Abstract
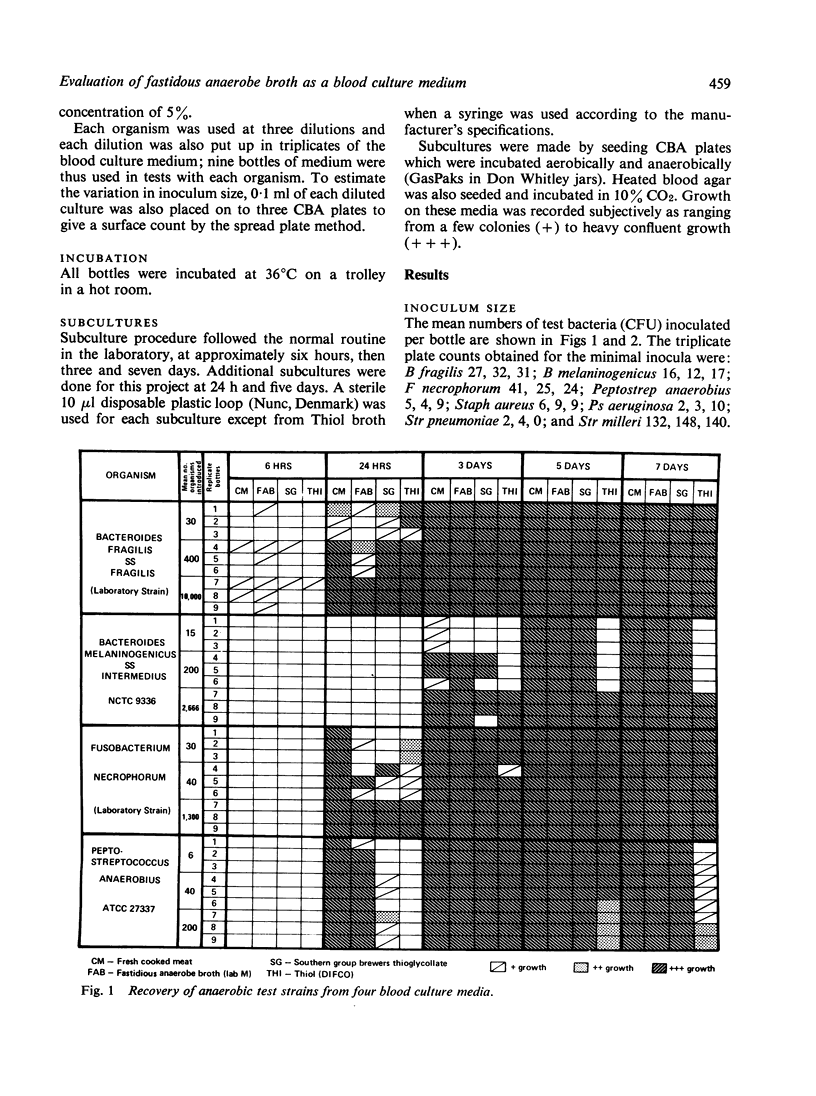
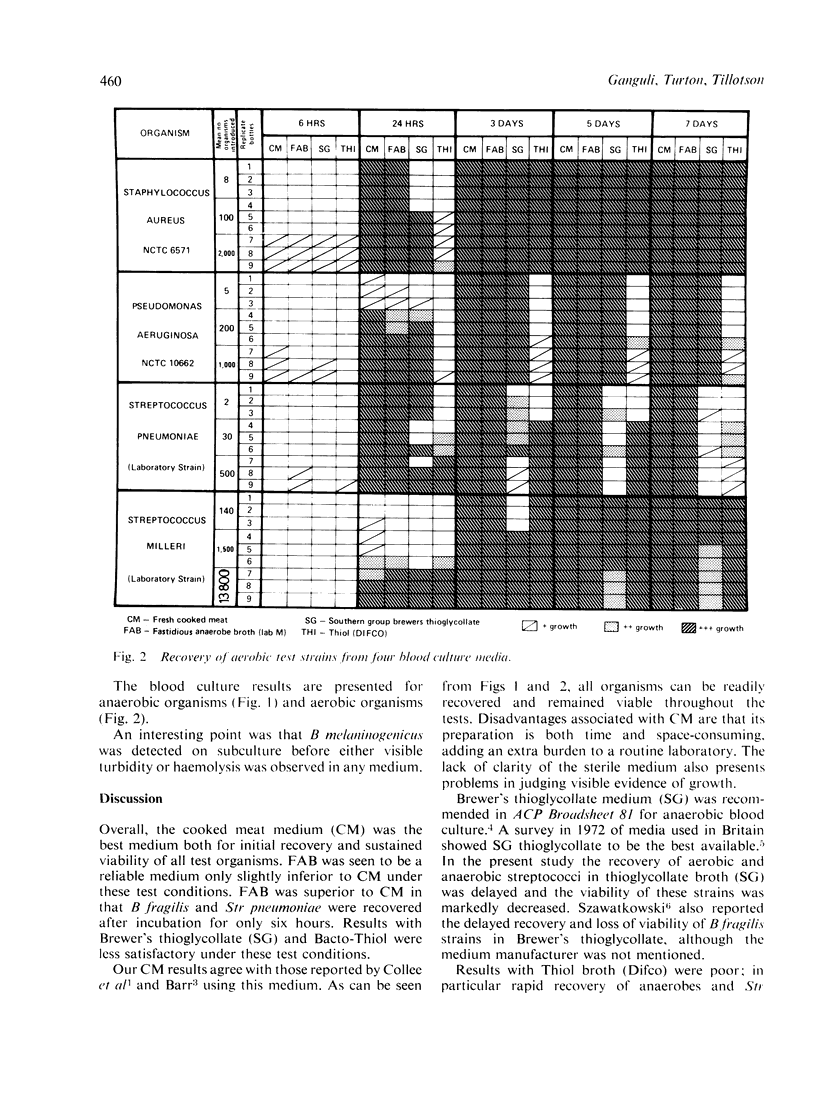
Three commercial blood culture media were compared with a freshly prepared cooked meat medium in tests to stimulate the recovery of small inocula of anaerobic and aerobic bacteria in routine blood cultures. The cooked meat medium gave the most reliable recovery and supported continued viability, whilst Fastidious Anaerobe Broth (LAB M) was a good alternative. Results with Southern Group thioglycollate and Difco Thiol were less satisfactory as delays in recovery and loss of viability occurred on continued incubation with some of the test strains.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barr J. G. A cooked meat blood culture medium; shelf-life and clinical evaluation compared with other systems. J Infect. 1980 Sep;2(3):247–258. doi: 10.1016/s0163-4453(80)90698-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collee J. G., Duerden B. I., Brown R. Recovery of anaerobic bacteria from small inocula: a model for blood culture studies. J Clin Pathol. 1977 Jul;30(7):609–614. doi: 10.1136/jcp.30.7.609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shanson D. C. An experimental assessment of different anaerobic blood culture methods. J Clin Pathol. 1974 Apr;27(4):273–279. doi: 10.1136/jcp.27.4.273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shanson D. C., Barnicoat An experimental comparison of Thiol broth with Brewer's thioglycollate for anaerobic blood cultures. J Clin Pathol. 1975 May;28(5):407–409. doi: 10.1136/jcp.28.5.407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szawatkowski M. V. A comparison of three readily available types of anaerobic blood culture media. Med Lab Sci. 1976 Jan;33(1):5–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


