Abstract
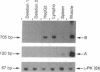
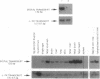
A transcript generated by the distal part of the Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD) gene was initially detected in cells where the full size 14-kilobase (kb) messenger RNA is not found at a significant level. This transcript, approximately 4.5 kb long, corresponds to the cysteine-rich and carboxyl-terminal domains of dystrophin. It begins with a novel 80- to 100-nucleotide exon containing an ATG start site for a new coding sequence of 17 nucleotides in-frame with the consecutive dystrophin cDNA sequence from exon 63. This result suggests the existence of a third promoter that would be localized about 8 kilobases upstream from exon 63 of the DMD gene. The distal transcript is widely distributed but is absent in adult skeletal and myometrial muscle. It is much more abundant in fetal tissues. With an antibody directed against the dystrophin carboxyl terminus, the protein corresponding to this transcript was detected as a 70- to 75-kDa entity on Western blots. It was found in all tissues analyzed except in skeletal muscle. It was not found in lymphoblastoid cells from a Duchenne patient with a complete deletion of the dystrophin gene. The role and subcellular localization of this protein is not known. It may explain extramuscular symptoms exhibited by some Duchenne patients.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bailey J. M., Davidson N. Methylmercury as a reversible denaturing agent for agarose gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1976 Jan;70(1):75–85. doi: 10.1016/s0003-2697(76)80049-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bar S., Barnea E., Levy Z., Neuman S., Yaffe D., Nudel U. A novel product of the Duchenne muscular dystrophy gene which greatly differs from the known isoforms in its structure and tissue distribution. Biochem J. 1990 Dec 1;272(2):557–560. doi: 10.1042/bj2720557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnea E., Zuk D., Simantov R., Nudel U., Yaffe D. Specificity of expression of the muscle and brain dystrophin gene promoters in muscle and brain cells. Neuron. 1990 Dec;5(6):881–888. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90348-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berwald-Netter Y., Martin-Moutot N., Koulakoff A., Couraud F. Na+-channel-associated scorpion toxin receptor sites as probes for neuronal evolution in vivo and in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):1245–1249. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.1245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blake D. J., Love D. R., Tinsley J., Morris G. E., Turley H., Gatter K., Dickson G., Edwards Y. H., Davies K. E. Characterization of a 4.8kb transcript from the Duchenne muscular dystrophy locus expressed in Schwannoma cells. Hum Mol Genet. 1992 May;1(2):103–109. doi: 10.1093/hmg/1.2.103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyce F. M., Beggs A. H., Feener C., Kunkel L. M. Dystrophin is transcribed in brain from a distant upstream promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 15;88(4):1276–1280. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.4.1276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlain J. S., Pearlman J. A., Muzny D. M., Gibbs R. A., Ranier J. E., Caskey C. T., Reeves A. A. Expression of the murine Duchenne muscular dystrophy gene in muscle and brain. Science. 1988 Mar 18;239(4846):1416–1418. doi: 10.1126/science.3347839. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chelly J., Concordet J. P., Kaplan J. C., Kahn A. Illegitimate transcription: transcription of any gene in any cell type. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2617–2621. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chelly J., Gilgenkrantz H., Lambert M., Hamard G., Chafey P., Récan D., Katz P., de la Chapelle A., Koenig M., Ginjaar I. B. Effect of dystrophin gene deletions on mRNA levels and processing in Duchenne and Becker muscular dystrophies. Cell. 1990 Dec 21;63(6):1239–1248. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90419-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chelly J., Hamard G., Koulakoff A., Kaplan J. C., Kahn A., Berwald-Netter Y. Dystrophin gene transcribed from different promoters in neuronal and glial cells. Nature. 1990 Mar 1;344(6261):64–65. doi: 10.1038/344064a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chelly J., Montarras D., Pinset C., Berwald-Netter Y., Kaplan J. C., Kahn A. Quantitative estimation of minor mRNAs by cDNA-polymerase chain reaction. Application to dystrophin mRNA in cultured myogenic and brain cells. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Feb 14;187(3):691–698. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb15355.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cognet M., Lone Y. C., Vaulont S., Kahn A., Marie J. Structure of the rat L-type pyruvate kinase gene. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jul 5;196(1):11–25. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90507-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feener C. A., Koenig M., Kunkel L. M. Alternative splicing of human dystrophin mRNA generates isoforms at the carboxy terminus. Nature. 1989 Apr 6;338(6215):509–511. doi: 10.1038/338509a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geng Y., Sicinski P., Gorecki D., Barnard P. J. Developmental and tissue-specific regulation of mouse dystrophin: the embryonic isoform in muscular dystrophy. Neuromuscul Disord. 1991;1(2):125–133. doi: 10.1016/0960-8966(91)90060-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman E. P., Brown R. H., Jr, Kunkel L. M. Dystrophin: the protein product of the Duchenne muscular dystrophy locus. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):919–928. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90579-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koenig M., Hoffman E. P., Bertelson C. J., Monaco A. P., Feener C., Kunkel L. M. Complete cloning of the Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) cDNA and preliminary genomic organization of the DMD gene in normal and affected individuals. Cell. 1987 Jul 31;50(3):509–517. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90504-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. An analysis of 5'-noncoding sequences from 699 vertebrate messenger RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Oct 26;15(20):8125–8148. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.20.8125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lederfein D., Levy Z., Augier N., Mornet D., Morris G., Fuchs O., Yaffe D., Nudel U. A 71-kilodalton protein is a major product of the Duchenne muscular dystrophy gene in brain and other nonmuscle tissues. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 15;89(12):5346–5350. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.12.5346. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loh E. Y., Elliott J. F., Cwirla S., Lanier L. L., Davis M. M. Polymerase chain reaction with single-sided specificity: analysis of T cell receptor delta chain. Science. 1989 Jan 13;243(4888):217–220. doi: 10.1126/science.2463672. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monaco A. P., Kunkel L. M. Cloning of the Duchenne/Becker muscular dystrophy locus. Adv Hum Genet. 1988;17:61–98. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4613-0987-1_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson L. V., Davison K., Falkous G., Harwood C., O'Donnell E., Slater C. R., Harris J. B. Dystrophin in skeletal muscle. I. Western blot analysis using a monoclonal antibody. J Neurol Sci. 1989 Dec;94(1-3):125–136. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(89)90223-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nizetić D., Zehetner G., Monaco A. P., Gellen L., Young B. D., Lehrach H. Construction, arraying, and high-density screening of large insert libraries of human chromosomes X and 21: their potential use as reference libraries. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 15;88(8):3233–3237. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.8.3233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowak L., Ascher P., Berwald-Netter Y. Ionic channels in mouse astrocytes in culture. J Neurosci. 1987 Jan;7(1):101–109. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-01-00101.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nudel U., Robzyk K., Yaffe D. Expression of the putative Duchenne muscular dystrophy gene in differentiated myogenic cell cultures and in the brain. Nature. 1988 Feb 18;331(6157):635–638. doi: 10.1038/331635a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proudfoot N. J. Transcriptional interference and termination between duplicated alpha-globin gene constructs suggests a novel mechanism for gene regulation. Nature. 1986 Aug 7;322(6079):562–565. doi: 10.1038/322562a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worton R. G., Thompson M. W. Genetics of Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Annu Rev Genet. 1988;22:601–629. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.22.120188.003125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]