Abstract
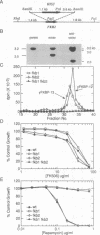
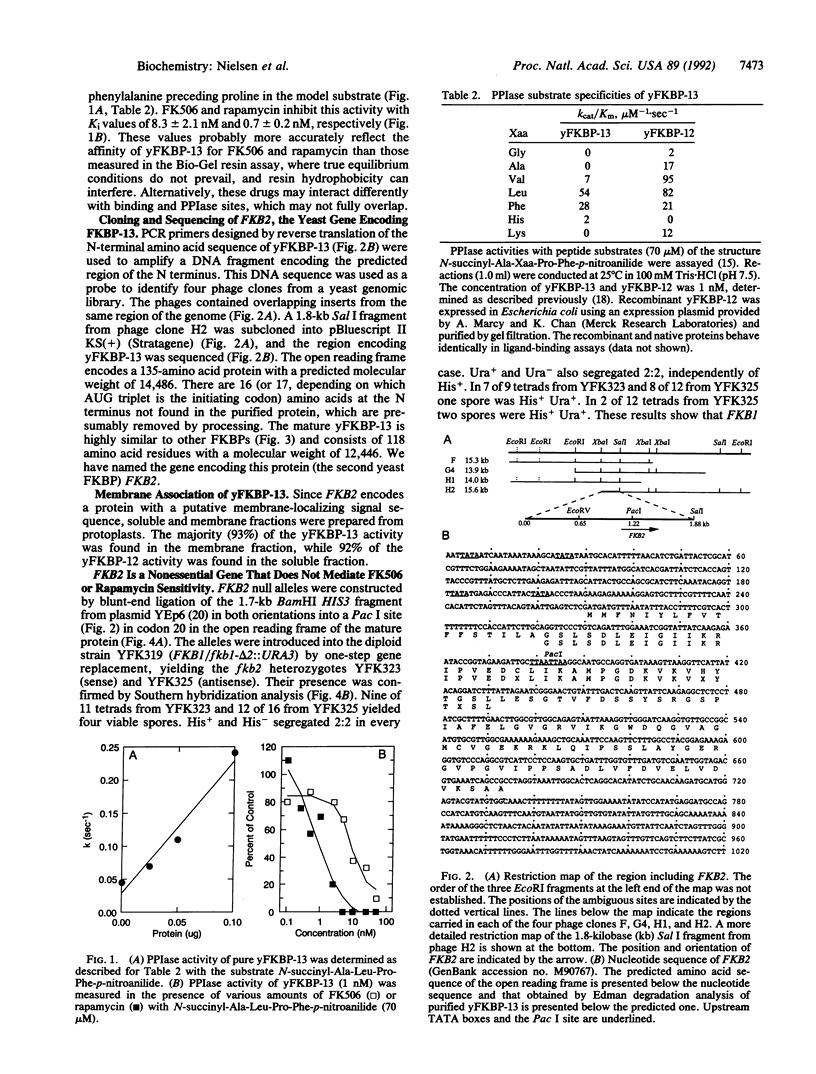
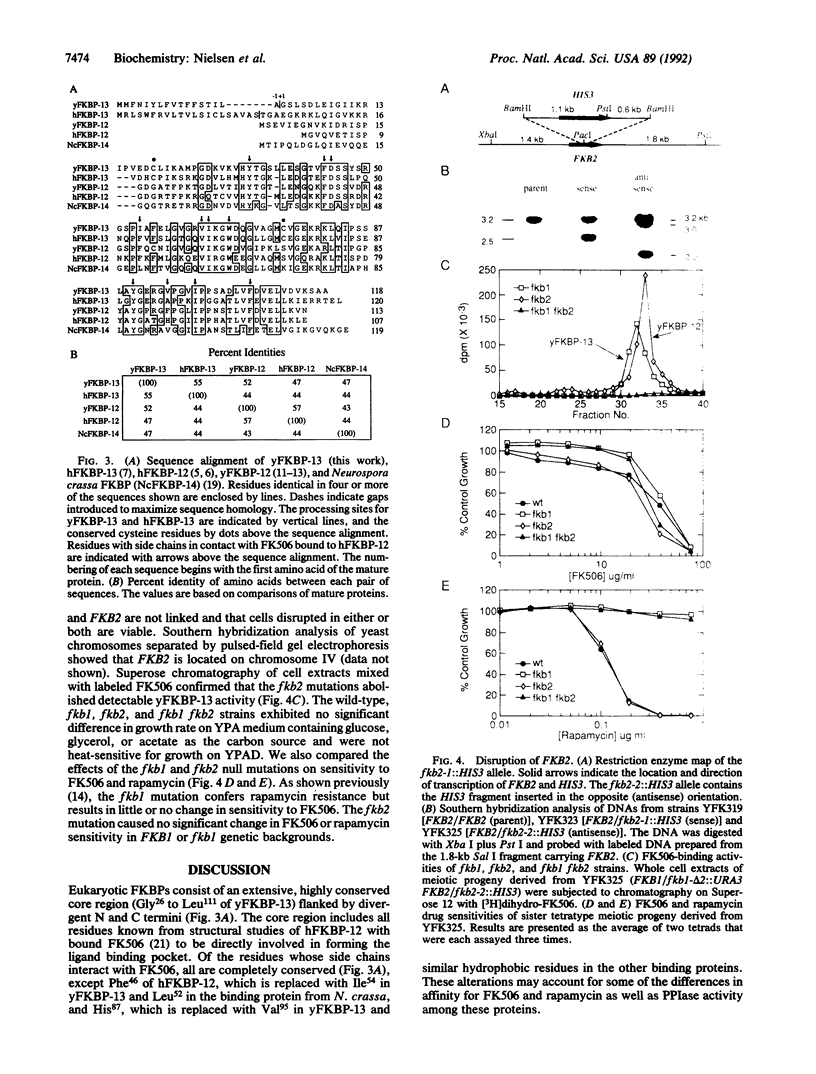
The immunosuppressants FK506 and rapamycin prevent T-cell activation and also inhibit the growth of certain strains of the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. It has previously been shown that yeast contains a 12-kDa cytosolic FK506-binding protein (yFKBP-12), which also possesses peptidylprolyl cis-trans isomerase activity, and that fkb1 strains lacking yFKBP-12 are resistant to rapamycin and sensitive to FK506. The absence of yFKBP-12 permitted the detection and isolation of a second FK506- and rapamycin-binding protein, which is about 13 kDa in size (yFKBP-13) and membrane-associated. Purified yFKBP-13 binds FK506 with 15-fold lower affinity than yFKBP-12 and has peptidylprolyl cis-trans isomerase activity with a similar substrate profile. The sequence of the first 37 N-terminal amino acids was determined, and the yFKBP-13 gene (FKB2) was cloned and sequenced. A hydrophobic putative signal sequence precedes the N terminus of the mature protein. yFKBP-13 most closely resembles the membrane-associated human FKBP-13, which also possesses a signal peptide, whereas yFKBP-12 most closely resembles human FKBP-12. fkb2 and fkb1 fkb2 mutants are viable and unaltered in their sensitivity to FK506, suggesting that yeast possesses an additional target for this drug. Furthermore, fkb2 null mutations confer no change in rapamycin sensitivity. These findings show that yFKBP-13 and yFKBP-12 have distinct functions within the cell.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arber S., Krause K. H., Caroni P. s-cyclophilin is retained intracellularly via a unique COOH-terminal sequence and colocalizes with the calcium storage protein calreticulin. J Cell Biol. 1992 Jan;116(1):113–125. doi: 10.1083/jcb.116.1.113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brizuela L., Chrebet G., Bostian K. A., Parent S. A. Antifungal properties of the immunosuppressant FK-506: identification of an FK-506-responsive yeast gene distinct from FKB1. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Sep;11(9):4616–4626. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.9.4616. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colley N. J., Baker E. K., Stamnes M. A., Zuker C. S. The cyclophilin homolog ninaA is required in the secretory pathway. Cell. 1991 Oct 18;67(2):255–263. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90177-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franzusoff A., Rothblatt J., Schekman R. Analysis of polypeptide transit through yeast secretory pathway. Methods Enzymol. 1991;194:662–674. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)94048-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman J., Weissman I. Two cytoplasmic candidates for immunophilin action are revealed by affinity for a new cyclophilin: one in the presence and one in the absence of CsA. Cell. 1991 Aug 23;66(4):799–806. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90123-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galat A., Lane W. S., Standaert R. F., Schreiber S. L. A rapamycin-selective 25-kDa immunophilin. Biochemistry. 1992 Mar 3;31(8):2427–2434. doi: 10.1021/bi00123a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison R. K., Stein R. L. Substrate specificities of the peptidyl prolyl cis-trans isomerase activities of cyclophilin and FK-506 binding protein: evidence for the existence of a family of distinct enzymes. Biochemistry. 1990 Apr 24;29(16):3813–3816. doi: 10.1021/bi00468a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heitman J., Movva N. R., Hiestand P. C., Hall M. N. FK 506-binding protein proline rotamase is a target for the immunosuppressive agent FK 506 in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 1;88(5):1948–1952. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.5.1948. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jin Y. J., Albers M. W., Lane W. S., Bierer B. E., Schreiber S. L., Burakoff S. J. Molecular cloning of a membrane-associated human FK506- and rapamycin-binding protein, FKBP-13. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 1;88(15):6677–6681. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.15.6677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koltin Y., Faucette L., Bergsma D. J., Levy M. A., Cafferkey R., Koser P. L., Johnson R. K., Livi G. P. Rapamycin sensitivity in Saccharomyces cerevisiae is mediated by a peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase related to human FK506-binding protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;11(3):1718–1723. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.3.1718. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koser P. L., Bergsma D. J., Cafferkey R., Eng W. K., McLaughlin M. M., Ferrara A., Silverman C., Kasyan K., Bossard M. J., Johnson R. K. The CYP2 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae encodes a cyclosporin A-sensitive peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase with an N-terminal signal sequence. Gene. 1991 Dec 1;108(1):73–80. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(91)90489-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebeau M. C., Massol N., Herrick J., Faber L. E., Renoir J. M., Radanyi C., Baulieu E. E. P59, an hsp 90-binding protein. Cloning and sequencing of its cDNA and preparation of a peptide-directed polyclonal antibody. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 5;267(7):4281–4284. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu J., Farmer J. D., Jr, Lane W. S., Friedman J., Weissman I., Schreiber S. L. Calcineurin is a common target of cyclophilin-cyclosporin A and FKBP-FK506 complexes. Cell. 1991 Aug 23;66(4):807–815. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90124-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maki N., Sekiguchi F., Nishimaki J., Miwa K., Hayano T., Takahashi N., Suzuki M. Complementary DNA encoding the human T-cell FK506-binding protein, a peptidylprolyl cis-trans isomerase distinct from cyclophilin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(14):5440–5443. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.14.5440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber S. L. Chemistry and biology of the immunophilins and their immunosuppressive ligands. Science. 1991 Jan 18;251(4991):283–287. doi: 10.1126/science.1702904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siekierka J. J., Wiederrecht G., Greulich H., Boulton D., Hung S. H., Cryan J., Hodges P. J., Sigal N. H. The cytosolic-binding protein for the immunosuppressant FK-506 is both a ubiquitous and highly conserved peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 5;265(34):21011–21015. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigal N. H., Dumont F. J. Cyclosporin A, FK-506, and rapamycin: pharmacologic probes of lymphocyte signal transduction. Annu Rev Immunol. 1992;10:519–560. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.10.040192.002511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Standaert R. F., Galat A., Verdine G. L., Schreiber S. L. Molecular cloning and overexpression of the human FK506-binding protein FKBP. Nature. 1990 Aug 16;346(6285):671–674. doi: 10.1038/346671a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struhl K., Stinchcomb D. T., Scherer S., Davis R. W. High-frequency transformation of yeast: autonomous replication of hybrid DNA molecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1035–1039. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sumner-Smith M., Bozzato R. P., Skipper N., Davies R. W., Hopper J. E. Analysis of the inducible MEL1 gene of Saccharomyces carlsbergensis and its secreted product, alpha-galactosidase (melibiase). Gene. 1985;36(3):333–340. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90188-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tropschug M., Wachter E., Mayer S., Schönbrunner E. R., Schmid F. X. Isolation and sequence of an FK506-binding protein from N. crassa which catalyses protein folding. Nature. 1990 Aug 16;346(6285):674–677. doi: 10.1038/346674a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Duyne G. D., Standaert R. F., Karplus P. A., Schreiber S. L., Clardy J. Atomic structure of FKBP-FK506, an immunophilin-immunosuppressant complex. Science. 1991 May 10;252(5007):839–842. doi: 10.1126/science.1709302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiederrecht G., Brizuela L., Elliston K., Sigal N. H., Siekierka J. J. FKB1 encodes a nonessential FK 506-binding protein in Saccharomyces cerevisiae and contains regions suggesting homology to the cyclophilins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 1;88(3):1029–1033. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.3.1029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yem A. W., Tomasselli A. G., Heinrikson R. L., Zurcher-Neely H., Ruff V. A., Johnson R. A., Deibel M. R., Jr The Hsp56 component of steroid receptor complexes binds to immobilized FK506 and shows homology to FKBP-12 and FKBP-13. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 15;267(5):2868–2871. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]