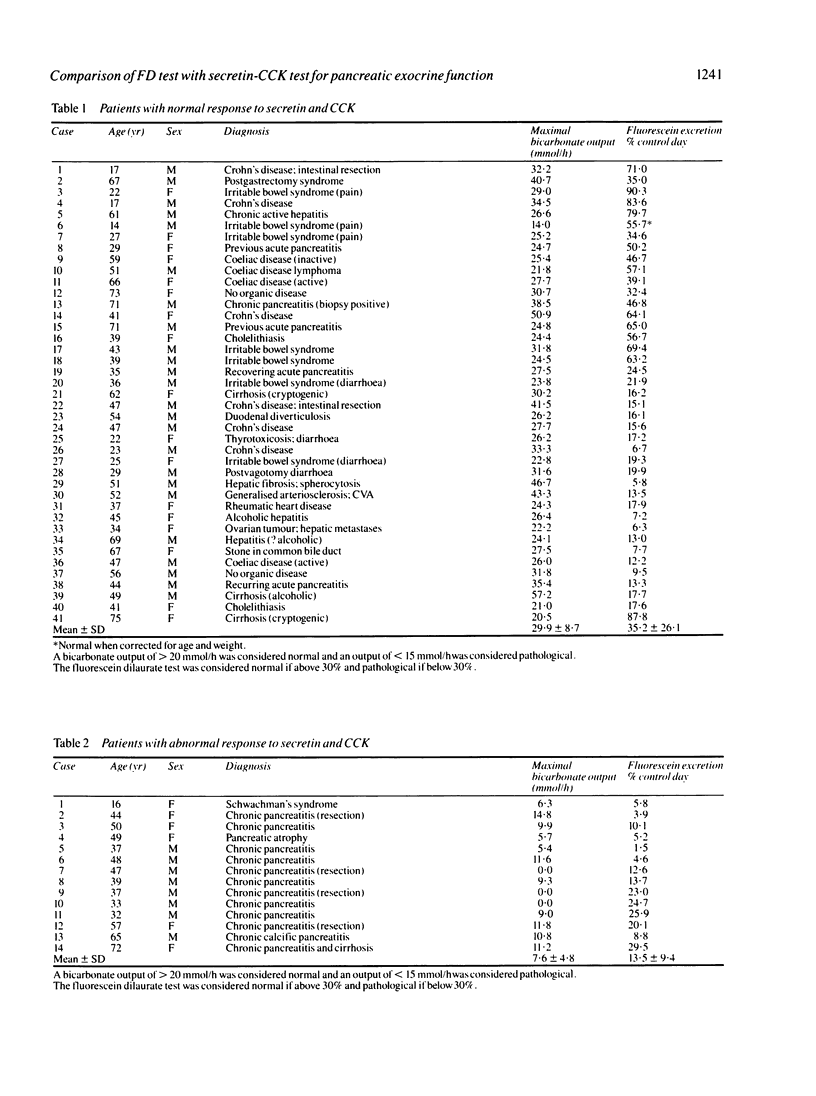
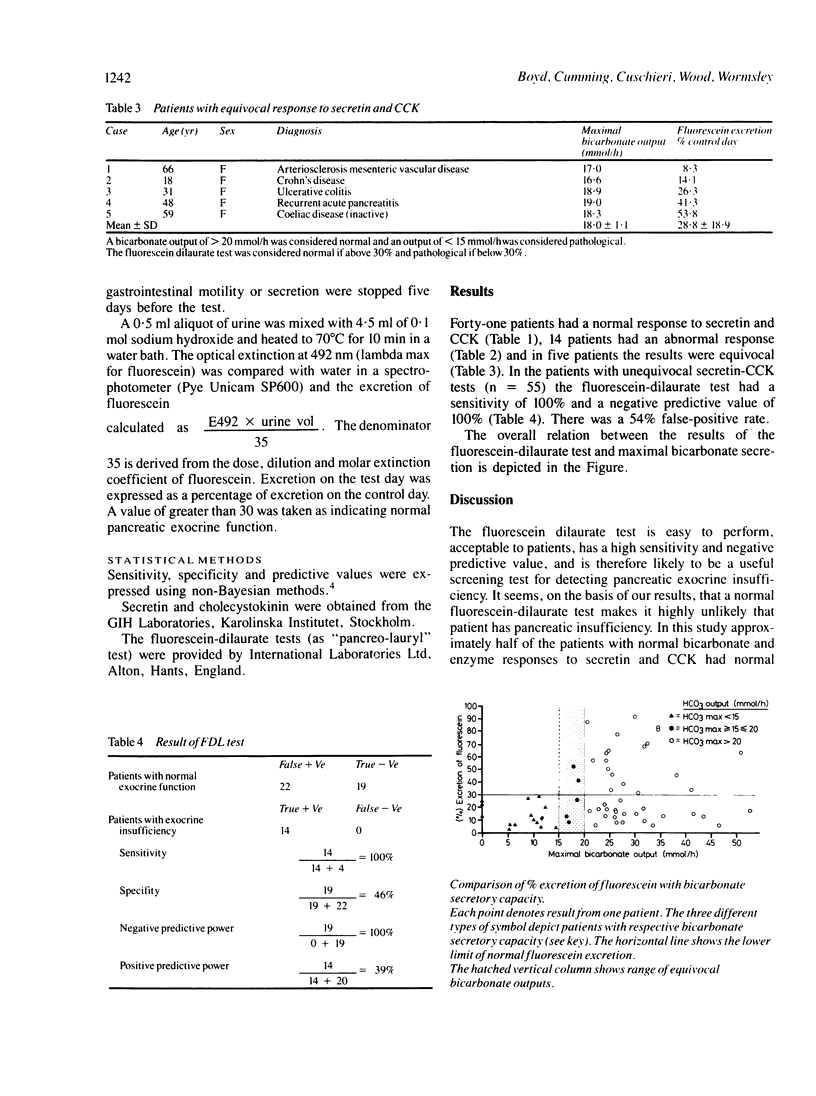
Abstract
In a prospective study of 60 patients undergoing investigation for possible exocrine pancreatic disease the fluorescein-dilaurate test was compared with the secretin-cholecystokinin (CCK) test. Forty one patients had a normal response to secretin-CCK, 14 patients had abnormal responses and in five patients the results were equivocal. Taking the secretin-CCK test as the diagnostic criterion, the fluorescein-dilaurate test had a sensitivity of 100% and a negative predictive value of 100%. There was a 54% false-positive rate. The fluorescein-dilaurate test is easy to perform and is a useful screening test for pancreatic exocrine insufficiency.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Kaffarnik H., Meyer-Bertenrath J. G. Zur Pankreasspezifität des oralen Funktionstests mit Fluorescein-Di- bzw. Monolaura. Verh Dtsch Ges Inn Med. 1971;77:524–526. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lankisch P. G., Schreiber A., Koop H. Der Pancreolauryl-Test im Vergleich zum NBT-PABA-Test. Suchtests für die Diagnostik der exokrinen Pankreasinsuffizienz? Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 1980 Oct 24;105(43):1487–1488. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1070896. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wormsley K. G. The response to infusion of a combination of secretin and pancreozymin in health and disease. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1969;4(7):623–632. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


