep 27;133(3):631–658. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1956.sp005615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
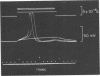
- BERANEK R. INTRACELLULAR STIMULATION MYOGRAPHY IN MAN. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1964 Mar;16:301–304. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(64)90114-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
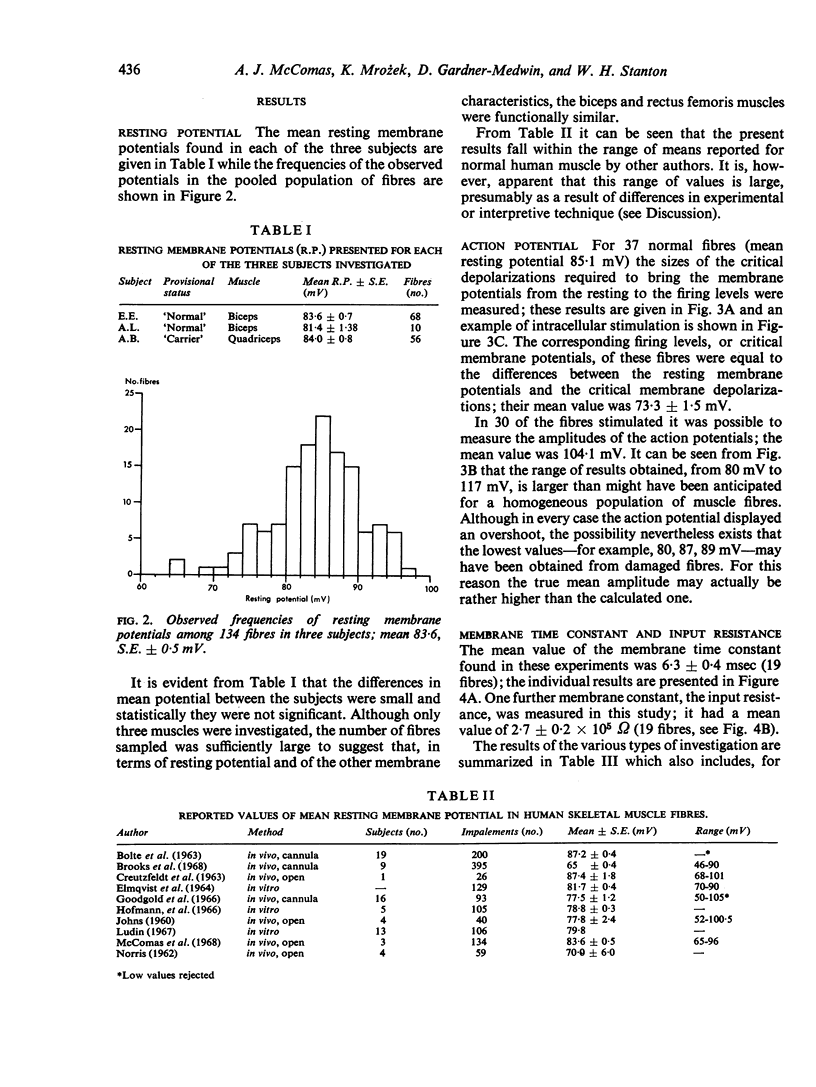
- BOLTE H. D., RIECKER G., ROHL D. [Measurements of the membrane potential of single cross-striated muscles of man in situ. Normal values]. Klin Wochenschr. 1963 Apr 15;41:356–359. doi: 10.1007/BF01487862. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOYD I. A., MARTIN A. R. Membrane constants of mammalian muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1959 Oct;147:450–457. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks J. E., Hongdalarom T. Intracellular electromyography. Resting and action potentials in normal human muscle. Arch Neurol. 1968 Mar;18(3):291–300. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1968.00470330081008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CREUTZFELDT O. D., ABBOTT B. C., FOWLER W. M., PEARSON C. M. MUSCLE MEMBRANE POTENTIALS IN EPISODIC ADYNAMIA. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1963 Jun;15:508–519. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(63)90071-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEL CASTILLO J., KATZ B. Local activity at a depolarized nerve-muscle junction. J Physiol. 1955 May 27;128(2):396–411. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1955.sp005315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELMQVIST D., HOFMANN W. W., KUGELBERG J., QUASTEL D. M. AN ELECTROPHYSIOLOGICAL INVESTIGATION OF NEUROMUSCULAR TRANSMISSION IN MYASTHENIA GRAVIS. J Physiol. 1964 Nov;174:417–434. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1964.sp007495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELMQVIST D., JOHNS T. R., THESLEFF S. A study of some electrophysiological properties of human intercostal muscle. J Physiol. 1960 Dec;154:602–607. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1960.sp006599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FATT P., KATZ B. An analysis of the end-plate potential recorded with an intracellular electrode. J Physiol. 1951 Nov 28;115(3):320–370. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1951.sp004675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner-Medwin D. Studies of the carrier state in the Duchenne type of muscular dystrophy. 2. Quantitative electromyography as a method of carrier detection. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1968 Apr;31(2):124–134. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.31.2.124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodgold J., Eberstein A. Transmembrane potentials of human muscle cells in vivo. Exp Neurol. 1966 Jul;15(3):338–346. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(66)90056-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann W. W., Alston W., Rowe G. A study of individual neuro-muscular junctions in myotonia. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1966 Dec;21(6):521–537. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(66)90171-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KEMP N. H., STAFFORD J. L., TANNER R. K. Acute leukaemia and Klinefelter's syndrome. Lancet. 1961 Aug 19;2(7199):434–435. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(61)92520-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KERNAN R. P. RESTING POTENTIAL OF ISOLATED RAT MUSCLES MEASURED IN PLASMA. Nature. 1963 Nov 2;200:474–475. doi: 10.1038/200474a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KLEEMAN F. J., PARTRIDGE L. D., GLASER G. H. Resting potential and muscle fiber size in hereditary mouse muscle dystrophy. Am J Phys Med. 1961 Dec;40:219–224. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LILEY A. W. An investigation of spontaneous activity at the neuromuscular junction of the rat. J Physiol. 1956 Jun 28;132(3):650–666. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1956.sp005555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McComas A. J., Mrozek K., Bradley W. G. The nature of the electrophysiological disorder in adynamia episodica. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1968 Oct;31(5):448–452. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.31.5.448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NORRIS F. H., Jr Unstable membrane potential in human myotonic muscle. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1962 Apr;14:197–201. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(62)90029-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PEARSON C. M., FOWLER W. M., WRIGHT S. W. X-chromosome mosaicism in females with muscular dystrophy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Jul;50:24–31. doi: 10.1073/pnas.50.1.24. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walton J. N., Pennington R. J. Studies on human muscular dystrophy with particular reference to methods of carrier detection. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1966 Sep 9;138(1):315–328. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1966.tb41173.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]