Abstract
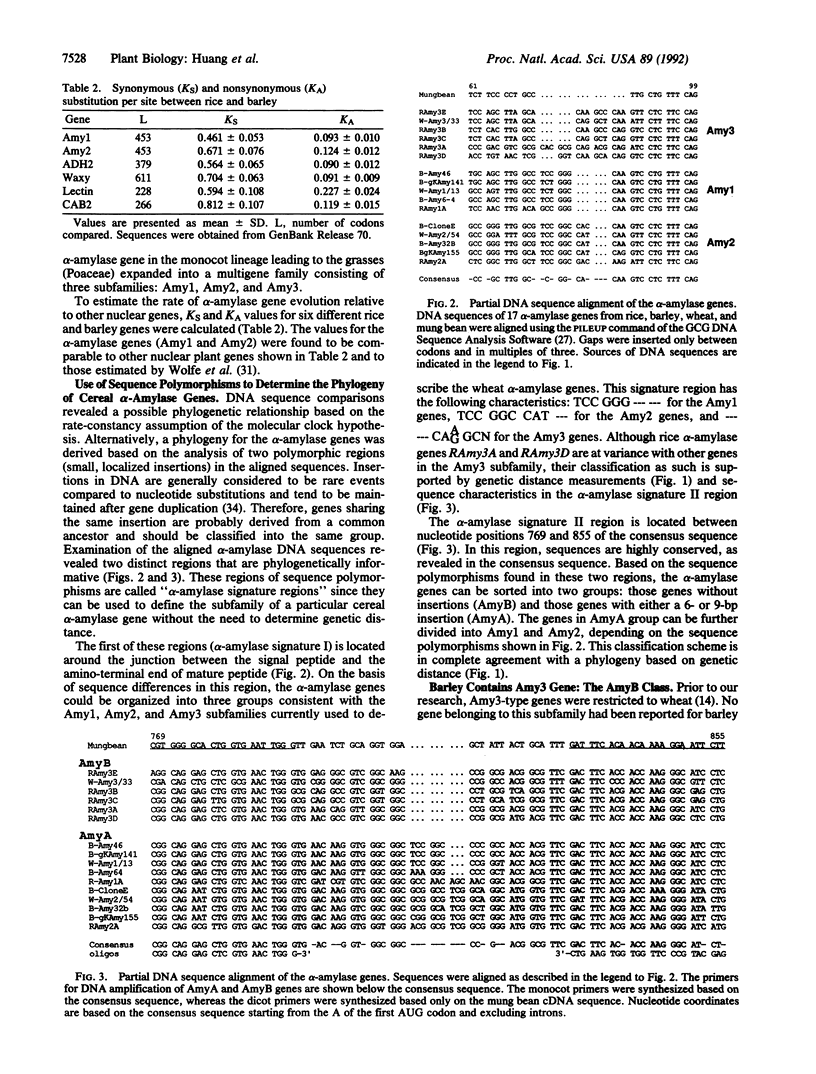
The DNA sequences for 17 plant genes for alpha-amylase (EC 3.2.1.1) were analyzed to determine their phylogenetic relationship. A phylogeny for these genes was obtained using two separate approaches, one based on molecular clock assumptions and the other based on a comparison of sequence polymorphisms (i.e., small and localized insertions) in the alpha-amylase genes. These polymorphisms are called "alpha-amylase signatures" because they are diagnostic of the gene subfamily to which a particular alpha-amylase gene belongs. Results indicate that the cereal alpha-amylase genes fall into two major classes: AmyA and AmyB. The AmyA class is subdivided into the Amy1 and Amy2 subfamilies previously used to classify alpha-amylase genes in barley and wheat. The AmyB class includes the Amy3 subfamily to which most of the alpha-amylase genes of rice belong. Using polymerase chain reaction and oligonucleotide primers that flank one of the two signature regions, we show that the AmyA and AmyB gene classes are present in approximately equal amounts in all grass species examined except barley. The AmyB (Amy3 subfamily) genes in the latter case are comparatively underrepresented. Additional evidence suggests that the AmyA genes appeared recently and may be confined to the grass family.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baulcombe D C, Huttly A K, Martienssen R A, Barker R F, Jarvis M G. A novel wheat alpha-amylase gene (alpha-Amy3). Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Aug;209(1):33–40. doi: 10.1007/BF00329833. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daussant J., Miyata S., Mitsui T., Akazawa T. Enzymic mechanism of starch breakdown in germinating rice seeds : 15. Immunochemical study on multiple forms of amylase. Plant Physiol. 1983 Jan;71(1):88–95. doi: 10.1104/pp.71.1.88. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang N., Koizumi N., Reinl S., Rodriguez R. L. Structural organization and differential expression of rice alpha-amylase genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Dec 11;18(23):7007–7014. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.23.7007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang N., Reinl S. J., Rodriguez R. L. RAmy2A; a novel alpha-amylase-encoding gene in rice. Gene. 1992 Feb 15;111(2):223–228. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(92)90690-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang N., Sutliff T. D., Litts J. C., Rodriguez R. L. Classification and characterization of the rice alpha-amylase multigene family. Plant Mol Biol. 1990 May;14(5):655–668. doi: 10.1007/BF00016499. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huttly A. K., Martienssen R. A., Baulcombe D. C. Sequence heterogeneity and differential expression of the alpha-Amy2 gene family in wheat. Mol Gen Genet. 1988 Oct;214(2):232–240. doi: 10.1007/BF00337716. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobsen J. V., Higgins T. J. Characterization of the alpha-Amylases Synthesized by Aleurone Layers of Himalaya Barley in Response to Gibberellic Acid. Plant Physiol. 1982 Dec;70(6):1647–1653. doi: 10.1104/pp.70.6.1647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khursheed B., Rogers J. C. Barley alpha-amylase genes. Quantitative comparison of steady-state mRNA levels from individual members of the two different families expressed in aleurone cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 15;263(35):18953–18960. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koizuka N., Tanaka Y., Morohashi Y. Isolation of a cDNA Clone for alpha-Amylase in Mung Bean Cotyledons : Analysis of alpha-Amylase mRNA Levels in Cotyledons during and following Germination of Mung Bean Seeds. Plant Physiol. 1990 Nov;94(3):1488–1491. doi: 10.1104/pp.94.3.1488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li W. H., Wu C. I., Luo C. C. A new method for estimating synonymous and nonsynonymous rates of nucleotide substitution considering the relative likelihood of nucleotide and codon changes. Mol Biol Evol. 1985 Mar;2(2):150–174. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyata S., Akazawa T. Enzymic mechanism of starch breakdown in germinating rice seeds : 12. Biosynthesis of alpha-amylase in relation to protein glycosylation. Plant Physiol. 1982 Jul;70(1):147–153. doi: 10.1104/pp.70.1.147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray M. G., Thompson W. F. Rapid isolation of high molecular weight plant DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Oct 10;8(19):4321–4325. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.19.4321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muthukrishnan S., Gill B. S., Swegle M., Chandra G. R. Structural genes for alpha-amylases are located on barley chromosomes 1 and 6. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 25;259(22):13637–13639. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Neill S. D., Kumagai M. H., Majumdar A., Huang N., Sutliff T. D., Rodriguez R. L. The alpha-amylase genes in Oryza sativa: characterization of cDNA clones and mRNA expression during seed germination. Mol Gen Genet. 1990 Apr;221(2):235–244. doi: 10.1007/BF00261726. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ou-Lee T. M., Turgeon R., Wu R. Interaction of a gibberellin-induced factor with the upstream region of an alpha-amylase gene in rice aleurone tissue. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(17):6366–6369. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.17.6366. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers J. C., Milliman C. Isolation and sequence analysis of a barley alpha-amylase cDNA clone. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jul 10;258(13):8169–8174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers J. C. Two barley alpha-amylase gene families are regulated differently in aleurone cells. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3731–3738. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith T. F., Waterman M. S., Fitch W. M. Comparative biosequence metrics. J Mol Evol. 1981;18(1):38–46. doi: 10.1007/BF01733210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutliff T. D., Huang N., Litts J. C., Rodriguez R. L. Characterization of an alpha-amylase multigene cluster in rice. Plant Mol Biol. 1991 Apr;16(4):579–591. doi: 10.1007/BF00023423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittier R. F., Dean D. A., Rogers J. C. Nucleotide sequence analysis of alpha-amylase and thiol protease genes that are hormonally regulated in barley aleurone cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Mar 25;15(6):2515–2535. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.6.2515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]