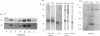Abstract
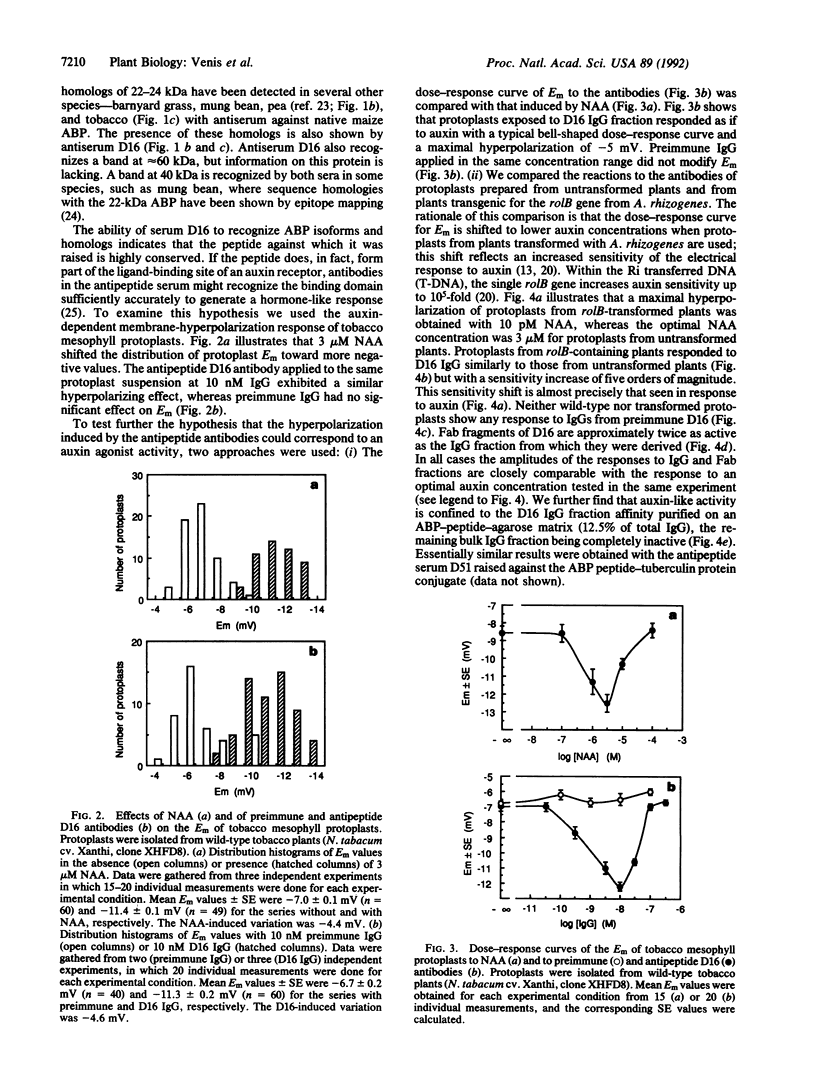
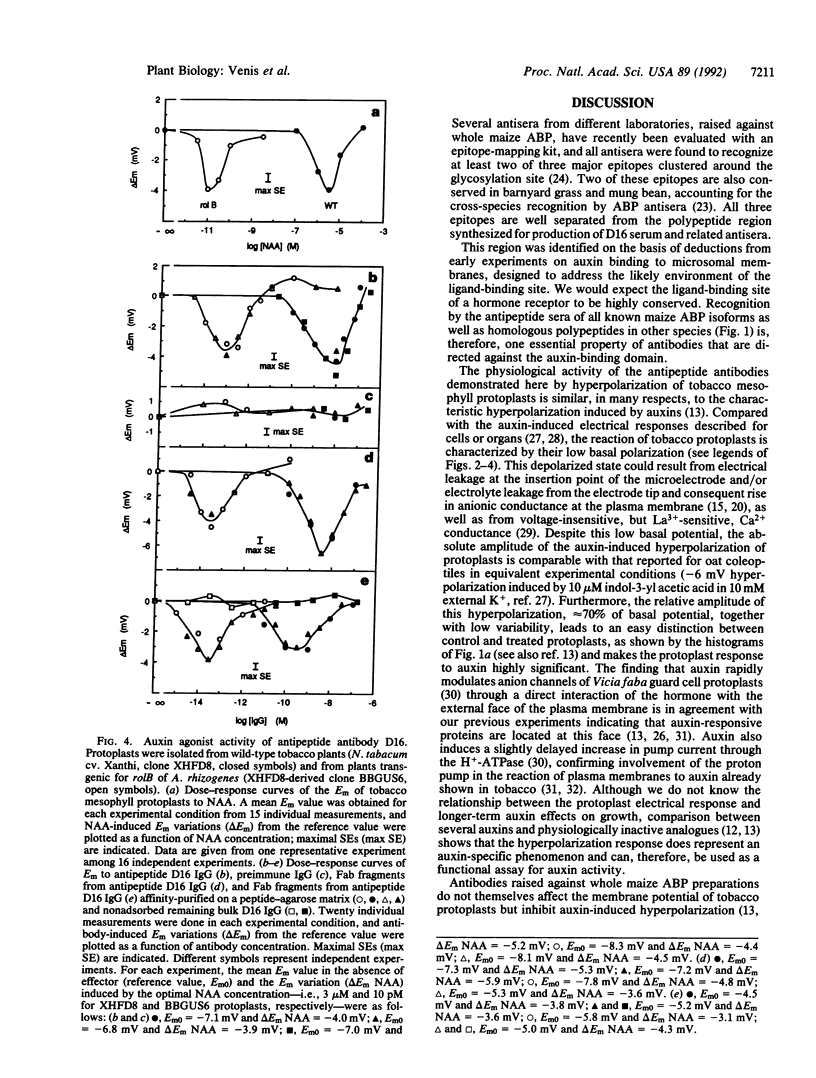
The major auxin-binding protein in maize membranes is thought to function as a physiological receptor. From earlier information, including the use of site-directed irreversible inhibitors, several of the amino acids likely to form part of the active auxin-binding site were provisionally assigned. Inspection of the amino acid sequence of the auxin-binding protein showed a short region containing all but one of these amino acids. We find that antisera raised against a synthetic peptide encompassing this region recognize all isoforms of the maize auxin-binding protein together with homologous polypeptides in other species. We further find that the antibodies hyperpolarize protoplast transmembrane potential in an auxin-like manner. We conclude that these antibodies display auxin agonist activity and that we have identified an essential portion of the auxin-binding site.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barbier-Brygoo H., Ephritikhine G., Klämbt D., Ghislain M., Guern J. Functional evidence for an auxin receptor at the plasmalemma of tobacco mesophyll protoplasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(3):891–895. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.3.891. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ephritikhine G., Barbier-Brygoo H., Muller J. F., Guern J. Auxin effect on the transmembrane potential difference of wild-type and mutant tobacco protoplasts exhibiting a differential sensitiity to auxin. Plant Physiol. 1987 Apr;83(4):801–804. doi: 10.1104/pp.83.4.801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felle H., Peters W., Palme K. The electrical response of maize to auxins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 May 7;1064(2):199–204. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(91)90302-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hesse T., Feldwisch J., Balshüsemann D., Bauw G., Puype M., Vandekerckhove J., Löbler M., Klämbt D., Schell J., Palme K. Molecular cloning and structural analysis of a gene from Zea mays (L.) coding for a putative receptor for the plant hormone auxin. EMBO J. 1989 Sep;8(9):2453–2461. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08380.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollenberg M. D. Mechanisms of receptor-mediated transmembrane signalling. Experientia. 1986 Jul 15;42(7):718–727. doi: 10.1007/BF01941517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inohara N., Shimomura S., Fukui T., Futai M. Auxin-binding protein located in the endoplasmic reticulum of maize shoots: molecular cloning and complete primary structure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(10):3564–3568. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.10.3564. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ketchum K. A., Poole R. J. Cytosolic calcium regulates a potassium current in corn (Zea mays) protoplasts. J Membr Biol. 1991 Feb;119(3):277–288. doi: 10.1007/BF01868732. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Löbler M., Klämbt D. Auxin-binding protein from coleoptile membranes of corn (Zea mays L.). I. Purification by immunological methods and characterization. J Biol Chem. 1985 Aug 15;260(17):9848–9853. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Löbler M., Klämbt D. Auxin-binding protein from coleoptile membranes of corn (Zea mays L.). II. Localization of a putative auxin receptor. J Biol Chem. 1985 Aug 15;260(17):9854–9859. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maddy A. H., Dunn M. J., Kelly P. G. The characterisation of membrane proteins by centrifugation and gel electrophoresis. A comparison of proteins prepared by different methods. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Nov 2;288(2):263–276. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(72)90247-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maurel C., Barbier-Brygoo H., Spena A., Tempé J., Guern J. Single rol Genes from the Agrobacterium rhizogenes T(L)-DNA Alter Some of the Cellular Responses to Auxin in Nicotiana tabacum. Plant Physiol. 1991 Sep;97(1):212–216. doi: 10.1104/pp.97.1.212. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Navé J. F., Benveniste P. Inactivation by phenylglyoxal of the specific binding of 1-naphthyl acetic Acid with membrane-bound auxin binding sites from maize coleoptiles. Plant Physiol. 1984 Apr;74(4):1035–1040. doi: 10.1104/pp.74.4.1035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palme K., Hesse T., Campos N., Garbers C., Yanofsky M. F., Schell J. Molecular analysis of an auxin binding protein gene located on chromosome 4 of Arabidopsis. Plant Cell. 1992 Feb;4(2):193–201. doi: 10.1105/tpc.4.2.193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senn A. P., Goldsmith M. H. Regulation of electrogenic proton pumping by auxin and fusicoccin as related to the growth of Avena coleoptiles. Plant Physiol. 1988 Sep;88(1):131–138. doi: 10.1104/pp.88.1.131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen W. H., Davioud E., David C., Barbier-Brygoo H., Tempé J., Guern J. High Sensitivity to Auxin is a Common Feature of Hairy Root. Plant Physiol. 1990 Oct;94(2):554–560. doi: 10.1104/pp.94.2.554. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen W. H., Petit A., Guern J., Tempé J. Hairy roots are more sensitive to auxin than normal roots. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(10):3417–3421. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.10.3417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimomura S., Sotobayashi T., Futai M., Fukui T. Purification and properties of an auxin-binding protein from maize shoot membranes. J Biochem. 1986 May;99(5):1513–1524. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a135621. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strosberg A. D. Interaction of anti-idiotypic antibodies with membrane receptors: practical considerations. Methods Enzymol. 1989;178:179–191. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(89)78015-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson M., Krull U. J., Venis M. A. A chemoreceptive bilayer lipid membrane based on an auxin-receptor ATPase electrogenic pump. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Jan 14;110(1):300–304. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91295-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tillmann U., Viola G., Kayser B., Siemeister G., Hesse T., Palme K., Löbler M., Klämbt D. cDNA clones of the auxin-binding protein from corn coleoptiles (Zea mays L.): isolation and characterization by immunological methods. EMBO J. 1989 Sep;8(9):2463–2467. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08381.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]