Abstract
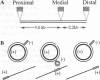
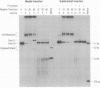
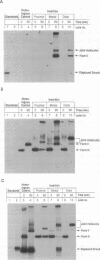
Previous studies have shown that the helical RecA nucleoprotein filament formed on a circular single strand of DNA causes the progressive, directional transfer of a complementary strand from naked linear duplex DNA to the nucleoprotein filament, even when the duplex contains a sizable heterologous insertion. Since RecA protein lacks demonstrable helicase activity, the mechanism by which it pushes strand exchange through long heterologous inserts has been a quandary. In the present study, a linear duplex substrate with an insertion of 110 base pairs in its middle yielded the expected products, whereas much less of the heteroduplex product was seen when the insertion was located at either end of the duplex substrate or 160 base pairs from the far end of the duplex substrate. In an ongoing reaction of the substrate with an insertion in its middle, P1 nuclease cleaved intermediates from the point of the insertion to various distal sites. Acting on a duplex substrate that contained a single nick located in the complementary strand just beyond the insertion, RecA protein formed joint molecules but failed to complete strand exchange. These data show that negative torsional stress is generated by distant homologous interactions that occur beyond the heterologous insertion and that such stress is essential for unwinding a heterologous insertion that otherwise halts strand exchange.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bedale W. A., Inman R. B., Cox M. M. RecA protein-facilitated DNA strand breaks. A mechanism for bypassing DNA structural barriers during strand exchange. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 5;266(10):6499–6510. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bianchi M. E., Radding C. M. Insertions, deletions and mismatches in heteroduplex DNA made by recA protein. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(2 Pt 1):511–520. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90185-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bramhill D., Kornberg A. Duplex opening by dnaA protein at novel sequences in initiation of replication at the origin of the E. coli chromosome. Cell. 1988 Mar 11;52(5):743–755. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90412-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham R. P., DasGupta C., Shibata T., Radding C. M. Homologous pairing in genetic recombination: recA protein makes joint molecules of gapped circular DNA and closed circular DNA. Cell. 1980 May;20(1):223–235. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90250-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham R. P., Wu A. M., Shibata T., DasGupta C., Radding C. M. Homologous pairing and topological linkage of DNA molecules by combined action of E. coli RecA protein and topoisomerase I. Cell. 1981 Apr;24(1):213–223. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90517-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DasGupta C., Radding C. M. Lower fidelity of RecA protein catalysed homologous pairing with a superhelical substrate. Nature. 1982 Jan 7;295(5844):71–73. doi: 10.1038/295071a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DasGupta C., Shibata T., Cunningham R. P., Radding C. M. The topology of homologous pairing promoted by RecA protein. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(2 Pt 2):437–446. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90354-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flory J., Tsang S. S., Muniyappa K. Isolation and visualization of active presynaptic filaments of recA protein and single-stranded DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(22):7026–7030. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.22.7026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn T. R., West S., Howard-Flanders P. RecA-mediated strand exchange reactions between duplex DNA molecules containing damaged bases, deletions, and insertions. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 25;263(15):7431–7436. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honigberg S. M., Radding C. M. The mechanics of winding and unwinding helices in recombination: torsional stress associated with strand transfer promoted by RecA protein. Cell. 1988 Aug 12;54(4):525–532. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90074-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard-Flanders P., West S. C., Stasiak A. Role of RecA protein spiral filaments in genetic recombination. Nature. 1984 May 17;309(5965):215–219. doi: 10.1038/309215a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koo H. S., Claassen L., Grossman L., Liu L. F. ATP-dependent partitioning of the DNA template into supercoiled domains by Escherichia coli UvrAB. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 15;88(4):1212–1216. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.4.1212. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kowalczykowski S. C. Biochemistry of genetic recombination: energetics and mechanism of DNA strand exchange. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1991;20:539–575. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.20.060191.002543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichten M. J., Fox M. S. Detection of non-homology-containing heteroduplex molecules. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jun 25;11(12):3959–3971. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.12.3959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu L. F., Wang J. C. Supercoiling of the DNA template during transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(20):7024–7027. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.20.7024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livneh Z., Lehman I. R. Recombinational bypass of pyrimidine dimers promoted by the recA protein of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(10):3171–3175. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.10.3171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohman T. M., Green J. M., Beyer R. S. Large-scale overproduction and rapid purification of the Escherichia coli ssb gene product. Expression of the ssb gene under lambda PL control. Biochemistry. 1986 Jan 14;25(1):21–25. doi: 10.1021/bi00349a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugh B. F., Cox M. M. recA protein binding to the heteroduplex product of DNA strand exchange. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 25;262(3):1337–1343. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugh B. F., Schutte B. C., Cox M. M. Extent of duplex DNA underwinding induced by RecA protein binding in the presence of ATP. J Mol Biol. 1989 Feb 5;205(3):487–492. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90219-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radding C. M. Helical interactions in homologous pairing and strand exchange driven by RecA protein. J Biol Chem. 1991 Mar 25;266(9):5355–5358. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao B. J., Dutreix M., Radding C. M. Stable three-stranded DNA made by RecA protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 15;88(8):2984–2988. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.8.2984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao B. J., Jwang B., Radding C. M. RecA protein reinitiates strand exchange on isolated protein-free DNA intermediates. An ADP-resistant process. J Mol Biol. 1990 Jun 20;213(4):789–809. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80264-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roca A. I., Cox M. M. The RecA protein: structure and function. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 1990;25(6):415–456. doi: 10.3109/10409239009090617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosselli W., Stasiak A. The ATPase activity of RecA is needed to push the DNA strand exchange through heterologous regions. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(13):4391–4396. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb05017.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rould E., Muniyappa K., Radding C. M. Unwinding of heterologous DNA by RecA protein during the search for homologous sequences. J Mol Biol. 1992 Jul 5;226(1):127–139. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90129-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schutte B. C., Cox M. M. Homology-dependent changes in adenosine 5'-triphosphate hydrolysis during recA protein promoted DNA strand exchange: evidence for long paranemic complexes. Biochemistry. 1987 Sep 8;26(18):5616–5625. doi: 10.1021/bi00392a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibata T., Cunningham R. P., Radding C. M. Homologous pairing in genetic recombination. Purification and characterization of Escherichia coli recA protein. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jul 25;256(14):7557–7564. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stasiak A., Di Capua E. The helicity of DNA in complexes with recA protein. Nature. 1982 Sep 9;299(5879):185–186. doi: 10.1038/299185a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. The pUC plasmids, an M13mp7-derived system for insertion mutagenesis and sequencing with synthetic universal primers. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstock G. M., McEntee K., Lehman I. R. Hydrolysis of nucleoside triphosphates catalyzed by the recA protein of Escherichia coli. Characterization of ATP hydrolysis. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 25;256(16):8829–8834. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstock G. M., McEntee K., Lehman I. R. Hydrolysis of nucleoside triphosphates catalyzed by the recA protein of Escherichia coli. Steady state kinetic analysis of ATP hydrolysis. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 25;256(16):8845–8849. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West S. C., Cassuto E., Howard-Flanders P. Postreplication repair in E. coli: strand exchange reactions of gapped DNA by RecA protein. Mol Gen Genet. 1982;187(2):209–217. doi: 10.1007/BF00331119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu A. M., Kahn R., DasGupta C., Radding C. M. Formation of nascent heteroduplex structures by RecA protein and DNA. Cell. 1982 Aug;30(1):37–44. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90009-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu H. Y., Shyy S. H., Wang J. C., Liu L. F. Transcription generates positively and negatively supercoiled domains in the template. Cell. 1988 May 6;53(3):433–440. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90163-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]