Abstract
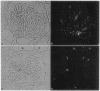
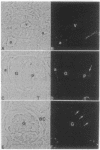
ZO-1 is a 225-kDa peripheral membrane protein present in all tight junctions. It was recently shown to consist of two isoforms that differ in the presence of an internal 80-amino acid domain termed motif-alpha. To obtain information on their distribution and potential functional significance we have localized the two isoforms in rat kidney by using antibodies that recognize either both ZO-1 isoforms or the larger, motif-alpha-containing isoform. By immunofluorescence, staining with both antibodies was demonstrated at all tight junctions of tubular epithelial cells and the epithelial cells of Bowman's capsule. In contrast, the motif-alpha-containing isoform was absent from the slit diaphragms of the glomerular epithelium and the tight junctions of glomerular and peritubular capillary endothelial cells. This restricted isoform expression was confirmed by immunoblot analysis comparing proteins from purified glomeruli with those from kidney cortex or medulla. Thus, while both isoforms are expressed in typical epithelial tight junctions, only a single isoform, lacking motif-alpha, is expressed in the highly specialized slit diaphragms, where the intercellular spaces are normally open, and in endothelial junctions, which are readily opened by physiologic signals. The differential expression of ZO-1 isoforms in structurally and functionally distinct junctions in the kidney suggests that they may contribute to defining the variable functional properties, in particular the lability of these intercellular junctions.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson J. M., Van Itallie C. M., Peterson M. D., Stevenson B. R., Carew E. A., Mooseker M. S. ZO-1 mRNA and protein expression during tight junction assembly in Caco-2 cells. J Cell Biol. 1989 Sep;109(3):1047–1056. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.3.1047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claude P., Goodenough D. A. Fracture faces of zonulae occludentes from "tight" and "leaky" epithelia. J Cell Biol. 1973 Aug;58(2):390–400. doi: 10.1083/jcb.58.2.390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friend D. S., Gilula N. B. Variations in tight and gap junctions in mammalian tissues. J Cell Biol. 1972 Jun;53(3):758–776. doi: 10.1083/jcb.53.3.758. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gumbiner B. Structure, biochemistry, and assembly of epithelial tight junctions. Am J Physiol. 1987 Dec;253(6 Pt 1):C749–C758. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1987.253.6.C749. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerjaschki D., Sharkey D. J., Farquhar M. G. Identification and characterization of podocalyxin--the major sialoprotein of the renal glomerular epithelial cell. J Cell Biol. 1984 Apr;98(4):1591–1596. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.4.1591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLean I. W., Nakane P. K. Periodate-lysine-paraformaldehyde fixative. A new fixation for immunoelectron microscopy. J Histochem Cytochem. 1974 Dec;22(12):1077–1083. doi: 10.1177/22.12.1077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnabel E., Anderson J. M., Farquhar M. G. The tight junction protein ZO-1 is concentrated along slit diaphragms of the glomerular epithelium. J Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;111(3):1255–1263. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.3.1255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnabel E., Dekan G., Miettinen A., Farquhar M. G. Biogenesis of podocalyxin--the major glomerular sialoglycoprotein--in the newborn rat kidney. Eur J Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;48(2):313–326. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson B. R., Anderson J. M., Bullivant S. The epithelial tight junction: structure, function and preliminary biochemical characterization. Mol Cell Biochem. 1988 Oct;83(2):129–145. doi: 10.1007/BF00226141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson B. R., Siliciano J. D., Mooseker M. S., Goodenough D. A. Identification of ZO-1: a high molecular weight polypeptide associated with the tight junction (zonula occludens) in a variety of epithelia. J Cell Biol. 1986 Sep;103(3):755–766. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.3.755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokuyasu K. T. Application of cryoultramicrotomy to immunocytochemistry. J Microsc. 1986 Aug;143(Pt 2):139–149. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2818.1986.tb02772.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokuyasu K. T. Use of poly(vinylpyrrolidone) and poly(vinyl alcohol) for cryoultramicrotomy. Histochem J. 1989 Mar;21(3):163–171. doi: 10.1007/BF01007491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willott E., Balda M. S., Heintzelman M., Jameson B., Anderson J. M. Localization and differential expression of two isoforms of the tight junction protein ZO-1. Am J Physiol. 1992 May;262(5 Pt 1):C1119–C1124. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1992.262.5.C1119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]