Abstract
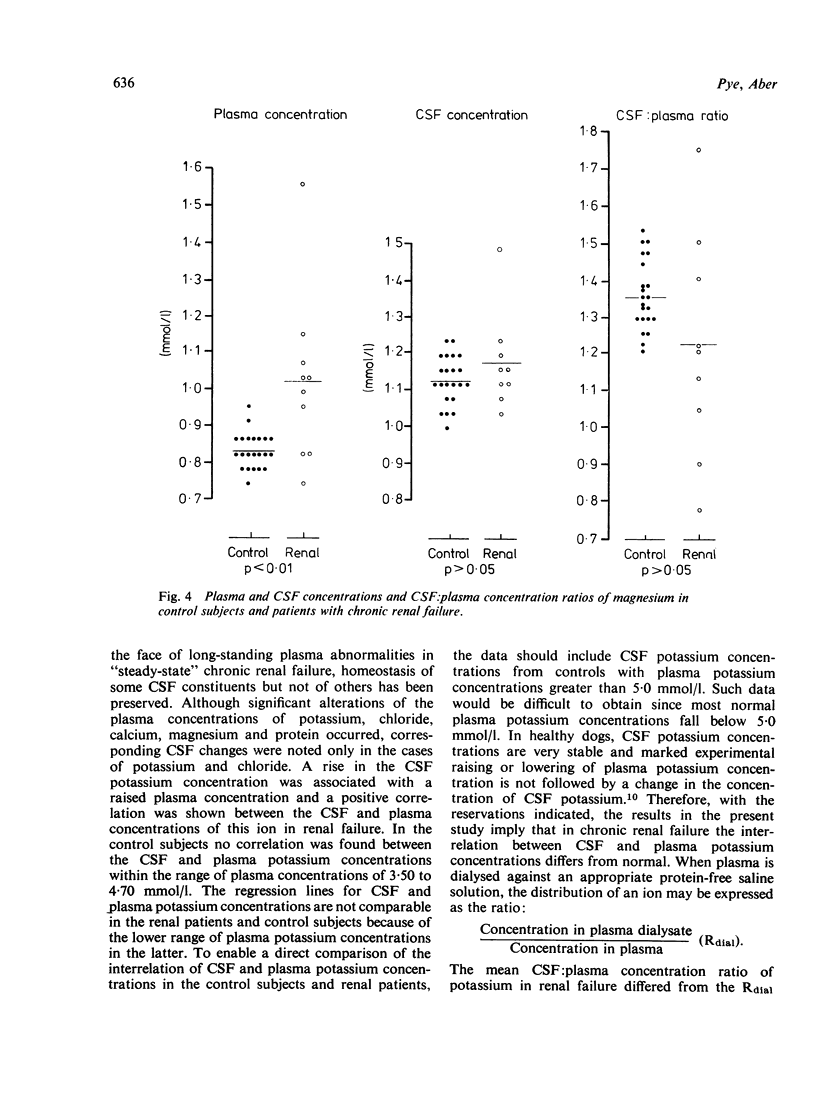
The concentrations of inorganic ions and glucose in the plasma and CSF of 11 patients with "steady-state" chronic renal failure have been measured and their CSF: plasma interrelations studied. The results have been compared with the corresponding data from 34 control subjects. In the patients with renal failure, there was a positive correlation between raised CSF and plasma potassium concentrations. In contrast to the impaired potassium homeostasis, normal CSF magnesium and calcium concentrations were observed despite wide variations in the plasma concentrations of these ions.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BOURDILLON R. B., FISCHER-WILLIAMS M., SMITH H. V., TAYLOR K. B. The entry of radiosodium and of bromide into human cerebrospinal fluid. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1957 May;20(2):79–97. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.20.2.79. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRADBURY M. W., STUBBS J., HUGHES I. E., PARKER P. THE DISTRIBUTION OF POTASSIUM, SODIUM, CHLORIDE AND UREA BETWEEN LUMBAR CEREBROSPINAL FLUID AND BLOOD SERUM IN HUMAN SUBJECTS. Clin Sci. 1963 Aug;25:97–105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COOPER E. S., LECHNER E., BELLET S. Relation between serum and cerebrospinal fluid electrolytes under normal and abnormal conditions. Am J Med. 1955 Apr;18(4):613–621. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(55)90462-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fermoso García J., Rodriguez Navarro I. Constantes del equilibrio ácido-base y de algunos cationes en el líquido cefalorraquídeo de pacientes con insuficiencia renal crónica descompensada. (III) Rev Clin Esp. 1975 May 15;137(3):229–235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNTER G., SMITH H. V. Calcium and magnesium in human cerebrospinal fluid. Nature. 1960 Apr 9;186:161–162. doi: 10.1038/186161a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heipertz R., Eickhoff K., Karstens K. H. Magnesium and inorganic phosphate content in CSF related to blood-brain barrier function in neurological disease. J Neurol Sci. 1979 Feb;40(2-3):87–95. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(79)90194-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pye I. F., McGale E. H., Stonier C., Hutchinson E. C., Aber G. M. Studies of cerebrospinal fluid and plasma amino acids in patients with steady-state chronic renal failure. Clin Chim Acta. 1979 Feb 15;92(1):65–72. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(79)90397-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHAW C. W., HOLLEY H. L. Sodium and potassium concentration in human cerebrospinal fluid. I. Normal values. J Lab Clin Med. 1951 Oct;38(4):574–576. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sambrook M. A. The relationship between cerebrospinal fluid and plasma electrolytes in patients with meningitis. J Neurol Sci. 1974 Oct;23(2):265–273. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(74)90230-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


